Lecture 23 ppt
... Current on one side of the loop flows in the opposite direction to the current on the other side of loop. So, the two sides gets deflected in opposite directions, as shown; hence it turns. After a half turn, the sides have reversed, so deflection is in the opposite direction – makes coil turns back. ...
... Current on one side of the loop flows in the opposite direction to the current on the other side of loop. So, the two sides gets deflected in opposite directions, as shown; hence it turns. After a half turn, the sides have reversed, so deflection is in the opposite direction – makes coil turns back. ...
Example 20-1.
... “A mathematician may say anything he pleases, but a physicist must be at least partially sane.”—J. Willard Gibbs ...
... “A mathematician may say anything he pleases, but a physicist must be at least partially sane.”—J. Willard Gibbs ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... we introduce new law called LAW OF NATURE 1 which unifies scalars and vectors. Since physics always seeks unification, so we unify scalars and vectors by using new law which is initiated from Maxwell’s equations. Keywords: Law of nature 1, Maxwell’s 2nd equation, moving charge, magnetic current dens ...
... we introduce new law called LAW OF NATURE 1 which unifies scalars and vectors. Since physics always seeks unification, so we unify scalars and vectors by using new law which is initiated from Maxwell’s equations. Keywords: Law of nature 1, Maxwell’s 2nd equation, moving charge, magnetic current dens ...
Electric Motors
... Magnets are surrounded by magnetic fields and attract certain metals (iron, nickel, and cobalt). This magnetic effect comes from a special alignment of the atomic structure of the material. All magnets have two poles, a north pole and a south pole. It is impossible to have a singular magnetic pole; ...
... Magnets are surrounded by magnetic fields and attract certain metals (iron, nickel, and cobalt). This magnetic effect comes from a special alignment of the atomic structure of the material. All magnets have two poles, a north pole and a south pole. It is impossible to have a singular magnetic pole; ...
Electromagnetic Induction Key Concept is Magnetic Flux
... 3) Constant Area, Constant B, Changing Cos φ: ...
... 3) Constant Area, Constant B, Changing Cos φ: ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2015 Semester
... – Still an excellent approximation when feature sizes are large compared with the wavelength of light ...
... – Still an excellent approximation when feature sizes are large compared with the wavelength of light ...
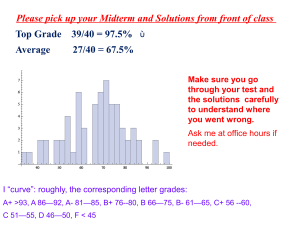
Top Grade 39/40 = 97.5% Average 27/40 = 67.5%
... Current on one side of the loop flows in the opposite direction to the current on the other side of loop. So, the two sides gets deflected in opposite directions, as shown; hence it turns. After a half turn, the sides have reversed, so deflection is in the opposite direction – makes coil turns back. ...
... Current on one side of the loop flows in the opposite direction to the current on the other side of loop. So, the two sides gets deflected in opposite directions, as shown; hence it turns. After a half turn, the sides have reversed, so deflection is in the opposite direction – makes coil turns back. ...
PHY2054_f11-10
... field points perpendicularly up through the plane of the coil. The direction is then reversed so that the final magnetic field has a magnitude of 1.1 T and points down through the coil. If the time required to reverse directions is 0.10 s, what average current flows through the coil during that time ...
... field points perpendicularly up through the plane of the coil. The direction is then reversed so that the final magnetic field has a magnitude of 1.1 T and points down through the coil. If the time required to reverse directions is 0.10 s, what average current flows through the coil during that time ...
Physics 122B Electromagnetism
... is that of a current loop. Consequently, an orbiting electron acts as a tiny magnetic dipole, with a north pole and a south pole. However, the atoms of most elements contain many electrons. Unlike the solar system, where all of the planets orbit in the same direction, electron orbits are arranged to ...
... is that of a current loop. Consequently, an orbiting electron acts as a tiny magnetic dipole, with a north pole and a south pole. However, the atoms of most elements contain many electrons. Unlike the solar system, where all of the planets orbit in the same direction, electron orbits are arranged to ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.