Magnetism can produce current.
... This is called a step-down transcoil of wire former. On the other hand, if the second coil has more loops than the first, the voltage in the second circuit will be higher than the original voltage. This transformer is called a step-up transformer. ...
... This is called a step-down transcoil of wire former. On the other hand, if the second coil has more loops than the first, the voltage in the second circuit will be higher than the original voltage. This transformer is called a step-up transformer. ...
AP Physics
... a nonconducting cart as shown below. The cart is placed on the inclined portion of a track and released from rest at position P1 at a height y0 above the horizontal portion of the track. It rolls with negligible friction down the incline and through a uniform magnetic field B in the region above the ...
... a nonconducting cart as shown below. The cart is placed on the inclined portion of a track and released from rest at position P1 at a height y0 above the horizontal portion of the track. It rolls with negligible friction down the incline and through a uniform magnetic field B in the region above the ...
File - Science with Ms. Tantri
... Relating Electricity & Magnetism 1. Under what conditions did the wire jump? 2. Are stationary electric charges affected by magnetic ...
... Relating Electricity & Magnetism 1. Under what conditions did the wire jump? 2. Are stationary electric charges affected by magnetic ...
Discovering Electricity Discussion Questions
... the phonograph in 1878 (This was the first machine that could record sound and play it back) and the first motion picture camera called a kinetograph in 1888. But it is the incandescent electric light bulb that he invented in 1879 for which he is most well known. Many others had tried to make electr ...
... the phonograph in 1878 (This was the first machine that could record sound and play it back) and the first motion picture camera called a kinetograph in 1888. But it is the incandescent electric light bulb that he invented in 1879 for which he is most well known. Many others had tried to make electr ...
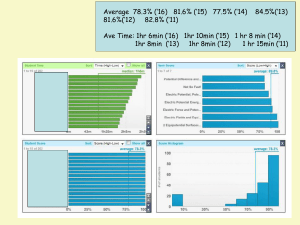
Average 78.3% (`16) 81.6% (`15) 77.5% (`14) 84.5%(`13) 81.6%(`12
... André-Marie Ampère in 1820 was able to devise through experimentation the formula for the angular dependence of the force between two current elements. In all these descriptions, the force was always given in terms of the properties of the objects involved and the distances between them rather than ...
... André-Marie Ampère in 1820 was able to devise through experimentation the formula for the angular dependence of the force between two current elements. In all these descriptions, the force was always given in terms of the properties of the objects involved and the distances between them rather than ...
Magnets and electricity - Rm. E
... Magnetic force: when you bring two magnets together, they exert a push or a pull on each other. Magnetic poles: two magnets can push each other apart because of their ends. Magnetic field: the area surrounding a magnet where magnetic forces can be detected. ...
... Magnetic force: when you bring two magnets together, they exert a push or a pull on each other. Magnetic poles: two magnets can push each other apart because of their ends. Magnetic field: the area surrounding a magnet where magnetic forces can be detected. ...
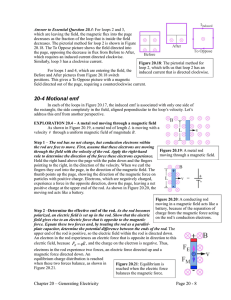
20-4 Motional emf
... In each of the loops in Figure 20.17, the induced emf is associated with only one side of the rectangle, the side completely in the field, aligned perpendicular to the loop’s velocity. Let’s address this emf from another perspective. EXPLORATION 20.4 – A metal rod moving through a magnetic field As ...
... In each of the loops in Figure 20.17, the induced emf is associated with only one side of the rectangle, the side completely in the field, aligned perpendicular to the loop’s velocity. Let’s address this emf from another perspective. EXPLORATION 20.4 – A metal rod moving through a magnetic field As ...
where B is the component of the magnetic field perpendicular to ℓ
... 21.2 Faraday’s Law To quantify the ideas of section 21.1, we define magnetic flux. In an earlier chapter we briefly touched on electric flux. This is the magnetic analog. Because we can’t “see” magnetic fields directly, we draw magnetic field lines to help us visualize the magnetic field. Remember ...
... 21.2 Faraday’s Law To quantify the ideas of section 21.1, we define magnetic flux. In an earlier chapter we briefly touched on electric flux. This is the magnetic analog. Because we can’t “see” magnetic fields directly, we draw magnetic field lines to help us visualize the magnetic field. Remember ...
