Physical and Chemical equilibrium
... (ii)At equilibrium, concentration of all reactants and products becomes constant (iii)Equilibrium is dynamic in nature i.e. reaction seems to be static because no change in concentration of reactants or product, but actually reaction takes place in both the directions with same speed (iv)Catalyst do ...
... (ii)At equilibrium, concentration of all reactants and products becomes constant (iii)Equilibrium is dynamic in nature i.e. reaction seems to be static because no change in concentration of reactants or product, but actually reaction takes place in both the directions with same speed (iv)Catalyst do ...
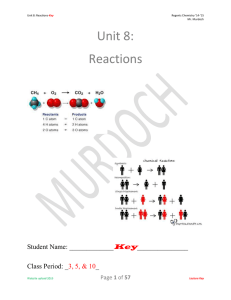
Ch 6 LAN 7th Intro Chem Chemical Reactions
... dioxide and water as indicated in the following reaction 2 C2H2 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 4 CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) When 26.0 g of acetylene is burned in sufficient oxygen for complete reaction, the theoretical yield of CO2 is 88.0 g Calculate the percent yield for this reaction if the actual yield is only 72.4 ...
... dioxide and water as indicated in the following reaction 2 C2H2 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 4 CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) When 26.0 g of acetylene is burned in sufficient oxygen for complete reaction, the theoretical yield of CO2 is 88.0 g Calculate the percent yield for this reaction if the actual yield is only 72.4 ...
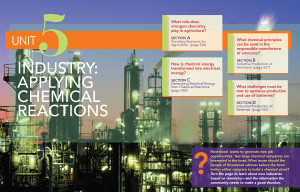
industry: applying chemical reactions
... small, clean test tube, which will serve as a blank. b. Add about one milliliter of iron(II) sulfate (FeSO4) solution to each of the two test tubes. Gently swirl to mix the contents of each tube. c. Obtain about one milliliter of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) for each tube. Your teacher will ...
... small, clean test tube, which will serve as a blank. b. Add about one milliliter of iron(II) sulfate (FeSO4) solution to each of the two test tubes. Gently swirl to mix the contents of each tube. c. Obtain about one milliliter of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) for each tube. Your teacher will ...
Web Appendix 6
... can never be computed without reference to a chemical reaction in which that compound is, directly or indirectly, a participant. Similarly, the normality of a solution can never be specified without knowledge about how the solution will be used. Equivalent Weights in Neutralization Reactions One equ ...
... can never be computed without reference to a chemical reaction in which that compound is, directly or indirectly, a participant. Similarly, the normality of a solution can never be specified without knowledge about how the solution will be used. Equivalent Weights in Neutralization Reactions One equ ...
as a PDF
... of a square. Four trichloroacetato bridging anions are alternatively above and below this square. The terminal oxygen atoms of the four tert-butyl peroxidic anions are located in the plane of the four palladium atoms and bridge these atoms two by two. The average Pd-Pd separation is 2.91 A. The mean ...
... of a square. Four trichloroacetato bridging anions are alternatively above and below this square. The terminal oxygen atoms of the four tert-butyl peroxidic anions are located in the plane of the four palladium atoms and bridge these atoms two by two. The average Pd-Pd separation is 2.91 A. The mean ...
Common Student Misconceptions
... • These substances exist as a mixture of ions and un-ionized molecules in solution. • The predominant form of the solute is the un-ionized molecule. • Example: acetic acid, HC2H3O2. HC2H3O2(aq) ⇋ H+(aq) + C2H3O2–(aq) • The double arrow means that the reaction is significant in both directions. • It ...
... • These substances exist as a mixture of ions and un-ionized molecules in solution. • The predominant form of the solute is the un-ionized molecule. • Example: acetic acid, HC2H3O2. HC2H3O2(aq) ⇋ H+(aq) + C2H3O2–(aq) • The double arrow means that the reaction is significant in both directions. • It ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... in water at room temperature compounds that dissolve in a solvent are said to be soluble, while those that do not are said to be insoluble NaCl is soluble in water, AgCl is insoluble in water the degree of solubility depends on the temperature even insoluble compounds dissolve, just not enough ...
... in water at room temperature compounds that dissolve in a solvent are said to be soluble, while those that do not are said to be insoluble NaCl is soluble in water, AgCl is insoluble in water the degree of solubility depends on the temperature even insoluble compounds dissolve, just not enough ...
