Torsion stiffness of a protein pair determined by magnetic
... The experimental arrangement is sketched in figure 1a. We use superparamagnetic particles (Dynal M-270 carboxyl, diameter 2.7 μm) that consist of a composite material of iron oxide nanoparticles in a polystyrene matrix. In order to be able to visualize the rotation of the particles by optical micro ...
... The experimental arrangement is sketched in figure 1a. We use superparamagnetic particles (Dynal M-270 carboxyl, diameter 2.7 μm) that consist of a composite material of iron oxide nanoparticles in a polystyrene matrix. In order to be able to visualize the rotation of the particles by optical micro ...
Group 1: Magnetism
... Explain and describe why the speed of light is the universal speed limit Explain, describe and discuss length contraction Describe and discuss relativistic length contraction mathematically Explain and describe the mass-energy relationship Describe and discuss nuclear reactions in terms of ...
... Explain and describe why the speed of light is the universal speed limit Explain, describe and discuss length contraction Describe and discuss relativistic length contraction mathematically Explain and describe the mass-energy relationship Describe and discuss nuclear reactions in terms of ...
electric motor - Science by Design
... electric motor with a few simple materials. This small motor models electromagnetism and the functioning of an electric motor. By running a current through the magnetic wire (bent in loops) we create an electro magnet (a moving electric charge produces an electric field and when the current carrying ...
... electric motor with a few simple materials. This small motor models electromagnetism and the functioning of an electric motor. By running a current through the magnetic wire (bent in loops) we create an electro magnet (a moving electric charge produces an electric field and when the current carrying ...
SOTERIA_WP2_ROB_20090324
... Beyond, total sunspot index (1-D time series) Importance of hemispheric asymmetries and time delays. Butterfly diagrams (North-South asymmetries) Active longitudes (position of heliospheric current sheet, CME angular ...
... Beyond, total sunspot index (1-D time series) Importance of hemispheric asymmetries and time delays. Butterfly diagrams (North-South asymmetries) Active longitudes (position of heliospheric current sheet, CME angular ...
Metamaterials and the Control of Electromagnetic Fields
... found to accommodate the desired configuration of fields. It was to answer the question of what parameters to choose for the metamaterial that we developed transformation optics [17, 18, 19, 20]. The idea is quite straightforward: start with a field pattern that obeys Maxwell’s equations for a syste ...
... found to accommodate the desired configuration of fields. It was to answer the question of what parameters to choose for the metamaterial that we developed transformation optics [17, 18, 19, 20]. The idea is quite straightforward: start with a field pattern that obeys Maxwell’s equations for a syste ...
Lorenz or Coulomb
... t B - E (the magnetic limit). Once again, we underline forcefully that we have only shown compatibility between some approximations of the full set of “Maxwell equations” with Galilean relativity. We will now present what we think to be a demonstration of the two Galilean limits. Indeed, the ...
... t B - E (the magnetic limit). Once again, we underline forcefully that we have only shown compatibility between some approximations of the full set of “Maxwell equations” with Galilean relativity. We will now present what we think to be a demonstration of the two Galilean limits. Indeed, the ...
File S1.
... minimal when the neurite is aligned with the y-axis and steeply increases if the alignment deviates from this optimal orientation (horizontal dashed straight lines). In contrast, stimulation with the cloverleaf coil results in a threshold that changes by less than 50% for all possible orientations o ...
... minimal when the neurite is aligned with the y-axis and steeply increases if the alignment deviates from this optimal orientation (horizontal dashed straight lines). In contrast, stimulation with the cloverleaf coil results in a threshold that changes by less than 50% for all possible orientations o ...
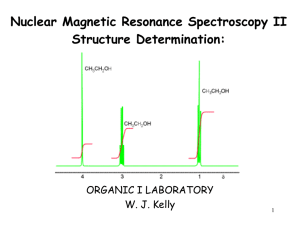
NMR Lecture II - Structure Determination
... they can change the nuclear spins of some elements, ...
... they can change the nuclear spins of some elements, ...
DISCOVERING AND ANALYZING MAGNETIC FIELDS
... around the straw, and putting loops of wire on top of one another while always recording the number of loops they wrapped around the straw. Wrapping the wire less tightly and putting loops of wire on top of one another decreased and increased the magnitude of the magnetic field respectively, changin ...
... around the straw, and putting loops of wire on top of one another while always recording the number of loops they wrapped around the straw. Wrapping the wire less tightly and putting loops of wire on top of one another decreased and increased the magnitude of the magnetic field respectively, changin ...
VIII. NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (NMR) SPECTROSCOPY
... proportional to H, the relation between them is more complicated. Upon increasing H, M increases only up to a limit. Ferromagnetic materials loose their ferromagnetism above a certain temperature, called the Curie-point (e.g., Fe: 769 C, Co: 1075 C, Ni: 360 C). Above this temperature ferromagneti ...
... proportional to H, the relation between them is more complicated. Upon increasing H, M increases only up to a limit. Ferromagnetic materials loose their ferromagnetism above a certain temperature, called the Curie-point (e.g., Fe: 769 C, Co: 1075 C, Ni: 360 C). Above this temperature ferromagneti ...
MAGNETISM IN THE EIGHTEENTH CENTURY H.H. Ricker III Email
... Newton’s approach failed when he learned that measurements of magnetic force indicated a law of the inverse cube instead of the expected law of inverse square. In Corollary V he explained this result as follows: “The power of gravity is of a different nature from the power of magnetism; for the mag ...
... Newton’s approach failed when he learned that measurements of magnetic force indicated a law of the inverse cube instead of the expected law of inverse square. In Corollary V he explained this result as follows: “The power of gravity is of a different nature from the power of magnetism; for the mag ...
PowerSources 2004 Word Template - IR@CSIR
... tube designers as the conventional single-beam amplifiers cannot fulfill the emerging requirements like high power, high operating frequency, high efficiency, large bandwidth, low noise, compact and light weight device [1-2]. Multibeam klystrons are highly promising candidates to meet most of such n ...
... tube designers as the conventional single-beam amplifiers cannot fulfill the emerging requirements like high power, high operating frequency, high efficiency, large bandwidth, low noise, compact and light weight device [1-2]. Multibeam klystrons are highly promising candidates to meet most of such n ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.