PDF Format - 6 slides per page - Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary
... industries. The question of its economical application to some purposes is still unsettled, but experiment has already proved that it will propel a street car better than a gas jet and give more light than a ...
... industries. The question of its economical application to some purposes is still unsettled, but experiment has already proved that it will propel a street car better than a gas jet and give more light than a ...
Chapter 30 - Faculty Personal Homepage
... motionless next to the wire such that its south end is near the coil and perpendicular to the plane of the coil as shown. The meter indicates that a current is flowing through the wire from the left toward the right. What, if anything, is wrong with this picture? a) The current should be flowing fro ...
... motionless next to the wire such that its south end is near the coil and perpendicular to the plane of the coil as shown. The meter indicates that a current is flowing through the wire from the left toward the right. What, if anything, is wrong with this picture? a) The current should be flowing fro ...
Chapter 9 THE MAGNETIC FIELD
... exploited by the Helmholtz arrangement of two such magnetic dipoles, shown in figure 7, where two identical coils separated by one radius produce a very uniform magnetic field along the axis near the centre of the coils. The off-axis field for the magnetic dipole is more complicated and will be deriv ...
... exploited by the Helmholtz arrangement of two such magnetic dipoles, shown in figure 7, where two identical coils separated by one radius produce a very uniform magnetic field along the axis near the centre of the coils. The off-axis field for the magnetic dipole is more complicated and will be deriv ...
talk-austin-07
... Electrons do not actually “spin”, they produce a magnetic moment that is equivalent to an electron spinning clockwise or anti-clockwise ...
... Electrons do not actually “spin”, they produce a magnetic moment that is equivalent to an electron spinning clockwise or anti-clockwise ...
PHYSICS 202/202P: AN INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICITY
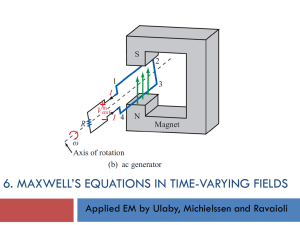
... Four Fundamental Laws about electromagnetism: MAXWELL’s EQUATIONS n Basis for many phenomena in Nature: ...
... Four Fundamental Laws about electromagnetism: MAXWELL’s EQUATIONS n Basis for many phenomena in Nature: ...
Faraday`s law and magnetic inductance (Parallel Lab)
... of the flux of the magnetic field passing that surface’s area, ℰ = This statement is known as the Faraday’s law. ...
... of the flux of the magnetic field passing that surface’s area, ℰ = This statement is known as the Faraday’s law. ...
MAGNETISM - Urbana School District #116
... magnetic forces. He also proposed that light was electromagnetic radiation. • In the late 19th century Pierre Curie discovered that magnets loose their magnetism above a certain temperature that later became known as the Curie point. • In the 1900's scientists discover superconductivity. Superconduc ...
... magnetic forces. He also proposed that light was electromagnetic radiation. • In the late 19th century Pierre Curie discovered that magnets loose their magnetism above a certain temperature that later became known as the Curie point. • In the 1900's scientists discover superconductivity. Superconduc ...
Magnetism ppt
... magnetic forces. He also proposed that light was electromagnetic radiation. • In the late 19th century Pierre Curie discovered that magnets loose their magnetism above a certain temperature that later became known as the Curie point. • In the 1900's scientists discover superconductivity. Superconduc ...
... magnetic forces. He also proposed that light was electromagnetic radiation. • In the late 19th century Pierre Curie discovered that magnets loose their magnetism above a certain temperature that later became known as the Curie point. • In the 1900's scientists discover superconductivity. Superconduc ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.