Plasma Theory Task: Describe plasma theory in 2 hours
... fluid descriptions (e.g., magnetohydrodynamics) various hybrids of these ...
... fluid descriptions (e.g., magnetohydrodynamics) various hybrids of these ...
Chapter 32: Maxwell`s Equation and EM Waves
... Producing electromagnetic waves • Electromagnetic waves are generated ultimately by accelerating electric charge. • Details of emitting systems depend on wavelength, with most efficient emitters being roughly a wavelength in size. • Radio waves are generated by alternating currents in metal ante ...
... Producing electromagnetic waves • Electromagnetic waves are generated ultimately by accelerating electric charge. • Details of emitting systems depend on wavelength, with most efficient emitters being roughly a wavelength in size. • Radio waves are generated by alternating currents in metal ante ...
Electrodynamic constraints on homogeneity and RF power deposition in multiple...
... μn is the target profile and Cn contains the spatial weighting induced by the B1+ fields of each coil. The actual excited profile obtained with the minimum SAR pulse can be calculated as μ% n = Cnf%n . A similar formulation applies when a single RF current source ...
... μn is the target profile and Cn contains the spatial weighting induced by the B1+ fields of each coil. The actual excited profile obtained with the minimum SAR pulse can be calculated as μ% n = Cnf%n . A similar formulation applies when a single RF current source ...
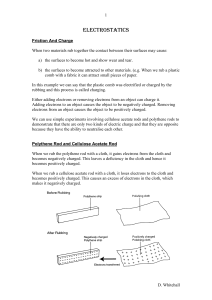
ELECTROSTATICS
... 1) In both cases the direction of the force on the positively charged particle is the same as the electric field direction but the force acting on the negatively charged particles moves in a reverse direction to the magnetic field. 2) The basic rule of like charges repelling and unlike charges attra ...
... 1) In both cases the direction of the force on the positively charged particle is the same as the electric field direction but the force acting on the negatively charged particles moves in a reverse direction to the magnetic field. 2) The basic rule of like charges repelling and unlike charges attra ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.