The Electric Field
... blue charge, which of them experiences the greater electric field due to the green charge? ...
... blue charge, which of them experiences the greater electric field due to the green charge? ...
Electric Field
... distance is increased? 2. How does the electric force change when either or both of the charges are increased? ...
... distance is increased? 2. How does the electric force change when either or both of the charges are increased? ...
Magnets and Magnetism
... magnetic force is a universal force. It is always present when magnetic poles come near one another. Think of the last time you worked with magnets. If you held two magnets in a certain way, they pulled together. When you turned one of the magnets around, they pushed apart. Why? The magnetic force b ...
... magnetic force is a universal force. It is always present when magnetic poles come near one another. Think of the last time you worked with magnets. If you held two magnets in a certain way, they pulled together. When you turned one of the magnets around, they pushed apart. Why? The magnetic force b ...
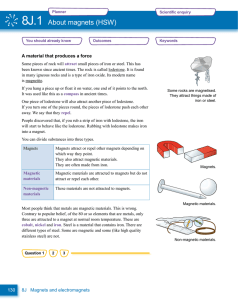
8J.1 About magnets (HSW)
... Electricity and magnetism An electric current has a magnetic field around it. This is a really important thing because, without it, we would not have electric motors and many other things that we take for granted. This important fact was discovered by accident by a scientist called Hans Christian Oe ...
... Electricity and magnetism An electric current has a magnetic field around it. This is a really important thing because, without it, we would not have electric motors and many other things that we take for granted. This important fact was discovered by accident by a scientist called Hans Christian Oe ...
Magnets, Electricity
... • A simple electric motor also includes components called brushes and a commutator. • The brushes are conducting pads connected to the battery. • The brushes make contact with the commutator, which is a conducting metal ring that is split. • The brushes and the commutator form a closed electric circ ...
... • A simple electric motor also includes components called brushes and a commutator. • The brushes are conducting pads connected to the battery. • The brushes make contact with the commutator, which is a conducting metal ring that is split. • The brushes and the commutator form a closed electric circ ...
Exam - 1 - SOLUTIONS
... 1. The drawings show three charges that have the same magnitude but different signs. In all cases the distance d between the charges is the same. The magnitude of the charges is |q|= 4.0 µC, and the distance between them is d = 5.0 mm. Determine the magnitude of the net force on charge 2 for each of ...
... 1. The drawings show three charges that have the same magnitude but different signs. In all cases the distance d between the charges is the same. The magnitude of the charges is |q|= 4.0 µC, and the distance between them is d = 5.0 mm. Determine the magnitude of the net force on charge 2 for each of ...
Unit 6: Thermal Physics
... methods of vector solutions of inclined plane problems. • State Newton's Second Law of Motion verbally and in the form of a mathematical statement. • Write the units of force, mass, and acceleration in SI, cgs, FPS units. • Define the units newton and slug and to be able to express them in SI, cgs, ...
... methods of vector solutions of inclined plane problems. • State Newton's Second Law of Motion verbally and in the form of a mathematical statement. • Write the units of force, mass, and acceleration in SI, cgs, FPS units. • Define the units newton and slug and to be able to express them in SI, cgs, ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.