Appendices and Glossary
... carbon atoms and two moles of oxygen atoms. The atom ratio and the mole ratio of the elements are identical! The chemical formula of an ionic compound does not tell us the number of atoms in a molecule because ionic substances are not molecular. However, it still gives the mole ratio of the elements ...
... carbon atoms and two moles of oxygen atoms. The atom ratio and the mole ratio of the elements are identical! The chemical formula of an ionic compound does not tell us the number of atoms in a molecule because ionic substances are not molecular. However, it still gives the mole ratio of the elements ...
BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY
... formation , and is denoted H0. The standard heat of formation of simple substance in its most stable modification shall be equal to zero. Calculation of the heat of the reaction from the heats of formation of the participating substances, is produced by the Hess’ law , the heat of the chemical reac ...
... formation , and is denoted H0. The standard heat of formation of simple substance in its most stable modification shall be equal to zero. Calculation of the heat of the reaction from the heats of formation of the participating substances, is produced by the Hess’ law , the heat of the chemical reac ...
Concept Development Studies in Chemistry
... There is a problem, however. We can illustrate with three compounds formed from hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. The three mass proportion measurements are given in the following table (Table 2.1: Mass Relationships for Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen Compounds). First we examine nitric oxide, to nd that ...
... There is a problem, however. We can illustrate with three compounds formed from hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. The three mass proportion measurements are given in the following table (Table 2.1: Mass Relationships for Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen Compounds). First we examine nitric oxide, to nd that ...
SQA CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure
... All substances are made up of particles called atoms, ions or molecules, and these particles are constantly moving. The degree of movement depends upon the state of the substance. This is known as the "kinetic model" of matter. In any sample of solution, liquid or gas there is a range of kinetic ene ...
... All substances are made up of particles called atoms, ions or molecules, and these particles are constantly moving. The degree of movement depends upon the state of the substance. This is known as the "kinetic model" of matter. In any sample of solution, liquid or gas there is a range of kinetic ene ...
input
... It is useful to note that this chapter of the manual can be searched online by means of the "gmshelp" command, if your computer is of the Unix type. A command such as "gmshelp scf" will display the $SCF input group. With no arguments, the gmshelp command will show you all input group names. Type "q" ...
... It is useful to note that this chapter of the manual can be searched online by means of the "gmshelp" command, if your computer is of the Unix type. A command such as "gmshelp scf" will display the $SCF input group. With no arguments, the gmshelp command will show you all input group names. Type "q" ...
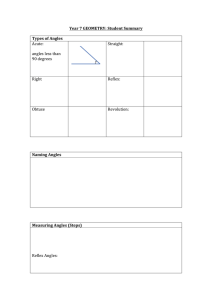
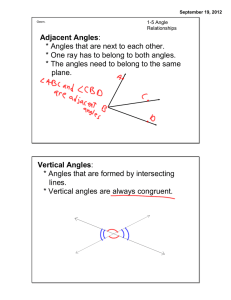
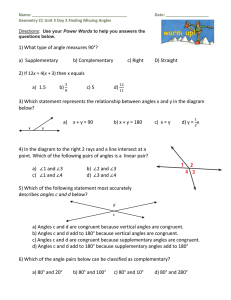
Adjacent Angles: * Angles that are next to each other. * One ray has
... * Angles may or may not be adjacent. ...
... * Angles may or may not be adjacent. ...
CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry
... This also provides a pattern that can often be used in identification. In both techniques some lines normally occur in the visible region (400-700 nm) but some applications use the ultraviolet region (200-400 nm). Both emission and absorption spectroscopy can be used to determine whether a certain s ...
... This also provides a pattern that can often be used in identification. In both techniques some lines normally occur in the visible region (400-700 nm) but some applications use the ultraviolet region (200-400 nm). Both emission and absorption spectroscopy can be used to determine whether a certain s ...
CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure
... All substances are made up of particles called atoms, ions or molecules, and these particles are constantly moving. The degree of movement depends upon the state of the substance. This is known as the 'kinetic model' of matter. In any sample of solution, liquid or gas there is a range of kinetic ene ...
... All substances are made up of particles called atoms, ions or molecules, and these particles are constantly moving. The degree of movement depends upon the state of the substance. This is known as the 'kinetic model' of matter. In any sample of solution, liquid or gas there is a range of kinetic ene ...
