magnetic
... Galvanometer - the historical name given to a moving coil electric current detector. When a current is passed through a coil in a magnetic field, the coil experiences a torque proportional to the current. If the coil's movement is opposed by a coil spring, then the amount of deflection of a needle a ...
... Galvanometer - the historical name given to a moving coil electric current detector. When a current is passed through a coil in a magnetic field, the coil experiences a torque proportional to the current. If the coil's movement is opposed by a coil spring, then the amount of deflection of a needle a ...
neutral - Mr Bernabo at Affton High School
... Any two objects which have an electric charge also exert a force on each other. ...
... Any two objects which have an electric charge also exert a force on each other. ...
CS 436 HCI Technology Basic Electricity/Electronics Review 1 Basic Quantities and Units
... Sometimes the human body/ground is used as one plate, and thus proximity of you (or your hand) can be inferred by determining the capacitance between you and a metal plate. Capacitors exhibit a form of complex resistance (1/conductance) called Impedance (1/admittance), equal to 1/sC, where ...
... Sometimes the human body/ground is used as one plate, and thus proximity of you (or your hand) can be inferred by determining the capacitance between you and a metal plate. Capacitors exhibit a form of complex resistance (1/conductance) called Impedance (1/admittance), equal to 1/sC, where ...
Document
... 8. What is the magnitude of the force on B if QB = +2 C? (A) ¼ N (B) ½ N (C) 2 N (D) 4 N 9. What is the magnitude of the force on A if QB = +2 C? (A) ¼ N (B) ½ N (C) 2 N (D) 4 N 10. What is the magnitude of the force on B if QA = QB = +2 C? (A) ¼ N (B) ½ N (C) 2 N (D) 4 N QA = QB = +1 C 11. What is ...
... 8. What is the magnitude of the force on B if QB = +2 C? (A) ¼ N (B) ½ N (C) 2 N (D) 4 N 9. What is the magnitude of the force on A if QB = +2 C? (A) ¼ N (B) ½ N (C) 2 N (D) 4 N 10. What is the magnitude of the force on B if QA = QB = +2 C? (A) ¼ N (B) ½ N (C) 2 N (D) 4 N QA = QB = +1 C 11. What is ...
Theme 1 Electricity
... A switch work by ... When the switch is open ... When the switch is closed ... In a series circuit ... In a parallel circuit ... I think bulb ? will be on / off when switch ? is open / closed. I think this because ... ...
... A switch work by ... When the switch is open ... When the switch is closed ... In a series circuit ... In a parallel circuit ... I think bulb ? will be on / off when switch ? is open / closed. I think this because ... ...
Document
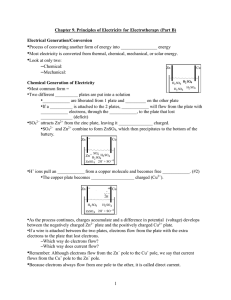
... 3. adding static charge to insulators a. rubbing dissimilar insulators together transfers electrons from one to the other b. excess electrons = negatively charged deficient electrons = positively charged c. total charge is unchanged (conservation of charge) 4. adding static charge to conductors a. c ...
... 3. adding static charge to insulators a. rubbing dissimilar insulators together transfers electrons from one to the other b. excess electrons = negatively charged deficient electrons = positively charged c. total charge is unchanged (conservation of charge) 4. adding static charge to conductors a. c ...
Curriculum Map Discipline: Science Course: AP Physics C
... Essential Questions: What is the difference between an electric and a magnetic field and how are they related? In what way are charges affected by magnetic fields? How can one use Ampere's law to calculate magnetic field strengths in various circuit configurations? Content: Relationship between magn ...
... Essential Questions: What is the difference between an electric and a magnetic field and how are they related? In what way are charges affected by magnetic fields? How can one use Ampere's law to calculate magnetic field strengths in various circuit configurations? Content: Relationship between magn ...
r - PolyU EIE
... • an equivalent form of Biot-Savart Law • Integral form: The line integral of H around any closed path C is equal to the current Ienc enclosed by the path (in a ...
... • an equivalent form of Biot-Savart Law • Integral form: The line integral of H around any closed path C is equal to the current Ienc enclosed by the path (in a ...
Physics Magnets and electromagnets revision
... • Metals that are magnetic = Iron, Steel, Cobalt and Nickel • Each magnet has two ends, called poles. The magnetic strength of a magnet is strongest at the two poles. • Two like poles will repel (e.g. North and North) • Two unlike poles will attract (e.g. North and South) • The only true test for a ...
