PHYS 210 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
... To pass this course, a student must have at least 50% on the final exam. ...
... To pass this course, a student must have at least 50% on the final exam. ...
Handout - Intro to Magnetism
... Diamagnetic materials are weakly repelled by magnets. Many common materials are diamagnetic: water, glass, copper, graphite, salt, lead, rubber, diamond, wood, and many plastics for example. Paramagnetic materials are weakly attracted to magnets. Examples: aluminum, oxygen, sodium, platinum, esseven ...
... Diamagnetic materials are weakly repelled by magnets. Many common materials are diamagnetic: water, glass, copper, graphite, salt, lead, rubber, diamond, wood, and many plastics for example. Paramagnetic materials are weakly attracted to magnets. Examples: aluminum, oxygen, sodium, platinum, esseven ...
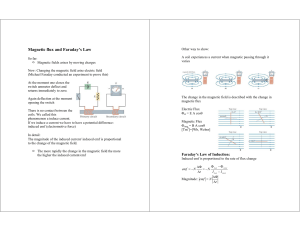
Electromagnetic Induction
... More about magnets • Common magnets are made of iron, nickel, and cobalt. – The spin of their e- do not cancel ...
... More about magnets • Common magnets are made of iron, nickel, and cobalt. – The spin of their e- do not cancel ...
Electricity and Magnetism Study Guide - Mr. L`s Room
... 5. What is static electricity? The build up of electrical charges that do not flow continuously. 6. Explain three ways electric charges known as static electricity can be transferred. Give examples of each. (1) Friction---transfer of electrons by rubbing 2 uncharged objects together. Electrons trans ...
... 5. What is static electricity? The build up of electrical charges that do not flow continuously. 6. Explain three ways electric charges known as static electricity can be transferred. Give examples of each. (1) Friction---transfer of electrons by rubbing 2 uncharged objects together. Electrons trans ...
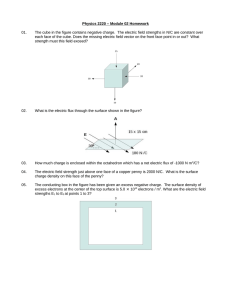
Exercise 1: As the bar in Figure below moves to the right, an electric
... Exercise 6: A 50-turn rectangular coil of dimensions 5.00 cm X 10.0 cm is allowed to fall from a position where B = 0 to a new position where B = 0.500 T and the magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of the coil. Calculate the magnitude of the average emf that is induced in the coil ...
... Exercise 6: A 50-turn rectangular coil of dimensions 5.00 cm X 10.0 cm is allowed to fall from a position where B = 0 to a new position where B = 0.500 T and the magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of the coil. Calculate the magnitude of the average emf that is induced in the coil ...
College Physics, PHYS 104, Behavioral Objectives, Unit III (b)
... Using a simple DC motor, be able to identify: (a) the field magnet, armature, commutator, electromagnet, and brushes and their physical roles, (b) with the split ring commutator, the polarity of each end when the armature is turned, position of the armature when polarity change occurs, role of armat ...
... Using a simple DC motor, be able to identify: (a) the field magnet, armature, commutator, electromagnet, and brushes and their physical roles, (b) with the split ring commutator, the polarity of each end when the armature is turned, position of the armature when polarity change occurs, role of armat ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.