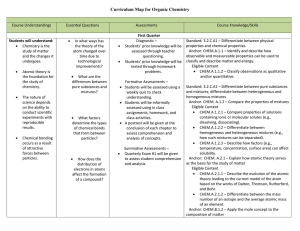
Organic Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
... compounds through both ionic and covalent bonding. Anchor: CHEM.A.1.1 – Identify and describe how observable and measureable properties can be used to classify and describe matter and energy. Eligible Content CHEM.A.1.1.4 – Relate the physical properties of matter to its atomic or molecular struct ...
... compounds through both ionic and covalent bonding. Anchor: CHEM.A.1.1 – Identify and describe how observable and measureable properties can be used to classify and describe matter and energy. Eligible Content CHEM.A.1.1.4 – Relate the physical properties of matter to its atomic or molecular struct ...
PDF - mockies – Mockiesgateacademy
... In using the term mole for ionic substances, we mean the number of formula units of the substance. For example, a mole of sodium carbonate, Na2CO3 is a quantity containing 6.023 x 1023 Na2CO3 units. But each formula unit of Na2CO3 contains 2 x 6.023 x 1023 Na+ ions and one CO32ions and 1 x 6.023 x 1 ...
... In using the term mole for ionic substances, we mean the number of formula units of the substance. For example, a mole of sodium carbonate, Na2CO3 is a quantity containing 6.023 x 1023 Na2CO3 units. But each formula unit of Na2CO3 contains 2 x 6.023 x 1023 Na+ ions and one CO32ions and 1 x 6.023 x 1 ...
CHEM 101 Fall 09 Final Exam (a)
... 12. What is the frequency (s-1) of a photon that has an energy of 4.38 × 10-18 J? a. 436 b. 6.61 × 1015 c. 1.45 × 10-16 d. 2.30 × 107 e. 1.31 × 10-9 13. Which answer shows all possible values of the second quantum number when n = 3? a. l = 0 b. l = 0, 1 c. l = 0, 1, 2 d. l = 0, 1, 2, 3 e. l = 0, 1, ...
... 12. What is the frequency (s-1) of a photon that has an energy of 4.38 × 10-18 J? a. 436 b. 6.61 × 1015 c. 1.45 × 10-16 d. 2.30 × 107 e. 1.31 × 10-9 13. Which answer shows all possible values of the second quantum number when n = 3? a. l = 0 b. l = 0, 1 c. l = 0, 1, 2 d. l = 0, 1, 2, 3 e. l = 0, 1, ...
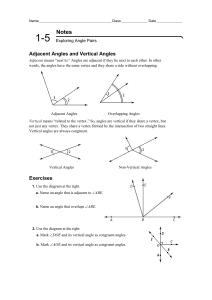
0042_hsm11gmtr_0105.indd
... Two angles that form a line are supplementary angles. Another term for these angles is a linear pair. However, any two angles with measures that sum to 180 are also considered supplementary angles. In both figures below, m1 = 120 and m2 = 60, so 1 and 2 are supplementary. ...
... Two angles that form a line are supplementary angles. Another term for these angles is a linear pair. However, any two angles with measures that sum to 180 are also considered supplementary angles. In both figures below, m1 = 120 and m2 = 60, so 1 and 2 are supplementary. ...
Holt Modern Chemistry Workbook: intro - ch 5
... vocabulary terms on this page: matter, mass, atom, element, and compound. ...
... vocabulary terms on this page: matter, mass, atom, element, and compound. ...
p-BLOCK ELEMENTS - einstein classes
... H3BO3 or (B(OH)3) cannot be titrated satisfactory with NaOH, as a sharp end point is not obtained. If certain organic polyhydroxy compounds such as glycerol, mannitol or sugars are added to the titration mixture, then B(OH)3 behaves as a strong monobasic acid. It can now be titrated with NaOH, and t ...
... H3BO3 or (B(OH)3) cannot be titrated satisfactory with NaOH, as a sharp end point is not obtained. If certain organic polyhydroxy compounds such as glycerol, mannitol or sugars are added to the titration mixture, then B(OH)3 behaves as a strong monobasic acid. It can now be titrated with NaOH, and t ...
Mechanochemistry: the varied applications of mechanical bond
... were cracked by breaking of intermolecular cohesive ligations producing very high surface area for the solid-solid reaction with equally micronized reagent crystallites or with liquids. A fair reactivity comparison for solid-liquid reactions would be the use of pre-milled C60 for the reaction with t ...
... were cracked by breaking of intermolecular cohesive ligations producing very high surface area for the solid-solid reaction with equally micronized reagent crystallites or with liquids. A fair reactivity comparison for solid-liquid reactions would be the use of pre-milled C60 for the reaction with t ...