The University of Burdwan Syllabus for B.Sc. (1+1+1 Pattern)
... If otherwise not stated, mathematical derivation and analysis are necessary at relevant places. ELECTROMAGNETISM (SI units and modern symbols are to be used) Group A [Electromagnetism is a single subject of electricity and magnetism. An electric charge appears to be static with respect to (w.r.t.) o ...
... If otherwise not stated, mathematical derivation and analysis are necessary at relevant places. ELECTROMAGNETISM (SI units and modern symbols are to be used) Group A [Electromagnetism is a single subject of electricity and magnetism. An electric charge appears to be static with respect to (w.r.t.) o ...
Chap 2.3 notes
... • The fundamental charge on an electron is 1.6 X 10-19 C. • 1 C = 1/ 1.6 X 10-19 = 6.25 X 1018 electrons or 6,250,000,000,000,000,000 electrons. ...
... • The fundamental charge on an electron is 1.6 X 10-19 C. • 1 C = 1/ 1.6 X 10-19 = 6.25 X 1018 electrons or 6,250,000,000,000,000,000 electrons. ...
Physics 2 for Electrical Engineering Ben Gurion University of the Negev , www.bgu.ac.il/atomchip
... Answer: (a) The falling magnet induces a circulating current in the tube. By Lenz’s law, the magnetic field of this current opposes the falling magnet, until the magnetic force exactly balances the force of gravity on the magnet, which falls with constant speed v. (b) Gravity, the only external forc ...
... Answer: (a) The falling magnet induces a circulating current in the tube. By Lenz’s law, the magnetic field of this current opposes the falling magnet, until the magnetic force exactly balances the force of gravity on the magnet, which falls with constant speed v. (b) Gravity, the only external forc ...
PHAS2201 - Electricity and magnetism
... In 1831 Faraday discovers electromagnetic induction and devises the first electrical generator. Faraday showed that a transient flow of current occurred in a closed circuit when the magnetic flux through the circuit was changed. In practice, this can be realized by moving a permanent magnet near the ...
... In 1831 Faraday discovers electromagnetic induction and devises the first electrical generator. Faraday showed that a transient flow of current occurred in a closed circuit when the magnetic flux through the circuit was changed. In practice, this can be realized by moving a permanent magnet near the ...
IGCSE-61-Magnetism & Electromagnetism Presentation
... The Earth’s magnetic field The earth’s magnetic field is similar in shape to that around a bar magnet. It is thought to be caused by electric currents flowing through the molten outer core of the Earth. At the present the field pattern is like that with a magnetic SOUTH pole situated somewhere belo ...
... The Earth’s magnetic field The earth’s magnetic field is similar in shape to that around a bar magnet. It is thought to be caused by electric currents flowing through the molten outer core of the Earth. At the present the field pattern is like that with a magnetic SOUTH pole situated somewhere belo ...
Magnetic cloud field intensities and solar wind velocities
... cycledistribution[e.g. Gonzalezctal., 1994]. On the other hand, it is also possiblethat magnetic clouds(followingshocks)are ]nest of t.!•cl,i•es asso- ...
... cycledistribution[e.g. Gonzalezctal., 1994]. On the other hand, it is also possiblethat magnetic clouds(followingshocks)are ]nest of t.!•cl,i•es asso- ...
Magnetic Field of a Bar Magnet
... where Qm is for your bar magnet. What is the direction of the magnetic field vector at locations on the X axis to the right of the + charge (north pole)? (Explain using what we know about the magnetic field near a north pole.) Explain where this equation came from. 5. The equation in step 4 is our p ...
... where Qm is for your bar magnet. What is the direction of the magnetic field vector at locations on the X axis to the right of the + charge (north pole)? (Explain using what we know about the magnetic field near a north pole.) Explain where this equation came from. 5. The equation in step 4 is our p ...
Electromagnetic Induction Notes
... • Principal reason most electric power is AC rather than DC – due to ease with which voltages can be increased or decreased • Reduces the amount of energy lost through the electrical lines transmitting the current ...
... • Principal reason most electric power is AC rather than DC – due to ease with which voltages can be increased or decreased • Reduces the amount of energy lost through the electrical lines transmitting the current ...
Scanning SQUID microscope

A Scanning SQUID Microscope is a sensitive near-field imaging system for the measurement of weak magnetic fields by moving a Superconducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID) across an area. The microscope can map out buried current-carrying wires by measuring the magnetic fields produced by the currents, or can be used to image fields produced by magnetic materials. By mapping out the current in an integrated circuit or a package, short circuits can be localized and chip designs can be verified to see that current is flowing where expected.