Skill Sheet 19-B Chemical Formulas
... Have you ever heard of sodium nitrate? It’s a preservative used in foods like hot dogs. The chemical formula for sodium nitrate is NaNO3. How many types of atoms does this compound contain? You are right if you said three: sodium, nitrogen, and oxygen. The nitrogen and oxygen atoms have a shared-ele ...
... Have you ever heard of sodium nitrate? It’s a preservative used in foods like hot dogs. The chemical formula for sodium nitrate is NaNO3. How many types of atoms does this compound contain? You are right if you said three: sodium, nitrogen, and oxygen. The nitrogen and oxygen atoms have a shared-ele ...
Realization of Bose-Einstein Condensation in dilute gases
... peak of atoms near the centre (zero-velocity region), corresponding to the ground state of the trap. (2) As the temperature was lowered below the transition temperature, the density of atoms in the peak increased abruptly, indicating a phase ...
... peak of atoms near the centre (zero-velocity region), corresponding to the ground state of the trap. (2) As the temperature was lowered below the transition temperature, the density of atoms in the peak increased abruptly, indicating a phase ...
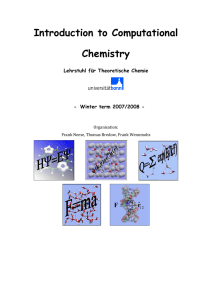
Introduction to Computational Chemistry
... to provide experimental chemists, who have not been exposed in depth to computational chemistry, with a working knowledge that allows them to tackle their own research problems with the now widely availabl ...
... to provide experimental chemists, who have not been exposed in depth to computational chemistry, with a working knowledge that allows them to tackle their own research problems with the now widely availabl ...
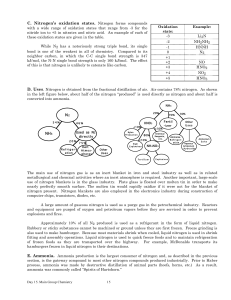
Nitrogen`s oxidation states
... The reaction is exothermic, however entropy does not favor the forward reaction. Thus the reaction is spontaneous at lower temperatures. Unfortunately, the reaction is kinetically slow except at higher temperatures. The conditions employed strikes a compromise between thermodynamics and kinetics. Th ...
... The reaction is exothermic, however entropy does not favor the forward reaction. Thus the reaction is spontaneous at lower temperatures. Unfortunately, the reaction is kinetically slow except at higher temperatures. The conditions employed strikes a compromise between thermodynamics and kinetics. Th ...
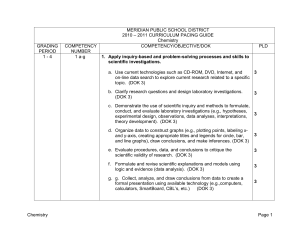
MERIDIAN PUBLIC SCHOOL DISTRICT
... Properties of acids and bases, including how they affect indicators and the relative pH of the solution Formation of acidic and basic solutions Definition of pH in terms of the hydronium ion concentration and the hydroxide ion concentration The pH or pOH from the hydrogen ion or hydroxide ion concen ...
... Properties of acids and bases, including how they affect indicators and the relative pH of the solution Formation of acidic and basic solutions Definition of pH in terms of the hydronium ion concentration and the hydroxide ion concentration The pH or pOH from the hydrogen ion or hydroxide ion concen ...
NOMENCLATURE OF IONIC COMPOUNDS CHEMISTRY 1405
... The prefixes mono, di, tri, tetra etc are used only for binary covalent compounds. ...
... The prefixes mono, di, tri, tetra etc are used only for binary covalent compounds. ...
Chapter 4: Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... Some acids have more than one ionizable hydrogen atom. They ionize in “steps” (more in Chapter 15). H2SO4 → H+ + HSO4– HSO4– → H+ + SO42– ...
... Some acids have more than one ionizable hydrogen atom. They ionize in “steps” (more in Chapter 15). H2SO4 → H+ + HSO4– HSO4– → H+ + SO42– ...
