Maxwell equations
... classical situations and describing all possible experiments However, there is still an opened question: ...
... classical situations and describing all possible experiments However, there is still an opened question: ...
Chapter 3
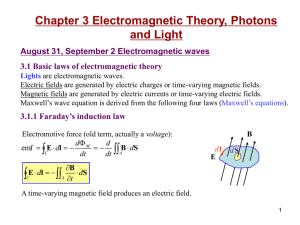
... Chapter 3 Electromagnetic Theory, Photons and Light August 31, September 2 Electromagnetic waves 3.1 Basic laws of electromagnetic theory Lights are electromagnetic waves. Electric fields are generated by electric charges or time-varying magnetic fields. Magnetic fields are generated by electric cur ...
... Chapter 3 Electromagnetic Theory, Photons and Light August 31, September 2 Electromagnetic waves 3.1 Basic laws of electromagnetic theory Lights are electromagnetic waves. Electric fields are generated by electric charges or time-varying magnetic fields. Magnetic fields are generated by electric cur ...
PHY 113, Summer 2007
... dielectric you need to use to fill the gap in the capacitor? 2. Two parallel plates of area 100 cm2 are given charges of equal magnitudes 8.9 x 10-7 C but opposite signs. The electric field within the dielectric material filling the space between the plates is 1.4 x 106 V/m. Calculate the dielectric ...
... dielectric you need to use to fill the gap in the capacitor? 2. Two parallel plates of area 100 cm2 are given charges of equal magnitudes 8.9 x 10-7 C but opposite signs. The electric field within the dielectric material filling the space between the plates is 1.4 x 106 V/m. Calculate the dielectric ...
HV Board project - INFN-LNF
... solar cells. • Conventionally it flows from positive pole to negative • It is used to give energy to small devices ...
... solar cells. • Conventionally it flows from positive pole to negative • It is used to give energy to small devices ...
Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
... The direction of magnetic field can be identified using Right Hand Thumb’s Rule. Let us assume that the current is moving in anti-clockwise direction in the loop. In that case, the magnetic field would be in clockwise direction; at the top of the loop. Moreover, it would be in anticlockwise directi ...
... The direction of magnetic field can be identified using Right Hand Thumb’s Rule. Let us assume that the current is moving in anti-clockwise direction in the loop. In that case, the magnetic field would be in clockwise direction; at the top of the loop. Moreover, it would be in anticlockwise directi ...
Magnetic field of the earth OBJEctiVE gEnEral
... geo-dynamo effect. Close to the surface of the earth, this field resembles that of a magnetic dipole with field lines emerging from the South Pole of the planet and circling back towards the North Pole. The angle between the actual magnetic field of the earth and the horizontal at a given point on t ...
... geo-dynamo effect. Close to the surface of the earth, this field resembles that of a magnetic dipole with field lines emerging from the South Pole of the planet and circling back towards the North Pole. The angle between the actual magnetic field of the earth and the horizontal at a given point on t ...
magnet - willisworldbio
... physics teacher, found that ________ and magnetism are related. • Oersted hypothesized that the electric current must produce a magnetic field around the wire, and the direction of the field changes with the _________ of the current. ...
... physics teacher, found that ________ and magnetism are related. • Oersted hypothesized that the electric current must produce a magnetic field around the wire, and the direction of the field changes with the _________ of the current. ...
Document
... faces, in terms of and to different observers. • Electromagnetic fields obey four general laws, called Maxwell’s equations. • Electromagnetic fields can exist without source charges or currents in the form of a selfsustaining electromagnetic wave. • Maxwell’s equations predict that all electromagnet ...
... faces, in terms of and to different observers. • Electromagnetic fields obey four general laws, called Maxwell’s equations. • Electromagnetic fields can exist without source charges or currents in the form of a selfsustaining electromagnetic wave. • Maxwell’s equations predict that all electromagnet ...
Magnetism Unit
... 1. Define magnetism as a force that attracts iron, nickel or cobalt. 2. State that magnetic force is invisible. 3. Identify magnets as either bar or horseshoe based on shape. 4. Name the poles of magnets as north or south. 5. Given a drawing of a magnet, draw lines representing magnetic force lines. ...
... 1. Define magnetism as a force that attracts iron, nickel or cobalt. 2. State that magnetic force is invisible. 3. Identify magnets as either bar or horseshoe based on shape. 4. Name the poles of magnets as north or south. 5. Given a drawing of a magnet, draw lines representing magnetic force lines. ...