Pirogov National Medical Univercity of Vinnitsa
... 5. Alkali metals should always be kept in a layer of inert against water and moisture kerosene. Alkali metals and crystalline alkali should be taken only with tweezers or a special forceps. Should wear goggles or a mask. After the end of the remark the remnants of these metals should be moved to a s ...
... 5. Alkali metals should always be kept in a layer of inert against water and moisture kerosene. Alkali metals and crystalline alkali should be taken only with tweezers or a special forceps. Should wear goggles or a mask. After the end of the remark the remnants of these metals should be moved to a s ...
Spring 2008
... A. increases the number of moles of A B. decreases the number of moles of A C. does not change the number of moles of A Answer B There are more molecules in the gas phase on the LH side, to increasing the P drives it to the right 27. For the reaction: aA(g) + bB(g) cC(g) + heat with a = 1, b=1 and c ...
... A. increases the number of moles of A B. decreases the number of moles of A C. does not change the number of moles of A Answer B There are more molecules in the gas phase on the LH side, to increasing the P drives it to the right 27. For the reaction: aA(g) + bB(g) cC(g) + heat with a = 1, b=1 and c ...
EQUILIBRIUM
... The equilibrium pressure of NH3 gas would decrease. In order for the pressure equilibrium constant, Kp, to remain constant, the equilibrium pressure of NH3 must decrease when the pressure of H2S is increased. Kp = (PNH3) (PH2S) (A complete explanation based on Le Chatelier's principle is also accept ...
... The equilibrium pressure of NH3 gas would decrease. In order for the pressure equilibrium constant, Kp, to remain constant, the equilibrium pressure of NH3 must decrease when the pressure of H2S is increased. Kp = (PNH3) (PH2S) (A complete explanation based on Le Chatelier's principle is also accept ...
EQUILIBRIUM
... The equilibrium pressure of NH3 gas would decrease. In order for the pressure equilibrium constant, Kp, to remain constant, the equilibrium pressure of NH3 must decrease when the pressure of H2S is increased. Kp = (PNH3) (PH2S) (A complete explanation based on Le Chatelier's principle is also accept ...
... The equilibrium pressure of NH3 gas would decrease. In order for the pressure equilibrium constant, Kp, to remain constant, the equilibrium pressure of NH3 must decrease when the pressure of H2S is increased. Kp = (PNH3) (PH2S) (A complete explanation based on Le Chatelier's principle is also accept ...
doc - Dartmouth College
... If atmospheric pressure is equal to 1.000 atm it can support a column of Hg which is 760.0 mm tall. Suppose a column of Hg is set up where the bath is open to the atmosphere, and the column height of Hg is 760.0 mm with the top of the enclosed column being a vacuum. Next, suppose some diethyl ether ...
... If atmospheric pressure is equal to 1.000 atm it can support a column of Hg which is 760.0 mm tall. Suppose a column of Hg is set up where the bath is open to the atmosphere, and the column height of Hg is 760.0 mm with the top of the enclosed column being a vacuum. Next, suppose some diethyl ether ...
Chapter 16: Energy and Chemical Change
... the water rushes down and does work by turning the turbines to produce electrical energy. Kinetic energy is energy of motion. You can observe kinetic energy in the motion around you. The potential energy of the dammed water is converted to kinetic energy as the dam gates are opened and the water flo ...
... the water rushes down and does work by turning the turbines to produce electrical energy. Kinetic energy is energy of motion. You can observe kinetic energy in the motion around you. The potential energy of the dammed water is converted to kinetic energy as the dam gates are opened and the water flo ...
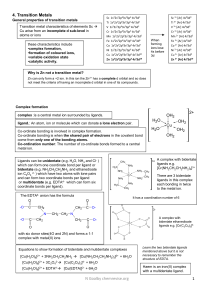
mod-5-revision-guide-4-transition-metals
... Catalysis Catalysts increase reaction rates without getting used up. They do this by providing an alternative route with a lower activation energy. Transition metals and their compounds can act as heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysts. ...
... Catalysis Catalysts increase reaction rates without getting used up. They do this by providing an alternative route with a lower activation energy. Transition metals and their compounds can act as heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysts. ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.