7TH CLASSES PHYSICS DAILY PLAN
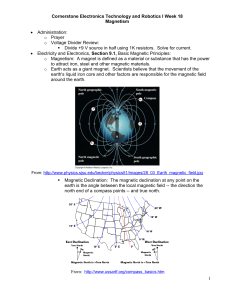
... If you have a magnetic material you can create an artificial magnet by rubbing it with another magnet.(SHOW!). In nature a magnet is an iron oxide (magnetite) but we can produce artificial magnets in different sizes and shapes, such as bar magnet, U shaped magnet horse-shoe magnet round magnet, etc… ...
... If you have a magnetic material you can create an artificial magnet by rubbing it with another magnet.(SHOW!). In nature a magnet is an iron oxide (magnetite) but we can produce artificial magnets in different sizes and shapes, such as bar magnet, U shaped magnet horse-shoe magnet round magnet, etc… ...
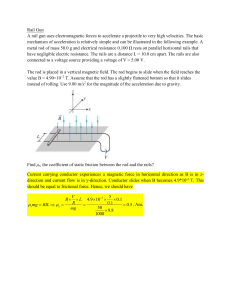
A rail gun uses electromagnetic forces to accelerate a projectile to
... mechanism of acceleration is relatively simple and can be illustrated in the following example. A metal rod of mass 50.0 g and electrical resistance 0.100 Ω rests on parallel horizontal rails that have negligible electric resistance. The rails are a distance L = 10.0 cm apart. The rails are also con ...
... mechanism of acceleration is relatively simple and can be illustrated in the following example. A metal rod of mass 50.0 g and electrical resistance 0.100 Ω rests on parallel horizontal rails that have negligible electric resistance. The rails are a distance L = 10.0 cm apart. The rails are also con ...
Appendix A. The Normal Geomagnetic Field in Hutchinson, Kansas ( ) Model: IGRF2000
... Y: East Component of the Magnetic Field This is the magnitude of vector constructed by projecting the total field vector onto an axis in the Eastward direction i.e. perpendicular to the X-axis. dY: The change in Y with respect to time. Z: Vertical Component of the Magnetic Field This is the magnitu ...
... Y: East Component of the Magnetic Field This is the magnitude of vector constructed by projecting the total field vector onto an axis in the Eastward direction i.e. perpendicular to the X-axis. dY: The change in Y with respect to time. Z: Vertical Component of the Magnetic Field This is the magnitu ...
Sources of Magnetic Field
... • In order to have a meter with a linear scale, the field lines in the gap should be always parallel to the plane of the coil as it rotates. • This could be achieved if we have a radial magnetic field. The soft iron cylinder gives us this field shape. ...
... • In order to have a meter with a linear scale, the field lines in the gap should be always parallel to the plane of the coil as it rotates. • This could be achieved if we have a radial magnetic field. The soft iron cylinder gives us this field shape. ...
Forces on Current Carrying Wires in Magnetic Fields
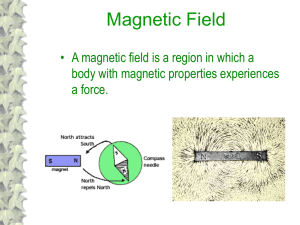
... Like electric charges – magnetic material follow the property that opposites attract and likes repel. The Geographic North pole of the earth is actually its magnetic south pole. Herriman High School - AP Physics 2 ...
... Like electric charges – magnetic material follow the property that opposites attract and likes repel. The Geographic North pole of the earth is actually its magnetic south pole. Herriman High School - AP Physics 2 ...
When a current-carrying loop is placed in a
... caused to grow by adding electrons to their domain. Some domains may even reorient to be aligned with the magnetic field. ...
... caused to grow by adding electrons to their domain. Some domains may even reorient to be aligned with the magnetic field. ...
doc - Cornerstone Robotics
... Electricity and Electronics, Section 9.2, Electric Current and Magnetism: o The Danish physicist Hans Christian Oersted was lecturing one day in 1820 on the possibility of electricity and magnetism being related to one another, and in the process demonstrated it conclusively by experiment in front o ...
... Electricity and Electronics, Section 9.2, Electric Current and Magnetism: o The Danish physicist Hans Christian Oersted was lecturing one day in 1820 on the possibility of electricity and magnetism being related to one another, and in the process demonstrated it conclusively by experiment in front o ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.