H - Deans Community High School
... changes that take place. • Trends in the periodic table • The relationship between the arrangement of elements in the periodic table and their bonding, structure and properties. • Polar covalent bonds in the context of the bonding continuum, followed before studying intermolecular forces. ...
... changes that take place. • Trends in the periodic table • The relationship between the arrangement of elements in the periodic table and their bonding, structure and properties. • Polar covalent bonds in the context of the bonding continuum, followed before studying intermolecular forces. ...
Answers to examination questions
... The oxygen molecule (O O) contains one double bond; the carbon dioxide molecule (O C O) contains two double bond and the tetrafluoroethene molecule contains one double bond. ...
... The oxygen molecule (O O) contains one double bond; the carbon dioxide molecule (O C O) contains two double bond and the tetrafluoroethene molecule contains one double bond. ...
幻灯片 1
... Relative stability of the isomers of metallasilapentalynes with the silicon atom at different positions. ...
... Relative stability of the isomers of metallasilapentalynes with the silicon atom at different positions. ...
Carbon Chemistry - North Allegheny School District
... bers of a series of molecules in which carbon and hydrogen atoms are joined by single covalent bonds. When all the bonds in a hydrocarbon are single bonds, the molecule is called a saturated hydrocarbon. It is called saturated because no additional hydrogen atoms can be added to the molecule. The ca ...
... bers of a series of molecules in which carbon and hydrogen atoms are joined by single covalent bonds. When all the bonds in a hydrocarbon are single bonds, the molecule is called a saturated hydrocarbon. It is called saturated because no additional hydrogen atoms can be added to the molecule. The ca ...
Chapter 4 - Jenkins Independent Schools
... Earth’s crust contains less than one percent carbon, yet all living things on Earth are made of carbon-containing compounds. Carbon’s ability to bond easily and form compounds is the basis of life on Earth. A carbon atom has four electrons in its outer energy level, so it can form covalent bonds wit ...
... Earth’s crust contains less than one percent carbon, yet all living things on Earth are made of carbon-containing compounds. Carbon’s ability to bond easily and form compounds is the basis of life on Earth. A carbon atom has four electrons in its outer energy level, so it can form covalent bonds wit ...
Chemistry - Set as Home Page
... 24. Molecular formula of CHCl3 and its Empirical formula is __________. 25. Molecular formula of benzene is C6H6 and its empirical formula is __________. 26. 58.5 is the __________ of NaCl. 27. 4.5 gms of nitrogen will have __________ molecules. 28. 28 gms of nitrogen will have __________ molecules. ...
... 24. Molecular formula of CHCl3 and its Empirical formula is __________. 25. Molecular formula of benzene is C6H6 and its empirical formula is __________. 26. 58.5 is the __________ of NaCl. 27. 4.5 gms of nitrogen will have __________ molecules. 28. 28 gms of nitrogen will have __________ molecules. ...
Lecture 1 - Алтайский государственный технический
... and 8 neutrons (8=14-6). This isotope is also known simply as "carbon 14". Carbon 12 is the most common form of carbon (~99% of all carbon). An atom of a specific isotope is called a nuclide. Since all atoms are composed of protons, electrons and neutrons, all chemical and physical differences betw ...
... and 8 neutrons (8=14-6). This isotope is also known simply as "carbon 14". Carbon 12 is the most common form of carbon (~99% of all carbon). An atom of a specific isotope is called a nuclide. Since all atoms are composed of protons, electrons and neutrons, all chemical and physical differences betw ...
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry
... In ionic compounds, electrons are transferred between atoms of different elements to form ions. But this is not the only way that compounds can be formed. Atoms can also make chemical bonds by sharing electrons equally between each other. Such bonds are called covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are form ...
... In ionic compounds, electrons are transferred between atoms of different elements to form ions. But this is not the only way that compounds can be formed. Atoms can also make chemical bonds by sharing electrons equally between each other. Such bonds are called covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are form ...
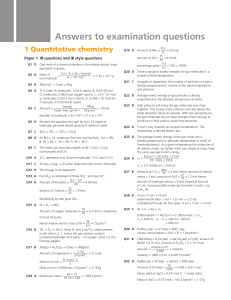
Answers to examination questions
... Q5 D The oxygen molecule (O=O) contains one double bond; the carbon dioxide molecule (O=C=O) contains two double bond and the tetrafluoroethene molecule contains one double bond. Q6 A B is trigonal planar (bond angles 120°); A, C and D are based upon a tetrahedral arrangement with four regio ...
