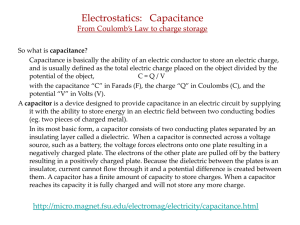
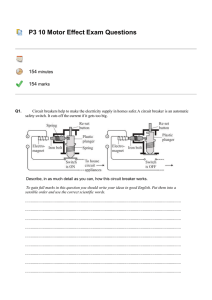
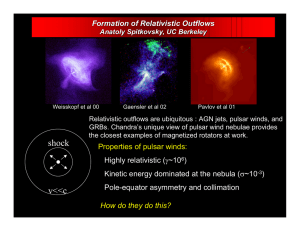
MAGNETS
... A: Yes. While magnets made of metal are by far the most common, the electrons in certain other materials can be rearranged to make them magnetic. Examples include plastic, rubber, and ceramic magnets. However, it takes special circumstances for nonmetallic items to be magnetized, so these types of m ...
... A: Yes. While magnets made of metal are by far the most common, the electrons in certain other materials can be rearranged to make them magnetic. Examples include plastic, rubber, and ceramic magnets. However, it takes special circumstances for nonmetallic items to be magnetized, so these types of m ...
Can the Imaginary Part of Permeability be Negative?
... required to be positive. The main point of the comments 关2,3兴 was that it is possible to envision a geometrical arrangement in which either one of these two terms is arbitrarily small while ⑀⬙共兲 and ⬙共兲 are properties of the medium and, therefore, are independent of the geometry. Therefore, both ...
... required to be positive. The main point of the comments 关2,3兴 was that it is possible to envision a geometrical arrangement in which either one of these two terms is arbitrarily small while ⑀⬙共兲 and ⬙共兲 are properties of the medium and, therefore, are independent of the geometry. Therefore, both ...
Modeling Magnetic Torque and Force, J. Abbott
... as shown in Fig. 1. We will explicitly consider ellipsoids, but it has been shown previously that many simple geometries can be accurately modeled magnetically as ellipsoids [16], [17]. The body coordinate frame is located at the center of mass with the X-axis aligned with the axis of symmetry. The ...
... as shown in Fig. 1. We will explicitly consider ellipsoids, but it has been shown previously that many simple geometries can be accurately modeled magnetically as ellipsoids [16], [17]. The body coordinate frame is located at the center of mass with the X-axis aligned with the axis of symmetry. The ...
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current
... If the self-inductance of an iron inductor increases from 0.01 mH to 10 mH on introducing the iron core into it, what is the relative permeability of the core material used? Twelve wires of equal length ‘l’ are connected to form a skeleton cube which moves with a velocity v perpendicular to the magn ...
... If the self-inductance of an iron inductor increases from 0.01 mH to 10 mH on introducing the iron core into it, what is the relative permeability of the core material used? Twelve wires of equal length ‘l’ are connected to form a skeleton cube which moves with a velocity v perpendicular to the magn ...
Recitation #4 Solution
... Since there is +Q inside shell, there must be –Q at r = R1 to make the total charge inside for R1 < r < R2 equal to zero, i.e. –Q on the inside surface of the shell. Since there was initially no net charge on the conductor, there must be +Q amount of charge some place to cancel the –Q on the inside ...
... Since there is +Q inside shell, there must be –Q at r = R1 to make the total charge inside for R1 < r < R2 equal to zero, i.e. –Q on the inside surface of the shell. Since there was initially no net charge on the conductor, there must be +Q amount of charge some place to cancel the –Q on the inside ...
Magnetism Magnetism
... Earth’s magnetic field is like that of a bar magnet A compass can be used to determine direction because Earth acts like a giant bar magnet. As shown in Figure 5, Earth’s magnetic field has both direction and strength. If you were to move northward along Earth’s surface with a compass whose needle c ...
... Earth’s magnetic field is like that of a bar magnet A compass can be used to determine direction because Earth acts like a giant bar magnet. As shown in Figure 5, Earth’s magnetic field has both direction and strength. If you were to move northward along Earth’s surface with a compass whose needle c ...