Theoretical study of a cold atom beam splitter
... of cold atom interferometers because of their intrinsic coherence. However, for certain applications such as atomic clocks, gyrometers and gravimeters, thermal ensembles of cold atoms are still preferred because they allow for the preparation of a larger number of atoms at a higher repetition rate [ ...
... of cold atom interferometers because of their intrinsic coherence. However, for certain applications such as atomic clocks, gyrometers and gravimeters, thermal ensembles of cold atoms are still preferred because they allow for the preparation of a larger number of atoms at a higher repetition rate [ ...
The quantum speed limit of optimal controlled phasegates for
... two-qubit gate operation involves atomic motional degrees of freedom [4, 5], most often following adiabatic processes. This implies frequencies much lower than those characteristic of the trap, typically around a few tens of kHz. When long-range interactions, like dipole-dipole forces between Rydber ...
... two-qubit gate operation involves atomic motional degrees of freedom [4, 5], most often following adiabatic processes. This implies frequencies much lower than those characteristic of the trap, typically around a few tens of kHz. When long-range interactions, like dipole-dipole forces between Rydber ...
Quantum Projection Noise in an Atomic Fountain: A High Stability
... Cs atoms are loaded into a magneto-optical trap. After the magnetic field has been switched off, the atoms are launched upward at ,4 mys and cooled to 1.6 mK. With laser and microwave pulses, we select only atoms in the jF 3, mF 0l quantum state. Atoms in mF fi 0 are pushed away by the radiation ...
... Cs atoms are loaded into a magneto-optical trap. After the magnetic field has been switched off, the atoms are launched upward at ,4 mys and cooled to 1.6 mK. With laser and microwave pulses, we select only atoms in the jF 3, mF 0l quantum state. Atoms in mF fi 0 are pushed away by the radiation ...
Document
... 1.Taylor’s Theory of active Sites According to his theory (the 1920's), the surface atoms of a crystal • may be higher than the mean level of the surface act as the active sites of a catalyst. Such crystal "peaks" have free valences and are capable of forming reactive intermediates. This ...
... 1.Taylor’s Theory of active Sites According to his theory (the 1920's), the surface atoms of a crystal • may be higher than the mean level of the surface act as the active sites of a catalyst. Such crystal "peaks" have free valences and are capable of forming reactive intermediates. This ...
Are Orbitals Observable? - HYLE-
... The continuing value of orbitals lies in their serving as basis sets, or a form of coordinate system, with which the wavefunction of an atom, ion, or molecule can be expanded mathematically. [Scerri 2001, p. S79] ...
... The continuing value of orbitals lies in their serving as basis sets, or a form of coordinate system, with which the wavefunction of an atom, ion, or molecule can be expanded mathematically. [Scerri 2001, p. S79] ...
Vorlesung Supramolekulare Chemie
... Ag+ form complexes with π-systems. These interactions are strong and are not considered non-covalent, because of the bonding situation involving the π-orbital of the unsaturated ligand and the d-orbitals of the metal ion. However, alkali- and earth alkali metal cations show much weaker interactions ...
... Ag+ form complexes with π-systems. These interactions are strong and are not considered non-covalent, because of the bonding situation involving the π-orbital of the unsaturated ligand and the d-orbitals of the metal ion. However, alkali- and earth alkali metal cations show much weaker interactions ...
File
... ratio of atoms of the elements in a compound Ex. H2O2 hydrogen peroxide Empirical formula = HO Ex. H2O water Empirical formula and molecular formula are the same ...
... ratio of atoms of the elements in a compound Ex. H2O2 hydrogen peroxide Empirical formula = HO Ex. H2O water Empirical formula and molecular formula are the same ...
Study of P,T-Parity Violation Effects in Polar Heavy
... of the electron. The benchmark upper limit on a nuclear EDM is obtained in atomic experiment on 199 Hg [13], |dHg | < 2.1 × 10−28 e·cm, from which the best restriction on the proton EDM, |dp | < 5.4 × 10−24 e·cm, was also recently obtained by Dzuba et al. [14] and Dmitriev & Sen’kov [15] (the previo ...
