viva Science lesson sequence planner-magnetism
... Key ideas: Magnetic force extends into the space surrounding the magnet. Magnets push and pull through some types of matter but not others. This activity involves a visual illusion, and can be quite compelling if set up in a room for students to discover. The paper clip floating is indeed a surprisi ...
... Key ideas: Magnetic force extends into the space surrounding the magnet. Magnets push and pull through some types of matter but not others. This activity involves a visual illusion, and can be quite compelling if set up in a room for students to discover. The paper clip floating is indeed a surprisi ...
Physics 2102 Spring 2002 Lecture 8
... F1 F3 iaB sin 90 iaB. The magnetic force on sides 2 and 4 is F2 F4 ibB sin(90 - ) ibB cos . These forces cancel in pairs and thus Fnet 0. The torque about the loop center C of F2 and F4 is zero because both forces pass through point C. The moment arm for F1 and F3 is equal to (b / ...
... F1 F3 iaB sin 90 iaB. The magnetic force on sides 2 and 4 is F2 F4 ibB sin(90 - ) ibB cos . These forces cancel in pairs and thus Fnet 0. The torque about the loop center C of F2 and F4 is zero because both forces pass through point C. The moment arm for F1 and F3 is equal to (b / ...
The field concepts of Faraday and Maxwell
... introduced, On the contrary, when the natural truth and the conventional representation of it most closely agree, then are we most advanced in our knowledge. The emission and the ether theories present such cases in relation to iight, The idea of a fluid or of two fluids is the same for electricity; ...
... introduced, On the contrary, when the natural truth and the conventional representation of it most closely agree, then are we most advanced in our knowledge. The emission and the ether theories present such cases in relation to iight, The idea of a fluid or of two fluids is the same for electricity; ...
Induced EMF - Purdue Physics
... Induced EMF has a direction such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it. ...
... Induced EMF has a direction such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it. ...
Why won`t my compass work the other side of the equator
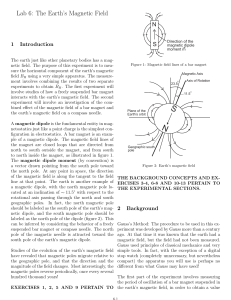
... Pupil learning outcomes: Pupils can: explain why a compass needle that floats horizontally in one hemisphere of the Earth dips downward and sticks against the compass baseplate in the other; use this explanation to describe the threedimensional magnetic field of the Earth. ...
... Pupil learning outcomes: Pupils can: explain why a compass needle that floats horizontally in one hemisphere of the Earth dips downward and sticks against the compass baseplate in the other; use this explanation to describe the threedimensional magnetic field of the Earth. ...
Ch.20 Induced voltages and Inductance Faraday`s Law
... Now the conductor is part of a closed loop. See pictures on page 667. Conducting bar of length L slides along two fixed parallel conducting rails. Let the stationary part of the loop have a resistance R. A uniform and constant B-field is perpendicular to the plane of the loop. As the bar is pulled ...
... Now the conductor is part of a closed loop. See pictures on page 667. Conducting bar of length L slides along two fixed parallel conducting rails. Let the stationary part of the loop have a resistance R. A uniform and constant B-field is perpendicular to the plane of the loop. As the bar is pulled ...
Title of PAPER - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... expressed are not always known and so this method will only work when sufficient research has been conducted. ...
... expressed are not always known and so this method will only work when sufficient research has been conducted. ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
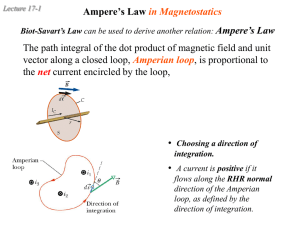
... Magnetic field associated with a current carrying conductor also depends upon the direction of flow of current. If we change the direction of flow of current then the direction of poles of magnetic field is also changes. Here logic is whenever moving charges are changing direction then poles also ch ...
... Magnetic field associated with a current carrying conductor also depends upon the direction of flow of current. If we change the direction of flow of current then the direction of poles of magnetic field is also changes. Here logic is whenever moving charges are changing direction then poles also ch ...
Force between magnets
Magnets exert forces and torques on each other due to the complex rules of electromagnetism. The forces of attraction field of magnets are due to microscopic currents of electrically charged electrons orbiting nuclei and the intrinsic magnetism of fundamental particles (such as electrons) that make up the material. Both of these are modeled quite well as tiny loops of current called magnetic dipoles that produce their own magnetic field and are affected by external magnetic fields. The most elementary force between magnets, therefore, is the magnetic dipole–dipole interaction. If all of the magnetic dipoles that make up two magnets are known then the net force on both magnets can be determined by summing up all these interactions between the dipoles of the first magnet and that of the second.It is always more convenient to model the force between two magnets as being due to forces between magnetic poles having magnetic charges 'smeared' over them. Such a model fails to account for many important properties of magnetism such as the relationship between angular momentum and magnetic dipoles. Further, magnetic charge does not exist. This model works quite well, though, in predicting the forces between simple magnets where good models of how the 'magnetic charge' is distributed is available.