Stellar Evolution
... planetary nebulae are produced by the expansion of a ‘fast stellar wind’ within a slowly expanding ’cloud’ which is denser near its equator than its poles.” • If so, where do the x-rays come from? ...
... planetary nebulae are produced by the expansion of a ‘fast stellar wind’ within a slowly expanding ’cloud’ which is denser near its equator than its poles.” • If so, where do the x-rays come from? ...
Chapter 2 - CP Physics
... • Can be used to measure the speed of the fluid flow • Swiftly moving fluids exert less pressure than do slowly moving fluids Section 9.7 ...
... • Can be used to measure the speed of the fluid flow • Swiftly moving fluids exert less pressure than do slowly moving fluids Section 9.7 ...
Magnetic Resonance Force Microscopy
... – most sample locations have no spin interacting with the resonant slice Æ zero baseline in previous plot ...
... – most sample locations have no spin interacting with the resonant slice Æ zero baseline in previous plot ...
Magnetism – Answer Key
... All posters must be neat, completed on poster paper and must be colorful. The name of your scientist must be clearly visible on your poster. Anyone who glances at your poster should be able to tell which scientist you researched. The "Wanted" poster theme must be followed. Meaning, your poster shoul ...
... All posters must be neat, completed on poster paper and must be colorful. The name of your scientist must be clearly visible on your poster. Anyone who glances at your poster should be able to tell which scientist you researched. The "Wanted" poster theme must be followed. Meaning, your poster shoul ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... E.g. if the current is caused by a north pole approaching the coil, this is the motion the current seeks to oppose→ the current flows in such a direction as to make that end of the coil into a north pole (i.e. opposes the north pole approaching). This means work must be done to push the magnet towar ...
... E.g. if the current is caused by a north pole approaching the coil, this is the motion the current seeks to oppose→ the current flows in such a direction as to make that end of the coil into a north pole (i.e. opposes the north pole approaching). This means work must be done to push the magnet towar ...
GFD 2013 Lecture 8: Rotating currents 1 Introduction
... Figure 7: A schematic diagram of baroclinic instability in a continuously stratified fluid. The horizontal (dashed) lines denote surfaces of constant pressure (or geopotential) surfaces, where p3 > p2 > p2 , and the inclined (continuous lines) denote lines of constant density (or isopycnal) surface ...
... Figure 7: A schematic diagram of baroclinic instability in a continuously stratified fluid. The horizontal (dashed) lines denote surfaces of constant pressure (or geopotential) surfaces, where p3 > p2 > p2 , and the inclined (continuous lines) denote lines of constant density (or isopycnal) surface ...
Chapter 20
... The emf is actually induced by a change in the quantity called the magnetic flux rather than simply by a change in the magnetic field Magnetic flux is defined in a manner similar to that of electrical flux Magnetic flux is proportional to both the strength of the magnetic field passing through the p ...
... The emf is actually induced by a change in the quantity called the magnetic flux rather than simply by a change in the magnetic field Magnetic flux is defined in a manner similar to that of electrical flux Magnetic flux is proportional to both the strength of the magnetic field passing through the p ...
flux linkage File
... If a coil is not at right angles to the uniform field then only a component of the flux passes through the coil ...
... If a coil is not at right angles to the uniform field then only a component of the flux passes through the coil ...
chapter20
... The emf is actually induced by a change in the quantity called the magnetic flux rather than simply by a change in the magnetic field Magnetic flux is defined in a manner similar to that of electrical flux Magnetic flux is proportional to both the strength of the magnetic field passing through the p ...
... The emf is actually induced by a change in the quantity called the magnetic flux rather than simply by a change in the magnetic field Magnetic flux is defined in a manner similar to that of electrical flux Magnetic flux is proportional to both the strength of the magnetic field passing through the p ...
Magnetism K-3 Teacher Guide
... The atoms that make up iron, nickel and cobalt, can all be aligned in the same direction creating poles. That’s what makes them magnetic—what allows them to be magnetized. Sometimes, if metals are placed in a magnetic field, even if they are not magnetic, they become magnetized just a little bit. Ma ...