... of the electron. The benchmark upper limit on a nuclear EDM is obtained in atomic experiment on 199 Hg [13], |dHg | < 2.1 × 10−28 e·cm, from which the best restriction on the proton EDM, |dp | < 5.4 × 10−24 e·cm, was also recently obtained by Dzuba et al. [14] and Dmitriev & Sen’kov [15] (the previo ...
A study of the structure and bonding of small aluminum oxide
... The details of the experimental apparatus have been published elsewhere and will only be given briefly.34 The apparatus is composed of a laser vaporization source, a modified Wiley–McLaren time-of-flight ~TOF! mass spectrometer65 and an improved magnetic-bottle TOF electron analyzer.24,66 A pulsed l ...
... The details of the experimental apparatus have been published elsewhere and will only be given briefly.34 The apparatus is composed of a laser vaporization source, a modified Wiley–McLaren time-of-flight ~TOF! mass spectrometer65 and an improved magnetic-bottle TOF electron analyzer.24,66 A pulsed l ...
Paper
... (atom shot noise) for cold clouds deep in the quantum degenerate regime. Strong suppression is observed for probe volumes containing more than 10 000 atoms. Measuring the level of suppression provides sensitive thermometry at low temperatures. After this method of sensitive noise measurements has be ...
... (atom shot noise) for cold clouds deep in the quantum degenerate regime. Strong suppression is observed for probe volumes containing more than 10 000 atoms. Measuring the level of suppression provides sensitive thermometry at low temperatures. After this method of sensitive noise measurements has be ...
N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 2.5 Transition Metals Substitution
... Why is Zn not a transition metal? Zn can only form a +2 ion. In this ion the Zn 2+ has a complete d orbital and so does not meet the criteria of having an incomplete d orbital in one of its compounds. ...
... Why is Zn not a transition metal? Zn can only form a +2 ion. In this ion the Zn 2+ has a complete d orbital and so does not meet the criteria of having an incomplete d orbital in one of its compounds. ...
Measurement and data processing and analysis
... significant figures of the measurement. There are two significant figures, for example, in 62 cm3 and five in 100.00 g. The zeros are significant here as they signify that the uncertainty range is (±) 0.01 g. The number of significant figures may not always be clear. If a time measurement is 1000 s, ...
... significant figures of the measurement. There are two significant figures, for example, in 62 cm3 and five in 100.00 g. The zeros are significant here as they signify that the uncertainty range is (±) 0.01 g. The number of significant figures may not always be clear. If a time measurement is 1000 s, ...
Squaring the Interface: "Surface-Assisted" Coordination Chemistry
... positioning of the involved metal atoms relative to the organic ligands. With regards to the ligands, nearedge X-ray adsorption fine structure (NEXAFS) studies have revealed that the ligand molecules are adsorbed with their phenyl rings almost parallel to the Cu(100) surface plane.[5] This kind of m ...
... positioning of the involved metal atoms relative to the organic ligands. With regards to the ligands, nearedge X-ray adsorption fine structure (NEXAFS) studies have revealed that the ligand molecules are adsorbed with their phenyl rings almost parallel to the Cu(100) surface plane.[5] This kind of m ...
PDF - mockies – Mockiesgateacademy
... matter which makes up our world and of the interactions between particles on which it depends. The ancient Greek philosophers had their own ideas of the nature of matter, proposing atoms as the smallest indivisible particles. However, although these ideas seems to fit with modern models of matter, s ...
... matter which makes up our world and of the interactions between particles on which it depends. The ancient Greek philosophers had their own ideas of the nature of matter, proposing atoms as the smallest indivisible particles. However, although these ideas seems to fit with modern models of matter, s ...
AP syllabus
... 11. Drawing and naming the s, p, d orbitals 12. Using Aufbau Principle, Hund’s Rule, and Pauli Exclusion Principle in writing electron configurations and orbital notation. 13. Using Periodic Chart and abbreviated notation to determine exceptions when filling orbitals 14. The basis for the periodic l ...
... 11. Drawing and naming the s, p, d orbitals 12. Using Aufbau Principle, Hund’s Rule, and Pauli Exclusion Principle in writing electron configurations and orbital notation. 13. Using Periodic Chart and abbreviated notation to determine exceptions when filling orbitals 14. The basis for the periodic l ...
Review - Discount Flies
... 18 g x 1 mole x 40.6 kJ x 1000 J = 40,600 J 18 g 1 mole 1 kJ 6,020 + 7,531 + 40,600 = 54,151 J ...
