Atomic number
... • Goldstein used a perforated cathode. A "ray" is produced in the holes in the cathode and travels in a direction opposite to the “cathode rays," which are streams of electrons. Goldstein called these positive rays canal rays because it looks like they are passing through a canal. In 1907 a study re ...
... • Goldstein used a perforated cathode. A "ray" is produced in the holes in the cathode and travels in a direction opposite to the “cathode rays," which are streams of electrons. Goldstein called these positive rays canal rays because it looks like they are passing through a canal. In 1907 a study re ...
Molecular Geometry Why?
... is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of electrons. In simple terms VSEPR means that all electron bonding domains and electron nonbonding domains aroun ...
... is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of electrons. In simple terms VSEPR means that all electron bonding domains and electron nonbonding domains aroun ...
atom
... the symbol of the element, the mass number and the atomic number. Mass number Atomic number ...
... the symbol of the element, the mass number and the atomic number. Mass number Atomic number ...
Ch-03 Notes
... 2) All atoms of an element are: identical in size, mass and other properties different from those of the other elements 3) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed 4) Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same relativ ...
... 2) All atoms of an element are: identical in size, mass and other properties different from those of the other elements 3) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed 4) Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same relativ ...
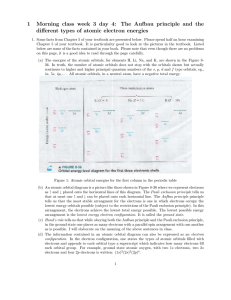
1 Morning class week 3 day 4: The Aufbau principle and the different
... (b) An atomic orbital diagram is a picture like those shown in Figure 8-36 where we represent electrons as ↑ and ↓ placed onto the horizontal lines of this diagram. The Pauli exclusion principle tells us that at most one ↑ and ↓ can be placed onto each horizontal line. The Aufbau principle principle ...
... (b) An atomic orbital diagram is a picture like those shown in Figure 8-36 where we represent electrons as ↑ and ↓ placed onto the horizontal lines of this diagram. The Pauli exclusion principle tells us that at most one ↑ and ↓ can be placed onto each horizontal line. The Aufbau principle principle ...
Electrons/Periodic Table Review Packet Name______________________________ Period_________
... Directions: Use your Periodic table to complete the worksheet. 1. What is the atomic symbol for silver? 2. What is the atomic mass of mercury? 3. Ni is the symbol for what element? ...
... Directions: Use your Periodic table to complete the worksheet. 1. What is the atomic symbol for silver? 2. What is the atomic mass of mercury? 3. Ni is the symbol for what element? ...
Unit 4 - The Periodic Table
... He, Ne and Ar are much higher on the graph because it takes more energy to remove an electron from these atoms (noble gasses are very stable). Li, Na and K are much lower on the graph because they have a single valence electron that is easier to remove. ...
... He, Ne and Ar are much higher on the graph because it takes more energy to remove an electron from these atoms (noble gasses are very stable). Li, Na and K are much lower on the graph because they have a single valence electron that is easier to remove. ...
atoms - schultz915
... a. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. b. Some but not all elements are composed of atoms. c. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of protons. d. Atoms are divisible. ...
... a. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. b. Some but not all elements are composed of atoms. c. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of protons. d. Atoms are divisible. ...
PowerPoint for Ch 2 Part 2 - Dr. Samples` Chemistry Classes
... which enabled him to measure the magnitude of the electric charge on electrons, and calculate their mass in grams. – Ernest Rutherford’s 1911 Gold-Foil Experiment, also called the Alpha-Scattering Experiment. This experiment enabled him to hypothesize the existence of protons in the nucleus of atoms ...
... which enabled him to measure the magnitude of the electric charge on electrons, and calculate their mass in grams. – Ernest Rutherford’s 1911 Gold-Foil Experiment, also called the Alpha-Scattering Experiment. This experiment enabled him to hypothesize the existence of protons in the nucleus of atoms ...
File
... Neils Bohr organized the electrons into energy levels. Electrons closer to the nucleus have less energy than electrons further from the nucleus. The first level holds only 2 electrons. The second level holds 8, third holds 18 and fourth 32. These numbers are reported on the periodic table. Each elem ...
... Neils Bohr organized the electrons into energy levels. Electrons closer to the nucleus have less energy than electrons further from the nucleus. The first level holds only 2 electrons. The second level holds 8, third holds 18 and fourth 32. These numbers are reported on the periodic table. Each elem ...
File
... amu). Based upon the average atomic mass of carbon (12.011 amu), which isotope of carbon do you think is the most abundant in nature? Explain your answer. An element has two naturally occurring isotopes. The mass of the first isotope is 64.9278 amu and the mass of the second isotope is 62.9296 amu. ...
... amu). Based upon the average atomic mass of carbon (12.011 amu), which isotope of carbon do you think is the most abundant in nature? Explain your answer. An element has two naturally occurring isotopes. The mass of the first isotope is 64.9278 amu and the mass of the second isotope is 62.9296 amu. ...
Resource for Final Exam Prep
... Things that you should know: (These are just a summary of each chapter. You are required to read relevant stuff from your textbook, because I might have missed few here and there) Chapter-1: Precision, Accuracy, atoms, elements, compounds, mixture, pure substance, extensive, intensive, physical-chem ...
