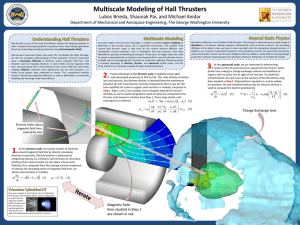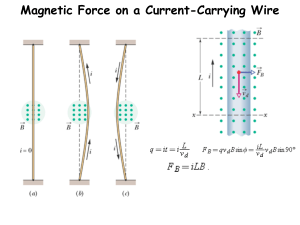
General Instructions
... Q4. The variability of oxidation states, a characteristic of transition elements, arises out of incomplete filling of d orbital’s in such a way that their oxidation states differ from each other by unity give example. Q5. Write iupac name of K3[Al(C2O4)3] Q6 At a site, low grade copper ores are avai ...
... Q4. The variability of oxidation states, a characteristic of transition elements, arises out of incomplete filling of d orbital’s in such a way that their oxidation states differ from each other by unity give example. Q5. Write iupac name of K3[Al(C2O4)3] Q6 At a site, low grade copper ores are avai ...
Document
... or shells (1, 2, 3, etc.) and orbitals (s, p, d, f) of an atom, starting with the innermost electrons. o Example: A lithium atom’s configuration is 1s22s1 o Superscripts mean two electrons are in the 1s orbital and one electron is in the 2s orbital. Several Rules are applied to the filling of electr ...
... or shells (1, 2, 3, etc.) and orbitals (s, p, d, f) of an atom, starting with the innermost electrons. o Example: A lithium atom’s configuration is 1s22s1 o Superscripts mean two electrons are in the 1s orbital and one electron is in the 2s orbital. Several Rules are applied to the filling of electr ...
here - Physics Teacher
... describes all the phenomena caused by magnets. Magnets nickel are objects that can attract other objects containing iron, ________________________ or ore cobalt. Around 600 BCE, the Greeks discovered an ________________________ called © ERPI Reproduction and adaptation permitted solely for classroom ...
... describes all the phenomena caused by magnets. Magnets nickel are objects that can attract other objects containing iron, ________________________ or ore cobalt. Around 600 BCE, the Greeks discovered an ________________________ called © ERPI Reproduction and adaptation permitted solely for classroom ...
magnetics_intro
... Ferromagnetic and Ferrimagnetic materials generally made up of domains with uniform magnetic direction Within domains the magnetic moments of atoms are aligned The domains form when cooled below the Curie Temperature Magnetic domains (bands) visible in Microcystalline grains of NdFeB ...
... Ferromagnetic and Ferrimagnetic materials generally made up of domains with uniform magnetic direction Within domains the magnetic moments of atoms are aligned The domains form when cooled below the Curie Temperature Magnetic domains (bands) visible in Microcystalline grains of NdFeB ...
Answer the questions below
... rod, and then passes an electric current through the wire, then: a. the steel rod becomes an electromagnet b. the steel rod becomes electrified and should not be touched c. the wire becomes magnetized ...
... rod, and then passes an electric current through the wire, then: a. the steel rod becomes an electromagnet b. the steel rod becomes electrified and should not be touched c. the wire becomes magnetized ...
Magnetism
... – Most of the time magnets are paired, and the fields cancel out – Magnetic domain – a region that has a large number of electrons with fields in the same direction – Magnetized – most of the domains are pointed in the same direction ...
... – Most of the time magnets are paired, and the fields cancel out – Magnetic domain – a region that has a large number of electrons with fields in the same direction – Magnetized – most of the domains are pointed in the same direction ...
Magnetochemistry

Magnetochemistry is concerned with the magnetic properties of chemical compounds. Magnetic properties arise from the spin and orbital angular momentum of the electrons contained in a compound. Compounds are diamagnetic when they contain no unpaired electrons. Molecular compounds that contain one or more unpaired electrons are paramagnetic. The magnitude of the paramagnetism is expressed as an effective magnetic moment, μeff. For first-row transition metals the magnitude of μeff is, to a first approximation, a simple function of the number of unpaired electrons, the spin-only formula. In general, spin-orbit coupling causes μeff to deviate from the spin-only formula. For the heavier transition metals, lanthanides and actinides, spin-orbit coupling cannot be ignored. Exchange interaction can occur in clusters and infinite lattices, resulting in ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism depending on the relative orientations of the individual spins.