... • Metals that are magnetic = Iron, Steel, Cobalt and Nickel • Each magnet has two ends, called poles. The magnetic strength of a magnet is strongest at the two poles. • Two like poles will repel (e.g. North and North) • Two unlike poles will attract (e.g. North and South) • The only true test for a ...
Document
... non-electrical energy) any electricity. They may either consume energy (i.e. convert from electrical form to a non-electrical form such as heat or light), or store energy (in electrostatic and electromagnetic fields). ...
... non-electrical energy) any electricity. They may either consume energy (i.e. convert from electrical form to a non-electrical form such as heat or light), or store energy (in electrostatic and electromagnetic fields). ...
PHYS2424 - SPRING 2000
... Shown below is a picture from a cloud chamber in which three particles (A, B, and C) are created. Given that an external magnetic field is directed out of the page as shown in the diagram, you are to determine whether each particle is positive, negative, or neutral and fill in the appropriate blank. ...
... Shown below is a picture from a cloud chamber in which three particles (A, B, and C) are created. Given that an external magnetic field is directed out of the page as shown in the diagram, you are to determine whether each particle is positive, negative, or neutral and fill in the appropriate blank. ...
Historical burdens on physics 42 Magnetic poles
... and which can easily be verified experimentally, cannot be treated. Coulomb’s law for magnetic poles is even not mentioned, although it is easier to verify than the corresponding electric law. It is not even possible to define the most fundamental property of a permanent magnet: i.e. that the total ...
... and which can easily be verified experimentally, cannot be treated. Coulomb’s law for magnetic poles is even not mentioned, although it is easier to verify than the corresponding electric law. It is not even possible to define the most fundamental property of a permanent magnet: i.e. that the total ...
WELCOME TO PHYSICS 1103
... •The rotor of the St. Louis motor is an electromagnet on a pivot. Permanent magnets attract and repel the rotor, causing it to spin. •To keep the rotor spinning, the magnetic poles of the electromagnet reverse when the current reverses ...
... •The rotor of the St. Louis motor is an electromagnet on a pivot. Permanent magnets attract and repel the rotor, causing it to spin. •To keep the rotor spinning, the magnetic poles of the electromagnet reverse when the current reverses ...
Introduction to Electrostatics
... In a conductor, free charges move in response to an applied Charge flows until ...
... In a conductor, free charges move in response to an applied Charge flows until ...
Practice Quiz (Chapter 25 Electromagnetic Induction) 1) Thrust a
... 1) Thrust a magnet into a coil of wire and the coil A) becomes an electromagnet. B) has a current in it. C) both of these D) neither of these Answer: C 2) Electromagnetic induction occurs in a coil when there is a change in A) electric field intensity in the coil. B) magnetic field intensity in the ...
... 1) Thrust a magnet into a coil of wire and the coil A) becomes an electromagnet. B) has a current in it. C) both of these D) neither of these Answer: C 2) Electromagnetic induction occurs in a coil when there is a change in A) electric field intensity in the coil. B) magnetic field intensity in the ...
Electricity

Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and flow of electric charge. Electricity gives a wide variety of well-known effects, such as lightning, static electricity, electromagnetic induction and electric current. In addition, electricity permits the creation and reception of electromagnetic radiation such as radio waves.In electricity, charges produce electromagnetic fields which act on other charges. Electricity occurs due to several types of physics: electric charge: a property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interactions. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. electric field (see electrostatics): an especially simple type of electromagnetic field produced by an electric charge even when it is not moving (i.e., there is no electric current). The electric field produces a force on other charges in its vicinity. electric potential: the capacity of an electric field to do work on an electric charge, typically measured in volts. electric current: a movement or flow of electrically charged particles, typically measured in amperes. electromagnets: Moving charges produce a magnetic field. Electric currents generate magnetic fields, and changing magnetic fields generate electric currents.In electrical engineering, electricity is used for: electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment; electronics which deals with electrical circuits that involve active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies.Electrical phenomena have been studied since antiquity, though progress in theoretical understanding remained slow until the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. Even then, practical applications for electricity were few, and it would not be until the late nineteenth century that engineers were able to put it to industrial and residential use. The rapid expansion in electrical technology at this time transformed industry and society. Electricity's extraordinary versatility means it can be put to an almost limitless set of applications which include transport, heating, lighting, communications, and computation. Electrical power is now the backbone of modern industrial society.