... Things that you should know: (These are just a summary of each chapter. You are required to read relevant stuff from your textbook, because I might have missed few here and there) Chapter-1: Precision, Accuracy, atoms, elements, compounds, mixture, pure substance, extensive, intensive, physical-chem ...
Atoms FlexBook Atoms FlexBook
... orbiting the nucleus and German scientist Max Planck’s idea of a quantum, which Planck published in 1901. A quantum (plural, quanta) is the minimum amount of energy that can be absorbed or released by matter. It is a discrete, or distinct, amount of energy. If energy were water and you wanted to add ...
... orbiting the nucleus and German scientist Max Planck’s idea of a quantum, which Planck published in 1901. A quantum (plural, quanta) is the minimum amount of energy that can be absorbed or released by matter. It is a discrete, or distinct, amount of energy. If energy were water and you wanted to add ...
ATOMS: THE BUILDING BLOCKS OF MATTER
... Most of the alpha particles passed directly through the foil because the atom is The deflected alpha particles are those that had a NUCLEAR ATOM MODEL An atom with a THE NUCLEUS PROTONS Positively charged subatomic particle Discovered a beam consisting of positive particles called “protons” using a ...
... Most of the alpha particles passed directly through the foil because the atom is The deflected alpha particles are those that had a NUCLEAR ATOM MODEL An atom with a THE NUCLEUS PROTONS Positively charged subatomic particle Discovered a beam consisting of positive particles called “protons” using a ...
Atoms - TeacherWeb
... nucleus are called valence electrons. These electrons form chemical bonds with other atoms and give elements their chemical properties. Atoms combine with other atoms to complete their outermost or last energy level, called the valence shell. ...
... nucleus are called valence electrons. These electrons form chemical bonds with other atoms and give elements their chemical properties. Atoms combine with other atoms to complete their outermost or last energy level, called the valence shell. ...
V. Chemical reactions
... e. How is the number of protons determined? by atomic number f. How is the number of neutrons determined? subtract atomic number from mass number g. How is the number of electrons determined in a neutral atom? Equal to the number of protons B) The nucleus a. What subatomic particles are located in t ...
... e. How is the number of protons determined? by atomic number f. How is the number of neutrons determined? subtract atomic number from mass number g. How is the number of electrons determined in a neutral atom? Equal to the number of protons B) The nucleus a. What subatomic particles are located in t ...
Chemistry Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 15. List the SI units for the following quantities: length, mass, temperature, time, amount of substance, luminous intensity, and electric current. 16. How many significant figures are in the following numbers: a. 702000m b. 40 crayons c. 0.00630100g d. 170.4380s 17. Convert 14.8g to micrograms. 18. ...
... 15. List the SI units for the following quantities: length, mass, temperature, time, amount of substance, luminous intensity, and electric current. 16. How many significant figures are in the following numbers: a. 702000m b. 40 crayons c. 0.00630100g d. 170.4380s 17. Convert 14.8g to micrograms. 18. ...
Chapter 2 Chemical Basis of Life
... Relate how the structure of water leads to hydrogen bonds. Describe how hydrogen bonding determines many properties of water. Describe water’s cohesive and adhesive properties. Explain the relevance of water’s unusual properties for living systems. Understand the dissociation products of water. Expl ...
... Relate how the structure of water leads to hydrogen bonds. Describe how hydrogen bonding determines many properties of water. Describe water’s cohesive and adhesive properties. Explain the relevance of water’s unusual properties for living systems. Understand the dissociation products of water. Expl ...
Lesson 5 Atomic Theory File
... - the nucleus of an atom is made up of protons and neutrons, while the electrons move freely around the nucleus Orally: it is the number of protons that give an element its characteristics (i.e. if you change the number of protons in a nucleus, you have changed the element!!!) - unlike charges (i.e. ...
... - the nucleus of an atom is made up of protons and neutrons, while the electrons move freely around the nucleus Orally: it is the number of protons that give an element its characteristics (i.e. if you change the number of protons in a nucleus, you have changed the element!!!) - unlike charges (i.e. ...
File - StarpointLearns
... Protons Electrons Neutrons Mass Atomic Nuclear # of Nuclear Element’s Atom ...
... Protons Electrons Neutrons Mass Atomic Nuclear # of Nuclear Element’s Atom ...
Protons Neutrons Electrons
... 10. Which of the atoms on the list must have received electrons from another atom? C, D and F. These atoms have more electrons than protons. Since the atom originally carried no charge, the only way they acquire extra electrons is by a transfer from another atom(s). Notice that each of these atoms a ...
... 10. Which of the atoms on the list must have received electrons from another atom? C, D and F. These atoms have more electrons than protons. Since the atom originally carried no charge, the only way they acquire extra electrons is by a transfer from another atom(s). Notice that each of these atoms a ...
Document
... A) alkali metals have the lowest ionization energy B) alkali metals have the highest ionization energy C) halogens metals have the lowest ionization energy D) inert gases metals have the lowest ionization energy ...
... A) alkali metals have the lowest ionization energy B) alkali metals have the highest ionization energy C) halogens metals have the lowest ionization energy D) inert gases metals have the lowest ionization energy ...