... Q5 D The oxygen molecule (O=O) contains one double bond; the carbon dioxide molecule (O=C=O) contains two double bond and the tetrafluoroethene molecule contains one double bond. Q6 A B is trigonal planar (bond angles 120°); A, C and D are based upon a tetrahedral arrangement with four regio ...
inorganic chemistry
... compared to chlorine is due to very small size of the fluorine atom. As a result, there are strong inter-electronic repulsions in the relatively small 2p subshell of fluorine and thus the incoming electron does not feel much attraction. Therefore, its electron affinity is small. Thus, electron affin ...
... compared to chlorine is due to very small size of the fluorine atom. As a result, there are strong inter-electronic repulsions in the relatively small 2p subshell of fluorine and thus the incoming electron does not feel much attraction. Therefore, its electron affinity is small. Thus, electron affin ...
127 - Chimica
... trianglar cluster of three osmium atoms with two osmium-osmium bonds, Os(l)-Os(2) = 2.793 (1)A and Os(1)-0s(3)= 2.873 (1)A. The nonbonding osmium-osmium distance, Os(2)--0s(3) = 3.492 (1) A, is bridged by the methoxide ligand. The hydride ligand, located crystallographically, bridges the Os(l)-Os(3) ...
... trianglar cluster of three osmium atoms with two osmium-osmium bonds, Os(l)-Os(2) = 2.793 (1)A and Os(1)-0s(3)= 2.873 (1)A. The nonbonding osmium-osmium distance, Os(2)--0s(3) = 3.492 (1) A, is bridged by the methoxide ligand. The hydride ligand, located crystallographically, bridges the Os(l)-Os(3) ...
document
... Next, count electron groups about the central atom. There are four (three single bonds and one lone pair), indicating a tetrahedral geometry of these groups about the P atom. However, because you must ignore the lone pair on P, the molecule is pyramidal in shape, with a predicted Br—P—B angle of les ...
... Next, count electron groups about the central atom. There are four (three single bonds and one lone pair), indicating a tetrahedral geometry of these groups about the P atom. However, because you must ignore the lone pair on P, the molecule is pyramidal in shape, with a predicted Br—P—B angle of les ...
Shape
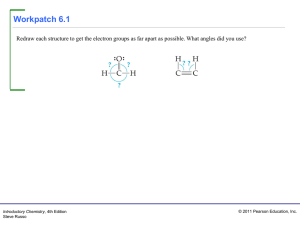
... ‣ Electron pairs, whether they be bonding or nonbonding, repel each other. ‣ By assuming the electron pairs are placed as far as possible from each other, we can predict the shape of the molecule. ‣ There are five basic arrangements of electron groups around a central atom. ‣ That’s based on a maxim ...
... ‣ Electron pairs, whether they be bonding or nonbonding, repel each other. ‣ By assuming the electron pairs are placed as far as possible from each other, we can predict the shape of the molecule. ‣ There are five basic arrangements of electron groups around a central atom. ‣ That’s based on a maxim ...
Preview Sample 1
... A) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of approximately 7 daltons and an atomic mass of 14. B) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of approximately 14 daltons and an atomic mass of 7. C) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of 14 and an atomic mass of 7 grams. D) The nitrogen atom has a mass number o ...
... A) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of approximately 7 daltons and an atomic mass of 14. B) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of approximately 14 daltons and an atomic mass of 7. C) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of 14 and an atomic mass of 7 grams. D) The nitrogen atom has a mass number o ...
11 myp covalent bonding
... Notice a few differences between the last diagram (the one in the previous slide) and this. – The core shells have been omitted – The nucleus is omitted – The electrons from the different atoms are distinguished by representing then as either circles (electrons originating in and belonging to Oxygen ...
... Notice a few differences between the last diagram (the one in the previous slide) and this. – The core shells have been omitted – The nucleus is omitted – The electrons from the different atoms are distinguished by representing then as either circles (electrons originating in and belonging to Oxygen ...
CHEMISTRY
... a solid, their answer is to cool it. Then, when I ask how they made the egg solid, and they reply that they applied heat, they realize the reaction isn’t as simple as it looks. I have the students observe the egg as it fries. Common observations are that an odor is produced and that the clear yellow ...
... a solid, their answer is to cool it. Then, when I ask how they made the egg solid, and they reply that they applied heat, they realize the reaction isn’t as simple as it looks. I have the students observe the egg as it fries. Common observations are that an odor is produced and that the clear yellow ...
Chemistry Olympiad Support Booklet
... Every year the Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) organises the selection of the UK team for the International Chemistry Olympiad (IChO). The IChO has been running for 40 years, and the UK has been involved since 1983. Next year, in July 2009, the UK will be hosting the competition, and almost 300 stu ...
... Every year the Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) organises the selection of the UK team for the International Chemistry Olympiad (IChO). The IChO has been running for 40 years, and the UK has been involved since 1983. Next year, in July 2009, the UK will be hosting the competition, and almost 300 stu ...