- Department of Chemistry, York University
... NB: C4H- would be very interesting because C4H is massively abundant in IRC+10216. The cyanopolyynyl radicals like C5N are also very promising because they have EA values of 4 eV or more, so attachment is very favourable, but these radicals aren't as abundant as ...
... NB: C4H- would be very interesting because C4H is massively abundant in IRC+10216. The cyanopolyynyl radicals like C5N are also very promising because they have EA values of 4 eV or more, so attachment is very favourable, but these radicals aren't as abundant as ...
Chemical Physics High-spin-low-spin transitions in Fe(II) complexes
... The important difference between them is that in the AOM all the ligand field parameters are fit to the experimental spectra for each ligand and are not transferable from one ligand to another even if the donor atom is the same. In our approach the electronic structure of the ligands is taken into a ...
... The important difference between them is that in the AOM all the ligand field parameters are fit to the experimental spectra for each ligand and are not transferable from one ligand to another even if the donor atom is the same. In our approach the electronic structure of the ligands is taken into a ...
Organic Chemistry - University of California, Riverside
... The general formulas R-X, R-OH, and R-NH2 suggest two different ways to view these classes of compounds. One way is for us to imagine that an alkyl group R replaces H in HNH2 (ammonia), H-OH (water), and the hydrogen halides H-X (X = F, Cl, Br, or I). We can also view haloalkanes (R-X), alcohols (R- ...
... The general formulas R-X, R-OH, and R-NH2 suggest two different ways to view these classes of compounds. One way is for us to imagine that an alkyl group R replaces H in HNH2 (ammonia), H-OH (water), and the hydrogen halides H-X (X = F, Cl, Br, or I). We can also view haloalkanes (R-X), alcohols (R- ...
8.3 Metals - UNSW Chemistry
... It is assumed that students can: ♦ apply an appropriate atomic model (Rutherford model) to describe atomic structure ♦ determine the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of a neutral or charged atom ♦ determine the number of electrons orbiting the nucleus of a neutral or charged atom ♦ use ...
... It is assumed that students can: ♦ apply an appropriate atomic model (Rutherford model) to describe atomic structure ♦ determine the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of a neutral or charged atom ♦ determine the number of electrons orbiting the nucleus of a neutral or charged atom ♦ use ...
The Periodic Electronegativity Table
... of p = 20 was established by comparison with independent chemical evidence that relates to ionization radii. A set of atomic radii, derived as an estimate to describe a single valence electron, uniformly spread over a characteristic sphere for each atom, has been known for a long time [18]. These ra ...
... of p = 20 was established by comparison with independent chemical evidence that relates to ionization radii. A set of atomic radii, derived as an estimate to describe a single valence electron, uniformly spread over a characteristic sphere for each atom, has been known for a long time [18]. These ra ...
Additional Review
... o all of matter is some combination of these four elements Alchemy [1500 AD] In the 1500’s many scientists were________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ While they were not able to create gold they did di ...
... o all of matter is some combination of these four elements Alchemy [1500 AD] In the 1500’s many scientists were________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ While they were not able to create gold they did di ...
Evidence of Bose-Einstein Condensation in an Atomic
... goal was realized in a rarified gas of spin-polarized, ultracold 87Rb atoms [4]. Because of the extraordinarily low temperatures that can be achieved in atomic gases, BEC can be studied in the low density regime where interatomic distances are much greater than the distance scale of atomatom interac ...
... goal was realized in a rarified gas of spin-polarized, ultracold 87Rb atoms [4]. Because of the extraordinarily low temperatures that can be achieved in atomic gases, BEC can be studied in the low density regime where interatomic distances are much greater than the distance scale of atomatom interac ...
5. Atomic models
... energy gap between the ground state and the excited state. This is an example of a `resonance’ phenomena, in which the frequency of the external field that interacts with the system matches with that of the internal frequency of the system (in this case, the energy gap which takes only quantised val ...
... energy gap between the ground state and the excited state. This is an example of a `resonance’ phenomena, in which the frequency of the external field that interacts with the system matches with that of the internal frequency of the system (in this case, the energy gap which takes only quantised val ...
