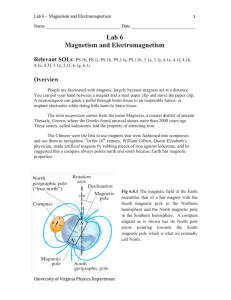
Chapter 3 GAUSS` LAW
... Gauss’ Law actually is one of Maxwell’s four laws of electromagnetism. Gauss’ Law is completely equivalent to Coulomb’s law for electrostatics or for slowly moving charges. However, Gauss’ law is more general and applies to electric fields arising from rapidly moving and accelerating charges. Really ...
... Gauss’ Law actually is one of Maxwell’s four laws of electromagnetism. Gauss’ Law is completely equivalent to Coulomb’s law for electrostatics or for slowly moving charges. However, Gauss’ law is more general and applies to electric fields arising from rapidly moving and accelerating charges. Really ...
Physics on the Guitar - Xraise Cornell
... At the core of magnetic pickups are magnets. Each magnet is oriented so that an imaginary line through the north and south poles will intersect with the string above it. A thin copper wire coiled around the magnet so that the axis of the coil aligns with the N-S axis of the magnet. The basic physics ...
... At the core of magnetic pickups are magnets. Each magnet is oriented so that an imaginary line through the north and south poles will intersect with the string above it. A thin copper wire coiled around the magnet so that the axis of the coil aligns with the N-S axis of the magnet. The basic physics ...
How To Find the Electric Field for a Continuous Charge Distribution
... makes your life easier. Here’s how to approach such problems. 1. First, draw the electric field lines, using considerations of symmetry. For instance, they radiate out radially from a spherically symmetric charge distribution. 2. Decide on a Gaussian surface in the region where you want to find the ...
... makes your life easier. Here’s how to approach such problems. 1. First, draw the electric field lines, using considerations of symmetry. For instance, they radiate out radially from a spherically symmetric charge distribution. 2. Decide on a Gaussian surface in the region where you want to find the ...
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current
... In India Domestic power supply is at 220 V, 50 Hz; while in USA it is 110 V, 50 Hz. Give one advantage and one disadvantage of 220 V supply over 110 supply. A coil of inductance L, a capacitor of capacitance C and resistor of resistance R all put in series with an alternating source of emd E = E0 si ...
... In India Domestic power supply is at 220 V, 50 Hz; while in USA it is 110 V, 50 Hz. Give one advantage and one disadvantage of 220 V supply over 110 supply. A coil of inductance L, a capacitor of capacitance C and resistor of resistance R all put in series with an alternating source of emd E = E0 si ...
2010S exam 2
... [20%] In an inkjet printer, letters are built up by squirting drops of ink at the paper from a rapidly moving nozzle. The ink drops, which have a mass of 15 ng each, leave the nozzle and travel toward the paper at 18 m/s, passing through a charging unit that gives each drop a positive charge q by re ...
... [20%] In an inkjet printer, letters are built up by squirting drops of ink at the paper from a rapidly moving nozzle. The ink drops, which have a mass of 15 ng each, leave the nozzle and travel toward the paper at 18 m/s, passing through a charging unit that gives each drop a positive charge q by re ...
Static Electricity
... Physics 5m: Students know static electric fields have as their source some arrangement of electric charges Focus Question: What happens when you shock someone? ...
... Physics 5m: Students know static electric fields have as their source some arrangement of electric charges Focus Question: What happens when you shock someone? ...
CHAPTER 18: ELECTRIC CHARGE AND ELECTRIC FIELD
... zero strength field at the center of the triangular configuration because of the vector nature of the electric field. Consider the two cases: (1) all charges have the same sign and (2) one charge ...
... zero strength field at the center of the triangular configuration because of the vector nature of the electric field. Consider the two cases: (1) all charges have the same sign and (2) one charge ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.