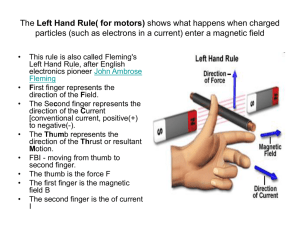
The Left Hand Rule - World of Teaching
... • An electric motor is a motor that uses electrical energy to produce mechanical energy, usually through the interaction of magnetic fields and currentcarrying conductors. • Electric motors are used in most, modern machines. Obvious uses would be in rotating machines such as fans, turbines, drills, ...
... • An electric motor is a motor that uses electrical energy to produce mechanical energy, usually through the interaction of magnetic fields and currentcarrying conductors. • Electric motors are used in most, modern machines. Obvious uses would be in rotating machines such as fans, turbines, drills, ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... If charges are not constrained to move within a wire, or other conductor, then the force on the charge as it passes through a magnetic field will change its direction of travel. As the force is perpendicular to the velocity (current direction) it alters the direction, but not the speed, of the parti ...
... If charges are not constrained to move within a wire, or other conductor, then the force on the charge as it passes through a magnetic field will change its direction of travel. As the force is perpendicular to the velocity (current direction) it alters the direction, but not the speed, of the parti ...
Electromagnetics-1
... then obtain an expression for current density Q. 12 A plane electromagnetic wave propagating in the x – direction has a wavelength 7.00 mm. The electric field is in the y – direction and its maximum magnitude is 42 V/m. Write suitable equations for the electric and magnetic fields of EM wave. Q. 13 ...
... then obtain an expression for current density Q. 12 A plane electromagnetic wave propagating in the x – direction has a wavelength 7.00 mm. The electric field is in the y – direction and its maximum magnitude is 42 V/m. Write suitable equations for the electric and magnetic fields of EM wave. Q. 13 ...
Electromagnetism - Smyrna Middle School
... • Faraday wrapped a current carrying wire around half of an iron ring and wrapped the other side with a wire connected to a galvanometer. • The only activity he recorded was at hookup and disconnection. • Electric current was produced in the second wire only when the magnetic field was changing. ...
... • Faraday wrapped a current carrying wire around half of an iron ring and wrapped the other side with a wire connected to a galvanometer. • The only activity he recorded was at hookup and disconnection. • Electric current was produced in the second wire only when the magnetic field was changing. ...
Magnetism.
... would move if put there (field lines). They gather most thickly where the force on the iron would be the greatest (larger field line density). ...
... would move if put there (field lines). They gather most thickly where the force on the iron would be the greatest (larger field line density). ...
Magnetic flux - Purdue Physics
... magnetic field is passing through a loop of wire. It is at a maximum when the field lines are perpendicular to the plane of the loop, and it is zero when the field lines are parallel to the plane of the loop. For a coil of N loops, the flux through the coil is equal to the flux through one loop, mul ...
... magnetic field is passing through a loop of wire. It is at a maximum when the field lines are perpendicular to the plane of the loop, and it is zero when the field lines are parallel to the plane of the loop. For a coil of N loops, the flux through the coil is equal to the flux through one loop, mul ...
Energy_Impact on Global - Saint Leo University Faculty
... Transmission of Electricity • Transmittal of Electrical Power over large distances is impractical; energy losses lead to very low efficiency • Problem is avoided by changing voltage at which electricity is transmitted • Principle behind a transformer ...
... Transmission of Electricity • Transmittal of Electrical Power over large distances is impractical; energy losses lead to very low efficiency • Problem is avoided by changing voltage at which electricity is transmitted • Principle behind a transformer ...
EAL and Science - Practical Pedagogies
... We tried a pin…a pencil sharpener…some iron filings and a piece of plastic…the magnet didn’t attract the pin. A Pupil Recount Our experiment was to find out what the magnet attracted. We discovered that a magnet attracts some kinds of metal. It attracted the iron filings, but not the pin. ...
... We tried a pin…a pencil sharpener…some iron filings and a piece of plastic…the magnet didn’t attract the pin. A Pupil Recount Our experiment was to find out what the magnet attracted. We discovered that a magnet attracts some kinds of metal. It attracted the iron filings, but not the pin. ...























