Magnetism
... poles • Magnetic field – region around a magnet in which magnetic effects are observed, which is produced by the motion of the electric charge. • Lines of force – closed arc from north to south pole, never cross, most concentrated at poles ...
... poles • Magnetic field – region around a magnet in which magnetic effects are observed, which is produced by the motion of the electric charge. • Lines of force – closed arc from north to south pole, never cross, most concentrated at poles ...
Magnetism
... Region where a magnetic influence (force) can be felt. Lines are drawn to represent the strength and direction of the field. Field is represented from N to S. ...
... Region where a magnetic influence (force) can be felt. Lines are drawn to represent the strength and direction of the field. Field is represented from N to S. ...
Coverage - Smart Science
... Recognise magnetism as a property and know some magnetic and non-magnetic materials. Know that magnets come with two poles – north and south. Describe simple interactions of magnets and correctly use the terms apply, repel. MOST students should (levels 5–6): Understand the difference between ...
... Recognise magnetism as a property and know some magnetic and non-magnetic materials. Know that magnets come with two poles – north and south. Describe simple interactions of magnets and correctly use the terms apply, repel. MOST students should (levels 5–6): Understand the difference between ...
Magnetism 4 Electromagnets
... Galvanometer Moving coil electric current detector. The amount of deflection of a needle attached to the coil is proportional to the current passing through the coil. ...
... Galvanometer Moving coil electric current detector. The amount of deflection of a needle attached to the coil is proportional to the current passing through the coil. ...
EM_INDUCTION
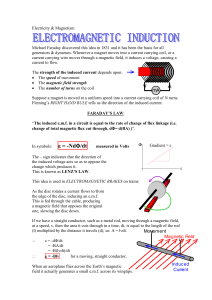
... The strength of the induced current depends upon: The speed of movement The magnetic field strength The number of turns on the coil Suppose a magnet is moved at a uniform speed into a current carrying coil of N turns. Fleming’s RIGHT HAND RULE tells us the direction of the induced current. FAR ...
... The strength of the induced current depends upon: The speed of movement The magnetic field strength The number of turns on the coil Suppose a magnet is moved at a uniform speed into a current carrying coil of N turns. Fleming’s RIGHT HAND RULE tells us the direction of the induced current. FAR ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... The number of field lines indicates the strength of the source of the magnet. • Every magnet creates an energy ...
... The number of field lines indicates the strength of the source of the magnet. • Every magnet creates an energy ...
Force between magnets
Magnets exert forces and torques on each other due to the complex rules of electromagnetism. The forces of attraction field of magnets are due to microscopic currents of electrically charged electrons orbiting nuclei and the intrinsic magnetism of fundamental particles (such as electrons) that make up the material. Both of these are modeled quite well as tiny loops of current called magnetic dipoles that produce their own magnetic field and are affected by external magnetic fields. The most elementary force between magnets, therefore, is the magnetic dipole–dipole interaction. If all of the magnetic dipoles that make up two magnets are known then the net force on both magnets can be determined by summing up all these interactions between the dipoles of the first magnet and that of the second.It is always more convenient to model the force between two magnets as being due to forces between magnetic poles having magnetic charges 'smeared' over them. Such a model fails to account for many important properties of magnetism such as the relationship between angular momentum and magnetic dipoles. Further, magnetic charge does not exist. This model works quite well, though, in predicting the forces between simple magnets where good models of how the 'magnetic charge' is distributed is available.