Practice Questions for I Year/I Part Engineering Physics
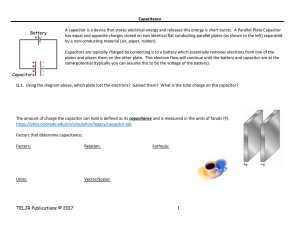
... of force on each charge. (1.05 N) 20. Two capacitors of capacitance 4 μF and 12μ F respectively are connected in series and the combination is connected momentarily across a 200V battery. The charged capacitors are now isolated and connected in parallel, similar charge plates being connected, togeth ...
... of force on each charge. (1.05 N) 20. Two capacitors of capacitance 4 μF and 12μ F respectively are connected in series and the combination is connected momentarily across a 200V battery. The charged capacitors are now isolated and connected in parallel, similar charge plates being connected, togeth ...
Lecture 20
... know are substances which have free electrons, which would move around the material if we applied electric field. Under equilibrium conditions, the electric field inside is zero and free charges, if they exist, can only exist on the surface of the conductor. This, of course, is not true if we connec ...
... know are substances which have free electrons, which would move around the material if we applied electric field. Under equilibrium conditions, the electric field inside is zero and free charges, if they exist, can only exist on the surface of the conductor. This, of course, is not true if we connec ...
The Link between Electric Current and Magnetic Field The Double
... considered in isolation. There is also the issue of a compression building up in the aether between the two dipoles. Due to the vorticity involved, the situation will be asymmetric and the mutual repulsion between these two dipoles will be caused by a combination of both centrifugal force and Corio ...
... considered in isolation. There is also the issue of a compression building up in the aether between the two dipoles. Due to the vorticity involved, the situation will be asymmetric and the mutual repulsion between these two dipoles will be caused by a combination of both centrifugal force and Corio ...
Quantum Mechanics_triboelectric effect
... Surface nano-effects are not well understood, and the atomic force microscope has enabled rapid progress in this field of physics. Because the surface of the material is now electrically charged, either negatively or positively, any contact with an uncharged conductive object or with an object havi ...
... Surface nano-effects are not well understood, and the atomic force microscope has enabled rapid progress in this field of physics. Because the surface of the material is now electrically charged, either negatively or positively, any contact with an uncharged conductive object or with an object havi ...
ΦB = BAcosθ - Purdue Physics
... magnetic field due to the current opposes the change in the magnetic flux that induces the current. Binduced always opposes the change in Opposition to Flux: the flux of B, but does not always point opposite it!!! ...
... magnetic field due to the current opposes the change in the magnetic flux that induces the current. Binduced always opposes the change in Opposition to Flux: the flux of B, but does not always point opposite it!!! ...
Electrostatic charges in vx B 1 fields: the Faraday disk
... the negative space charge withoutaffecting the electric field inside the cylinder. Now close the switch SW in the circuit of the generator.Conduction electrons escape at the axis into the external circuit, where the v x B is zero, and return at the rim. The field J/a in the disk points in the direct ...
... the negative space charge withoutaffecting the electric field inside the cylinder. Now close the switch SW in the circuit of the generator.Conduction electrons escape at the axis into the external circuit, where the v x B is zero, and return at the rim. The field J/a in the disk points in the direct ...
Summary (Electric Field and Electric Charge)
... • Spheres of different radius enclose the charge. Does the electric flux dependent on the radius? • There are different ways to understand this: • Count the field lines • Replace the charge with a light bulb and the electric flux with the light emitted ...
... • Spheres of different radius enclose the charge. Does the electric flux dependent on the radius? • There are different ways to understand this: • Count the field lines • Replace the charge with a light bulb and the electric flux with the light emitted ...
SPH 618 Optical and Laser Physics University of Nairobi, Kenya
... spectrum where anomalous dispersion takes place. A positive imaginary component of the refractive index implies that the wave is absorbed as it propagates through the medium, so the regions of the spectrum where is appreciable are called regions of resonant absorption. Anomalous dispersion and reson ...
... spectrum where anomalous dispersion takes place. A positive imaginary component of the refractive index implies that the wave is absorbed as it propagates through the medium, so the regions of the spectrum where is appreciable are called regions of resonant absorption. Anomalous dispersion and reson ...
Development of Land Adjacent to or within the
... transmission lines are defined as overhead or underground powerlines that carry 110kV (kilovolts) or greater. EMFs occur everywhere. The human body produces EMFs as nerve impulses, which are transferred through the body. However, they are very weak. The Earth has an EMF (its magnetic field) which is ...
... transmission lines are defined as overhead or underground powerlines that carry 110kV (kilovolts) or greater. EMFs occur everywhere. The human body produces EMFs as nerve impulses, which are transferred through the body. However, they are very weak. The Earth has an EMF (its magnetic field) which is ...
Electricity

Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and flow of electric charge. Electricity gives a wide variety of well-known effects, such as lightning, static electricity, electromagnetic induction and electric current. In addition, electricity permits the creation and reception of electromagnetic radiation such as radio waves.In electricity, charges produce electromagnetic fields which act on other charges. Electricity occurs due to several types of physics: electric charge: a property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interactions. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. electric field (see electrostatics): an especially simple type of electromagnetic field produced by an electric charge even when it is not moving (i.e., there is no electric current). The electric field produces a force on other charges in its vicinity. electric potential: the capacity of an electric field to do work on an electric charge, typically measured in volts. electric current: a movement or flow of electrically charged particles, typically measured in amperes. electromagnets: Moving charges produce a magnetic field. Electric currents generate magnetic fields, and changing magnetic fields generate electric currents.In electrical engineering, electricity is used for: electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment; electronics which deals with electrical circuits that involve active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies.Electrical phenomena have been studied since antiquity, though progress in theoretical understanding remained slow until the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. Even then, practical applications for electricity were few, and it would not be until the late nineteenth century that engineers were able to put it to industrial and residential use. The rapid expansion in electrical technology at this time transformed industry and society. Electricity's extraordinary versatility means it can be put to an almost limitless set of applications which include transport, heating, lighting, communications, and computation. Electrical power is now the backbone of modern industrial society.