Electrical Energy and Magnetism
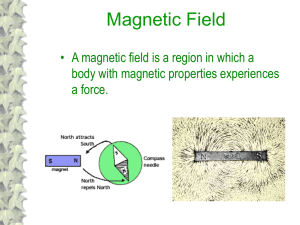
... Characteristics of Magnets Every magnet has two poles (N and S) and is surrounded by a magnetic field This field exerts a force on other magnetic material Magnetic poles are where the magnetic force exerted by the magnet is strongest Depending on which ends of the magnets are close together, the ma ...
... Characteristics of Magnets Every magnet has two poles (N and S) and is surrounded by a magnetic field This field exerts a force on other magnetic material Magnetic poles are where the magnetic force exerted by the magnet is strongest Depending on which ends of the magnets are close together, the ma ...
Guass`s Law for magnetism
... • Current flows to either antenna (like a capacitor) • Electric field produced • Magnetic field produced (right hand rule) ...
... • Current flows to either antenna (like a capacitor) • Electric field produced • Magnetic field produced (right hand rule) ...
Chapter 10 Magnetic Fields and Induction
... from North to South. This labeling of directions is purely conventional. It is simply the direction that a compass needle would point if it were placed in the magnetic field. The number of magnetic field lines in a given area is a qualitative measure of the strength of the magnetic field in that are ...
... from North to South. This labeling of directions is purely conventional. It is simply the direction that a compass needle would point if it were placed in the magnetic field. The number of magnetic field lines in a given area is a qualitative measure of the strength of the magnetic field in that are ...
Phys 202 Fall 2000
... – surface charges: conducting and insulating planes, disks, surfaces of conductors Gauss’ law! – volume charges: insulating spheres, conductors (E=0 inside). • Electric flux, Gauss’ law, applied to spherical, cylindrical, plane symmetry • Electric potential of a single charge, of several charges, of ...
... – surface charges: conducting and insulating planes, disks, surfaces of conductors Gauss’ law! – volume charges: insulating spheres, conductors (E=0 inside). • Electric flux, Gauss’ law, applied to spherical, cylindrical, plane symmetry • Electric potential of a single charge, of several charges, of ...
electricitymagnetismnewsletter-1g4md3i
... Dear Parents, The purpose of this newsletter is to give you an overview of what your child will be learning during our current unit of study in science. Please take a moment to look over the different sections of this newsletter. You will see example questions, important terms to know, and some exte ...
... Dear Parents, The purpose of this newsletter is to give you an overview of what your child will be learning during our current unit of study in science. Please take a moment to look over the different sections of this newsletter. You will see example questions, important terms to know, and some exte ...
Slide 1
... Faraday’s Law of Induction; Lenz’s Law Problem Solving: Lenz’s Law 1. Determine whether the magnetic flux is increasing, decreasing, or unchanged. 2. The magnetic field due to the induced current points in the opposite direction to the original field if the flux is increasing; in the same direction ...
... Faraday’s Law of Induction; Lenz’s Law Problem Solving: Lenz’s Law 1. Determine whether the magnetic flux is increasing, decreasing, or unchanged. 2. The magnetic field due to the induced current points in the opposite direction to the original field if the flux is increasing; in the same direction ...
week11-faraday
... usually results from certain types of high energy explosions, (such as a nuclear explosion), or from a suddenly fluctuating magnetic field. The resulting rapidly changing A electric fields and magnetic fields couple with electrical/electronic systems to produce damaging current and voltage surges. T ...
... usually results from certain types of high energy explosions, (such as a nuclear explosion), or from a suddenly fluctuating magnetic field. The resulting rapidly changing A electric fields and magnetic fields couple with electrical/electronic systems to produce damaging current and voltage surges. T ...
Lesson 2 Magnetism Notes File
... The solenoid’s magnetic field _______________ the iron core. As a result, the field inside the solenoid with the iron core can be more than 1,000 times greater than the field inside the solenoid without the iron core. ...
... The solenoid’s magnetic field _______________ the iron core. As a result, the field inside the solenoid with the iron core can be more than 1,000 times greater than the field inside the solenoid without the iron core. ...
NAME 1. In the plinko applet explain why the balls fall... 2. Explain how the self inductance varies with the number...
... 3. A rail gun is constructed as shown. Derive an expression for how the circuit behaves and another one for how the rail moves. Please make explicit the dependence of each parameter in these equations on other variables. That is, if a capacitance appears as C then I interpret that as it having no ot ...
... 3. A rail gun is constructed as shown. Derive an expression for how the circuit behaves and another one for how the rail moves. Please make explicit the dependence of each parameter in these equations on other variables. That is, if a capacitance appears as C then I interpret that as it having no ot ...
CITRUS COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CREDIT COURSE
... A circulating charge G. Cyclotrons and synchrotrons H. Measuring e/m for the electron ...
... A circulating charge G. Cyclotrons and synchrotrons H. Measuring e/m for the electron ...
Manetism and Electricity
... 2. A magnet is surrounded by an invisible ___________________________________________________. 3. Spinning coils and magnets form a(n) ______________________________________________. 4. What are aligned inside a magnet that give it a north and a south end? ___________________ 5. Which of the followi ...
... 2. A magnet is surrounded by an invisible ___________________________________________________. 3. Spinning coils and magnets form a(n) ______________________________________________. 4. What are aligned inside a magnet that give it a north and a south end? ___________________ 5. Which of the followi ...
Scanning SQUID microscope

A Scanning SQUID Microscope is a sensitive near-field imaging system for the measurement of weak magnetic fields by moving a Superconducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID) across an area. The microscope can map out buried current-carrying wires by measuring the magnetic fields produced by the currents, or can be used to image fields produced by magnetic materials. By mapping out the current in an integrated circuit or a package, short circuits can be localized and chip designs can be verified to see that current is flowing where expected.