... The atoms that make up iron, nickel and cobalt, can all be aligned in the same direction creating poles. That’s what makes them magnetic—what allows them to be magnetized. Sometimes, if metals are placed in a magnetic field, even if they are not magnetic, they become magnetized just a little bit. Ma ...
Electromagnetism www.AssignmentPoint.com Electromagnetism is
... electricity and magnetism, while both capable of causing attraction and repulsion of objects, were distinct effects. Mariners had noticed that lightning strikes had the ability to disturb a compass needle, but the link between lightning and electricity was not confirmed until Benjamin Franklin's pro ...
... electricity and magnetism, while both capable of causing attraction and repulsion of objects, were distinct effects. Mariners had noticed that lightning strikes had the ability to disturb a compass needle, but the link between lightning and electricity was not confirmed until Benjamin Franklin's pro ...
PY 405 – Electromagnetic Fields and Waves – Syllabus v. 1– 2010
... Physics 405 is the first semester of the upper-level course on electricity and magnetism. PY 355 (Methods of Theoretical Physics) is the prerequisite for this course. Of course, it is assumed that you have passed the prerequisites for PY 355. If you do not meet these requirements, you must consult w ...
... Physics 405 is the first semester of the upper-level course on electricity and magnetism. PY 355 (Methods of Theoretical Physics) is the prerequisite for this course. Of course, it is assumed that you have passed the prerequisites for PY 355. If you do not meet these requirements, you must consult w ...
Axion Induced Oscillating Electric Dipole Moments
... The same issue arises in the case of the anomaly. The result is intrinsically oscillatory (the nonlocal makes the source for the vector potential transverse, ie, not Coulombic) . The above Feynman amplitudes can be written as : ...
... The same issue arises in the case of the anomaly. The result is intrinsically oscillatory (the nonlocal makes the source for the vector potential transverse, ie, not Coulombic) . The above Feynman amplitudes can be written as : ...
THE LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ANGULAR MOMENTUM
... The directions of the vectors of the magnetic moments M e and the directions of the vectors of their angular momentum h of both electrons coincide (Fig.4,a). Let us call this structure orthohydrogen. If the above-mentioned vectors are opposite (Fig.4b), such a structure is parahydrogen [10], [11]. L ...
... The directions of the vectors of the magnetic moments M e and the directions of the vectors of their angular momentum h of both electrons coincide (Fig.4,a). Let us call this structure orthohydrogen. If the above-mentioned vectors are opposite (Fig.4b), such a structure is parahydrogen [10], [11]. L ...
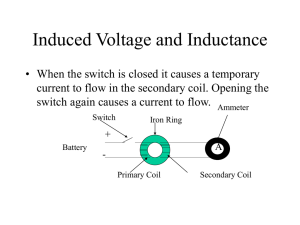
Induced Voltage and Inductance
... that turns mechanical energy into electrical energy. It consists of a wire loop that is rotated in a magnetic field. • Consider a loop of area A with N number of loops in a magnetic field of B moving at an angular speed of then E=NBA sin t when t = 90o or 270o then E= Emax=NBA ...
... that turns mechanical energy into electrical energy. It consists of a wire loop that is rotated in a magnetic field. • Consider a loop of area A with N number of loops in a magnetic field of B moving at an angular speed of then E=NBA sin t when t = 90o or 270o then E= Emax=NBA ...
Magnetohydrodynamics

Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) (magneto fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is the study of the magnetic properties of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such magneto-fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes. The word magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is derived from magneto- meaning magnetic field, hydro- meaning water, and -dynamics meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970.The fundamental concept behind MHD is that magnetic fields can induce currents in a moving conductive fluid, which in turn polarizes the fluid and reciprocally changes the magnetic field itself. The set of equations that describe MHD are a combination of the Navier-Stokes equations of fluid dynamics and Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. These differential equations must be solved simultaneously, either analytically or numerically.