Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context
... 31) In comparing covalent bonds and ionic bonds, which of the following would you expect? A) An atom can form covalent bonds with multiple partner atoms, but only a single ionic bond with a single partner atom. B) Covalent bonds and ionic bonds occupy opposite ends of a continuous spectrum, from nea ...
... 31) In comparing covalent bonds and ionic bonds, which of the following would you expect? A) An atom can form covalent bonds with multiple partner atoms, but only a single ionic bond with a single partner atom. B) Covalent bonds and ionic bonds occupy opposite ends of a continuous spectrum, from nea ...
1 1.1. The Facility and Experimental Setup
... which includes a wide variety of information about the physical and engineering properties of the mirror assembly, including, for example, the effects of gravity, offloader stresses, epoxy shrinkage, surface deformations and roughness, rigid body position of the optical elements, etc. After the mode ...
... which includes a wide variety of information about the physical and engineering properties of the mirror assembly, including, for example, the effects of gravity, offloader stresses, epoxy shrinkage, surface deformations and roughness, rigid body position of the optical elements, etc. After the mode ...
Chapter 2
... • In this series of elements, the mass number (A) varies but the atomic number (Z) is constant. • This means that we are looking at a series of isotopes. ...
... • In this series of elements, the mass number (A) varies but the atomic number (Z) is constant. • This means that we are looking at a series of isotopes. ...
PDF (chapter_8)
... those considered in this work. Measured drift times, reduced ion mobilities (in N2 drift gas), and determined ΩD for the 9 ammonium cations chosen for this study are listed in Table 1 along with their respective molecular weights. The 12-4 potential model, which has proven satisfactory to model expe ...
... those considered in this work. Measured drift times, reduced ion mobilities (in N2 drift gas), and determined ΩD for the 9 ammonium cations chosen for this study are listed in Table 1 along with their respective molecular weights. The 12-4 potential model, which has proven satisfactory to model expe ...
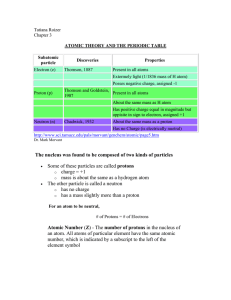
atomic theory and the periodic table
... Each orbital has a name. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The "1" represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The "s" tells you about the shape of the orbital. s orbitals are spherically symmetric around the nucleus - in e ...
... Each orbital has a name. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The "1" represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The "s" tells you about the shape of the orbital. s orbitals are spherically symmetric around the nucleus - in e ...
EE 2 Fall 2007
... material although our discussion is valid for any semiconductor • A semiconductor with donor type of impurity is called n-type semiconductor since there are more electrons than holes. • Similarly, a semiconductor with acceptor type of impurity is called ptype semiconductor since there are more holes ...
... material although our discussion is valid for any semiconductor • A semiconductor with donor type of impurity is called n-type semiconductor since there are more electrons than holes. • Similarly, a semiconductor with acceptor type of impurity is called ptype semiconductor since there are more holes ...
CHAPTER TWO ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS For Review 1. a
... and neutrons which can be broken down into quarks. For our purpose, electrons, neutrons, and protons are the key smaller parts of an atom. b. All atoms of hydrogen have 1 proton in the nucleus. Different isotopes of hydrogen have 0, 1, or 2 neutrons in the nucleus. Because we are talking about atoms ...
... and neutrons which can be broken down into quarks. For our purpose, electrons, neutrons, and protons are the key smaller parts of an atom. b. All atoms of hydrogen have 1 proton in the nucleus. Different isotopes of hydrogen have 0, 1, or 2 neutrons in the nucleus. Because we are talking about atoms ...
chemistry I review pwrpt.
... •Each path has a specific energy requirement. •These circular paths are called energy levels. •Limited number of electrons on each http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/ energy level. ...
... •Each path has a specific energy requirement. •These circular paths are called energy levels. •Limited number of electrons on each http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/ energy level. ...
Electrons
... Atomic Number and Atomic Mass • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be appro ...
... Atomic Number and Atomic Mass • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be appro ...
Semester 1 exam review
... 17. The largest hot cross bun was made by staff at Pegrums Bakery in the UK. The bun weighed 94.35 lbs and had a diameter of 4 ft 3 in. What was its weight in grams? 18. The human bladder can hold up to 2 cups of urine. (for those of you that need to go to the bathroom all the time) How many liters ...
... 17. The largest hot cross bun was made by staff at Pegrums Bakery in the UK. The bun weighed 94.35 lbs and had a diameter of 4 ft 3 in. What was its weight in grams? 18. The human bladder can hold up to 2 cups of urine. (for those of you that need to go to the bathroom all the time) How many liters ...
Wizard Test Maker
... (2) propanal (4) water 6856 Which Group 14 element is classified as a metal? (1) carbon (3) silicon (2) germanium (4) tin 6763 An element that has a low first ionization energy and good conductivity of heat and electricity is classified as a (3) nonmetal (1) metal (2) metalloid (4) noble gas 6709 A ...
... (2) propanal (4) water 6856 Which Group 14 element is classified as a metal? (1) carbon (3) silicon (2) germanium (4) tin 6763 An element that has a low first ionization energy and good conductivity of heat and electricity is classified as a (3) nonmetal (1) metal (2) metalloid (4) noble gas 6709 A ...