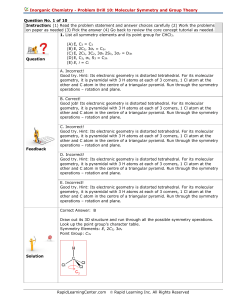
Problem Solving Drill - Rapid Learning Center
... on paper as needed (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 5. A chiral molecule is a molecule that cannot be superimposed on its mirror image. The only chiral point groups are: C1, Cn, Dn, (T, O, and I). The last three are very uncommon, so virtually all chiral ...
... on paper as needed (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 5. A chiral molecule is a molecule that cannot be superimposed on its mirror image. The only chiral point groups are: C1, Cn, Dn, (T, O, and I). The last three are very uncommon, so virtually all chiral ...
Advanced Higher Chemistry Resource Guide
... number of bonding and nonbonding electron pairs is 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6, respectively. Electron pair repulsions decrease in strength in the order: non-bonding pair/nonbonding pair > non-bonding pair/bonding pair > bonding pair/bonding pair. These different strengths of electron pair repulsion account fo ...
... number of bonding and nonbonding electron pairs is 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6, respectively. Electron pair repulsions decrease in strength in the order: non-bonding pair/nonbonding pair > non-bonding pair/bonding pair > bonding pair/bonding pair. These different strengths of electron pair repulsion account fo ...
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry
... while the highly branched alkane C8H18 causes little knocking and is assigned an octane rating of 100. A gasoline with an octane rating of 87 causes the same knocking as a mixture that is 87% in the branched alkane and 13% of the straight chain alkane. Alkenes are organic compounds that contain carb ...
... while the highly branched alkane C8H18 causes little knocking and is assigned an octane rating of 100. A gasoline with an octane rating of 87 causes the same knocking as a mixture that is 87% in the branched alkane and 13% of the straight chain alkane. Alkenes are organic compounds that contain carb ...
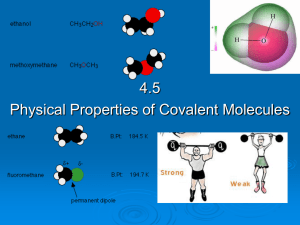
4.5 Physical properties of molecular covalent
... Covalent molecules are not charged because they are overall neutral and therefore do not conduct electricity. • Some covalent molecules can react with water and produce free ions which can carry an electrical current. • E.g. ammonia, NH3 NH3 (l) + H2O (l) ↔ NH4+ (aq) + OH- (aq) ...
... Covalent molecules are not charged because they are overall neutral and therefore do not conduct electricity. • Some covalent molecules can react with water and produce free ions which can carry an electrical current. • E.g. ammonia, NH3 NH3 (l) + H2O (l) ↔ NH4+ (aq) + OH- (aq) ...
MidtermReview2012
... 3. When a small amount of carbon is mixed in with molten iron, the cooled resulting alloy is called steel. Would you consider the iron to be changed physically or chemically? Explain. ...
... 3. When a small amount of carbon is mixed in with molten iron, the cooled resulting alloy is called steel. Would you consider the iron to be changed physically or chemically? Explain. ...
Bent's rule

Bent's rule describes and explains the relationship between the isovalent hybridization of central atoms in molecules and the electronegativities of substituents. The rule was stated by Henry Bent as follows: ""Atomic s character concentrates in orbitals directed toward electropositive substituents"".The chemical structure of a molecule is intimately related to its properties and reactivity. Valence bond theory proposes that molecular structures are due to covalent bonds between the atoms and that each bond consists of two overlapping and typically hybridised atomic orbitals. Traditionally, p-block elements in molecules are assumed to hybridise strictly as spn, where n is either 1, 2, or 3. In addition, the hybrid orbitals are all assumed to be equivalent (i.e. the n+1 spn orbitals have the same p character). Results from this approach are usually good, but they can be improved upon by allowing hybridised orbitals with noninteger and unequal p character. Bent's rule provides a qualitative estimate as to how these hybridised orbitals should be constructed. Bent's rule is that in a molecule, a central atom bonded to multiple groups will hybridise so that orbitals with more s character are directed towards electropositive groups, while orbitals with more p character will be directed towards groups that are more electronegative. By removing the assumption that all hybrid orbitals are equivalent spn orbitals, better predictions and explanations of properties such as molecular geometry and bond strength can be obtained.Bent's rule can be generalized to d-block elements as well. The hybridisation of a metal center is arranged so that orbitals with more s character are directed towards ligands that form bonds with more covalent character. Equivalently, orbitals with more d character are directed towards groups that form bonds of greater ionic character.