best electric field
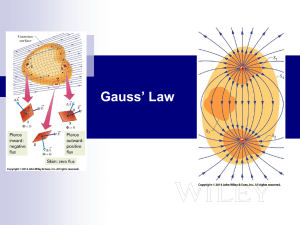
... • IF an electric field moves charges and conductors are full of electrons which can move, where will all the electrons go? B. spread out on outer surface since the charges move away from another to lower their energy • the charges on opposite sides cancel out forces so E=0 inside ...
... • IF an electric field moves charges and conductors are full of electrons which can move, where will all the electrons go? B. spread out on outer surface since the charges move away from another to lower their energy • the charges on opposite sides cancel out forces so E=0 inside ...
Gauss* Law
... 1. Yes, the larger the radius the more flux lines will penetrate through the surface 2. No, the flux is independent of the radius 3. I have to calculate again for a different radius ...
... 1. Yes, the larger the radius the more flux lines will penetrate through the surface 2. No, the flux is independent of the radius 3. I have to calculate again for a different radius ...
Your Magnet Safety Team - Center for In Vivo Microscopy
... • Visitors may never assist or work in the lab • Visitors may not enter the lab after hours ...
... • Visitors may never assist or work in the lab • Visitors may not enter the lab after hours ...
electromagnetic induction
... Whenever there is a change in the magnetic flux linked with a coil, there is also a change of flux linked with the neighbouring coil, producing an induced emf in the second coil. This phenomenon of producing an induced emf in a coil due to the change in current in the other coil is known as mutual i ...
... Whenever there is a change in the magnetic flux linked with a coil, there is also a change of flux linked with the neighbouring coil, producing an induced emf in the second coil. This phenomenon of producing an induced emf in a coil due to the change in current in the other coil is known as mutual i ...
Electromagnetism - KCPE-KCSE
... This is shown by the field lines being closest together near to the wire. The strength of the field increases if the electric current is increased. ...
... This is shown by the field lines being closest together near to the wire. The strength of the field increases if the electric current is increased. ...
5G50.52 Energy Storage with Superconductors
... This meant that liquid nitrogen, which is both less expensive and easier to store than liquid helium, could be used to cool the perovskites sufficiently that they become superconductive. The temperature at which a material becomes a superconductor is known as its critical temperature, Tc , and there ...
... This meant that liquid nitrogen, which is both less expensive and easier to store than liquid helium, could be used to cool the perovskites sufficiently that they become superconductive. The temperature at which a material becomes a superconductor is known as its critical temperature, Tc , and there ...
Electricity
... • Electricity - movement of electrical charges – Electric current is the flow of electrons from negative to positive – An electric current will occur in a conductive metal when an electric potential exists – Electric potential is the difference between the charge at the – end and the + end – Electri ...
... • Electricity - movement of electrical charges – Electric current is the flow of electrons from negative to positive – An electric current will occur in a conductive metal when an electric potential exists – Electric potential is the difference between the charge at the – end and the + end – Electri ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.