Chemistry - Bourbon County Schools
... Explain ionic stability, recognize typical ionic configurations, and predict ionic configurations for elements (e.g., electron configurations, Lewis dot models) Describe the nature of the chemical bond with respect to valence ...
... Explain ionic stability, recognize typical ionic configurations, and predict ionic configurations for elements (e.g., electron configurations, Lewis dot models) Describe the nature of the chemical bond with respect to valence ...
Questions - SMK Raja Perempuan Ipoh
... 2.4 THE ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF AN ATOM 1. The elektron are filled in specific shells. Every shell can be filled only with a certain number of electrons. For the elements with proton number 1-20:First shell can filled with a maximum of ……………. electrons Second shell can filled with a maximum of …………… ...
... 2.4 THE ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF AN ATOM 1. The elektron are filled in specific shells. Every shell can be filled only with a certain number of electrons. For the elements with proton number 1-20:First shell can filled with a maximum of ……………. electrons Second shell can filled with a maximum of …………… ...
Topic 1: Quantitative Chemistry
... 4.1.5: State that transition elements can form more than one ion. 4.1.6: Predict whether a compound of two elements would be ionic from the position of the elements in the periodic table or negativity values.4.1.7: State the formula of common polyatomic ions formed by non-metals in periods 2 and 3. ...
... 4.1.5: State that transition elements can form more than one ion. 4.1.6: Predict whether a compound of two elements would be ionic from the position of the elements in the periodic table or negativity values.4.1.7: State the formula of common polyatomic ions formed by non-metals in periods 2 and 3. ...
NYS Regents Chemistry
... specific energy. The further the level is away from the nucleus the greater the energy of the electrons in it. 1. Bright line spectrum: When an electron in an atom gains just the right amount of energy, from an outside source, electron can shift to a higher energy state (excited state). However, the ...
... specific energy. The further the level is away from the nucleus the greater the energy of the electrons in it. 1. Bright line spectrum: When an electron in an atom gains just the right amount of energy, from an outside source, electron can shift to a higher energy state (excited state). However, the ...
Web Supplement 7.2
... In the preceding equations, the dissolved copper and zinc species are shown as ions having a +2 charge, i.e., Cu2+ (aq) and Zn2+ (aq). Chemists have extended this concept of charge to chemically bound atoms by assigning its atom an oxidation number. The rules for determining the oxidation number of ...
... In the preceding equations, the dissolved copper and zinc species are shown as ions having a +2 charge, i.e., Cu2+ (aq) and Zn2+ (aq). Chemists have extended this concept of charge to chemically bound atoms by assigning its atom an oxidation number. The rules for determining the oxidation number of ...
Chapter 2
... compound, the total charges from the cations and anions must cancel-out (or sum to zero). • Therefore, Mg needs to lose 6 electrons (3 2+) and N gain those 6 electrons (2 3-). • The resulting formula is: Mg3N2. ...
... compound, the total charges from the cations and anions must cancel-out (or sum to zero). • Therefore, Mg needs to lose 6 electrons (3 2+) and N gain those 6 electrons (2 3-). • The resulting formula is: Mg3N2. ...
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are ""strong bonds"" such as covalent or ionic bonds and ""weak bonds"" such as Dipole-dipole interaction, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.Since opposite charges attract via a simple electromagnetic force, the negatively charged electrons that are orbiting the nucleus and the positively charged protons in the nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitutes the chemical bond. Due to the matter wave nature of electrons and their smaller mass, they must occupy a much larger amount of volume compared with the nuclei, and this volume occupied by the electrons keeps the atomic nuclei relatively far apart, as compared with the size of the nuclei themselves. This phenomenon limits the distance between nuclei and atoms in a bond.In general, strong chemical bonding is associated with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules, crystals, metals and diatomic gases—indeed most of the physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure and the bulk properties of matter.All bonds can be explained by quantum theory, but, in practice, simplification rules allow chemists to predict the strength, directionality, and polarity of bonds. The octet rule and VSEPR theory are two examples. More sophisticated theories are valence bond theory which includes orbital hybridization and resonance, and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method which includes ligand field theory. Electrostatics are used to describe bond polarities and the effects they have on chemical substances.