CHM 423 Coordination Chemistry
... donors. Thus a Lewis acid must have empty suitable orbitals to accommodate the donated electron pairs. The presence of empty suitable orbitals in transition metals (Cu, Co, Fe etc) and some compounds (BF3, BeCl2 with empty p-orbital) and ions (H+) of main block elements makes them to act as Lewis ac ...
... donors. Thus a Lewis acid must have empty suitable orbitals to accommodate the donated electron pairs. The presence of empty suitable orbitals in transition metals (Cu, Co, Fe etc) and some compounds (BF3, BeCl2 with empty p-orbital) and ions (H+) of main block elements makes them to act as Lewis ac ...
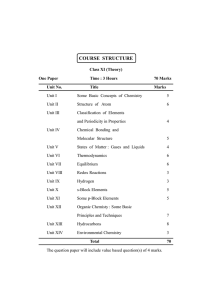
COURSE STRUCTURE
... In all physical and chemical changes, the total mass of reactants is equal to that of products. Law of constant composition : A chemical compound is always found to be made of same elements combined together in the same fixed ratio by mass. Law of multiple proportion : Two elements combined together ...
... In all physical and chemical changes, the total mass of reactants is equal to that of products. Law of constant composition : A chemical compound is always found to be made of same elements combined together in the same fixed ratio by mass. Law of multiple proportion : Two elements combined together ...
1) What type of angle measures 90°? a) Supplementary b
... a) Angles c and d are congruent because vertical angles are congruent. b) Angles c and d add to 180° because vertical angles are congruent. c) Angles c and d are congruent because supplementary angles are congruent. d) Angles c and d add to 180° because supplementary angles add to 180° 6) Which of t ...
... a) Angles c and d are congruent because vertical angles are congruent. b) Angles c and d add to 180° because vertical angles are congruent. c) Angles c and d are congruent because supplementary angles are congruent. d) Angles c and d add to 180° because supplementary angles add to 180° 6) Which of t ...
chm 205 - National Open University of Nigeria
... hexagons (Fig. 1.2). The bond length is 142 pm showing some multiple bond character, intermediate between a double and a single bond. Different layers are at a distance of 335 pm from each other and are thus held by weak van der Waals forces only. These layers can slide over one another easily, impa ...
... hexagons (Fig. 1.2). The bond length is 142 pm showing some multiple bond character, intermediate between a double and a single bond. Different layers are at a distance of 335 pm from each other and are thus held by weak van der Waals forces only. These layers can slide over one another easily, impa ...
幻灯片 1
... Section A4 The table divides naturally into s, p, d and f blocks according to the outer electron configurations. s and p blocks form the main groups, the d block the transition elements, and the f block the lanthanides and actinides. ...
... Section A4 The table divides naturally into s, p, d and f blocks according to the outer electron configurations. s and p blocks form the main groups, the d block the transition elements, and the f block the lanthanides and actinides. ...
Bent's rule

Bent's rule describes and explains the relationship between the isovalent hybridization of central atoms in molecules and the electronegativities of substituents. The rule was stated by Henry Bent as follows: ""Atomic s character concentrates in orbitals directed toward electropositive substituents"".The chemical structure of a molecule is intimately related to its properties and reactivity. Valence bond theory proposes that molecular structures are due to covalent bonds between the atoms and that each bond consists of two overlapping and typically hybridised atomic orbitals. Traditionally, p-block elements in molecules are assumed to hybridise strictly as spn, where n is either 1, 2, or 3. In addition, the hybrid orbitals are all assumed to be equivalent (i.e. the n+1 spn orbitals have the same p character). Results from this approach are usually good, but they can be improved upon by allowing hybridised orbitals with noninteger and unequal p character. Bent's rule provides a qualitative estimate as to how these hybridised orbitals should be constructed. Bent's rule is that in a molecule, a central atom bonded to multiple groups will hybridise so that orbitals with more s character are directed towards electropositive groups, while orbitals with more p character will be directed towards groups that are more electronegative. By removing the assumption that all hybrid orbitals are equivalent spn orbitals, better predictions and explanations of properties such as molecular geometry and bond strength can be obtained.Bent's rule can be generalized to d-block elements as well. The hybridisation of a metal center is arranged so that orbitals with more s character are directed towards ligands that form bonds with more covalent character. Equivalently, orbitals with more d character are directed towards groups that form bonds of greater ionic character.