Kinetic aspects of the vortex-induced
... At RX-points, electrons are accelerated in the +Z-direction (almost same as the parallel direction) by the negative reconnection electric field. At re-RX points, electrons are accelerated in the -Z-direction (almost same as the anti-parallel direction) by the positive reconnection electric field. ...
... At RX-points, electrons are accelerated in the +Z-direction (almost same as the parallel direction) by the negative reconnection electric field. At re-RX points, electrons are accelerated in the -Z-direction (almost same as the anti-parallel direction) by the positive reconnection electric field. ...
A molecular orbital method for inorganic molecules: application to
... (30) R. A. Berg and 0. Sinanoglu, J. Chem. Phys., 32, 1082 (1960). (31) R. A. Berg, L. Wharton, W. Klemperer, A. Buchler, and J . L. Stauffer, ibid., 43, 2416 (1965). (32) P. H. Kasai and W, Weltner, ibid.,43, 2557 (1965). (33) W. Weltner, Jr., and D. McLeod, Jr., J . Phys. Chem., 69, 348 ...
... (30) R. A. Berg and 0. Sinanoglu, J. Chem. Phys., 32, 1082 (1960). (31) R. A. Berg, L. Wharton, W. Klemperer, A. Buchler, and J . L. Stauffer, ibid., 43, 2416 (1965). (32) P. H. Kasai and W, Weltner, ibid.,43, 2557 (1965). (33) W. Weltner, Jr., and D. McLeod, Jr., J . Phys. Chem., 69, 348 ...
2.ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS
... tube into a chamber where the atoms collide with electrons from an electron beam (cathode rays). The force of a collision can knock an electron from an atom. The positive neon atoms produced this way are drawn toward a negative grid, and some of them pass through slits to form a beam of positive ele ...
... tube into a chamber where the atoms collide with electrons from an electron beam (cathode rays). The force of a collision can knock an electron from an atom. The positive neon atoms produced this way are drawn toward a negative grid, and some of them pass through slits to form a beam of positive ele ...
Final "I Can Statements" Answer Key
... _____24. I can state the relationship between temperature and volume for gases (assuming constant pressure). _____25. I can state the relationship between temperature and pressure for gases (assuming constant volume). _____26. I can state Avogadro’s ...
... _____24. I can state the relationship between temperature and volume for gases (assuming constant pressure). _____25. I can state the relationship between temperature and pressure for gases (assuming constant volume). _____26. I can state Avogadro’s ...
Your views are welcomed upon the theme of
... under natural conditions because of the high charge. O3- and Mg+ do not have such electronic arrangements and are not commonly found. This same type of pattern extends (with exceptions) to molecules. So in NH3, for example, all of the atoms are said to have noble gas electronic structures. Of course ...
... under natural conditions because of the high charge. O3- and Mg+ do not have such electronic arrangements and are not commonly found. This same type of pattern extends (with exceptions) to molecules. So in NH3, for example, all of the atoms are said to have noble gas electronic structures. Of course ...
Crystal Field Theory, gemstones and color
... stoichiometry of the mineral is correct. Note, there are two water molecules (black spheres, Wa) present in this structure; deselect them to remove them from view from the toolbar. ...
... stoichiometry of the mineral is correct. Note, there are two water molecules (black spheres, Wa) present in this structure; deselect them to remove them from view from the toolbar. ...
Metastable inner-shell molecular state

Metastable Innershell Molecular State (MIMS) is a class of ultra-high-energy short-lived molecules have the binding energy up to 1,000 times larger and bond length up to 100 times smaller than typical molecules. MIMS is formed by inner-shell electrons that are normally resistant to molecular formation. However, in stellar conditions, the inner-shell electrons become reactive to form molecular structures (MIMS) from combinations of all elements in the periodic table. MIMS upon dissociation can emit x-ray photons with energies up to 100 keV at extremely high conversion efficiencies from compression energy to photon energy. MIMS is predicted to exist and dominate radiation processes in extreme astrophysical environments, such as large planet cores, star interiors, and black hole and neutron star surroundings. There, MIMS is predicted to enable highly energy-efficient transformation of the stellar compression energy into the radiation energy.The right schematic illustration shows the proposed four stages of the K-shell MIMS (K-MIMS) formation and x-ray generation process. Stage I: Individual atoms are subjected to the stellar compression and ready for absorbing the compression energy. Stage II: The outer electron shells fuse together under increasing ""stellar"" pressure. Stage III: At the peak pressure, via pressure ionization K-shell orbits form the K-MIMS, which is vibrationally hot and encapsulated by a Rydberg-like pseudo-L-Shell structure. Stage IV: The K-MIMS cools down by ionizing (""boiling-off"") a number of pseudo-L-shell electrons and subsequent optical decay by emitting an x-ray photon. The dissociated atoms return their original atoms states and are ready for absorbing the compression energy.MIMS also can be readily produced in laboratory and industrial environments, such as hypervelocity particle impact, laser fusion and z-machine. MIMS can be exploited for highly energy-efficient production of high intensity x-ray beams for a wide range of innovative applications, such as photolithography, x-ray lasers, and inertial fusion.