... 18 g x 1 mole x 40.6 kJ x 1000 J = 40,600 J 18 g 1 mole 1 kJ 6,020 + 7,531 + 40,600 = 54,151 J ...
14.1 Redox equations
... Work out formulae of the species before and after the change; balance if required Work out oxidation state of the element before and after the change Add electrons to one side of the equation so that the oxidation states balance If the charges on the species (ions and electrons) on either side of th ...
... Work out formulae of the species before and after the change; balance if required Work out oxidation state of the element before and after the change Add electrons to one side of the equation so that the oxidation states balance If the charges on the species (ions and electrons) on either side of th ...
Relative Atomic Masses
... You might have to look at these data very hard to see it, but there is a pattern that is obvious once you see it. In the column for the Mass of Oxygen, the three values listed have a simple relationship: each one is a multiple of 0.57. We can see this most clearly if we divide each of the masses for ...
... You might have to look at these data very hard to see it, but there is a pattern that is obvious once you see it. In the column for the Mass of Oxygen, the three values listed have a simple relationship: each one is a multiple of 0.57. We can see this most clearly if we divide each of the masses for ...
as PDF - Heriot
... years.1–6 Despite the fact that the main spectroscopic features have been described for a wide range of Cr (III) complexes, the nature of reactive states and photochemical relaxation mechanisms is still not known for many of them. Often with transition metal complexes electronic transitions from the ...
... years.1–6 Despite the fact that the main spectroscopic features have been described for a wide range of Cr (III) complexes, the nature of reactive states and photochemical relaxation mechanisms is still not known for many of them. Often with transition metal complexes electronic transitions from the ...
Answer
... Phosphorus reacts with oxygen gas to form tetraphosphorusdecaoxide. 4 P(s) + 5O2(g)P4O10(s) If 26.8 g of phosphorus are used, what mass of oxygen gas is consumed? ...
... Phosphorus reacts with oxygen gas to form tetraphosphorusdecaoxide. 4 P(s) + 5O2(g)P4O10(s) If 26.8 g of phosphorus are used, what mass of oxygen gas is consumed? ...
Η - Knockhardy
... Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the following reaction, given that the standard enthalpies of formation of water, nitrogen dioxide and nitric acid are -286, +33 and -173 kJ mol-1 respectively. [ the value for oxygen is ZERO as it is an element ] 2H2O(l) applying Hess’s Law ... ...
... Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the following reaction, given that the standard enthalpies of formation of water, nitrogen dioxide and nitric acid are -286, +33 and -173 kJ mol-1 respectively. [ the value for oxygen is ZERO as it is an element ] 2H2O(l) applying Hess’s Law ... ...
Solid-State and High-Resolution Liquid 119Sn NMR Spectroscopy
... Cl, can be rationalized in terms of the variation of the ArSn-X bond angle θ. As θ decreases from 110.13° to 99.68° in Table 2, the hybrid orbital containing the lone pair gains more s character. This gain in s character at tin translates into increased shielding owing to the increased electron dens ...
... Cl, can be rationalized in terms of the variation of the ArSn-X bond angle θ. As θ decreases from 110.13° to 99.68° in Table 2, the hybrid orbital containing the lone pair gains more s character. This gain in s character at tin translates into increased shielding owing to the increased electron dens ...
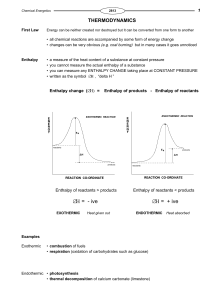
H o - CashmereChemistry
... The chemical potential energy is not lost but is converted into increased kinetic energy of all the particles (both reactants and products) and also transferred to the surroundings. ...
... The chemical potential energy is not lost but is converted into increased kinetic energy of all the particles (both reactants and products) and also transferred to the surroundings. ...
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are ""strong bonds"" such as covalent or ionic bonds and ""weak bonds"" such as Dipole-dipole interaction, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.Since opposite charges attract via a simple electromagnetic force, the negatively charged electrons that are orbiting the nucleus and the positively charged protons in the nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitutes the chemical bond. Due to the matter wave nature of electrons and their smaller mass, they must occupy a much larger amount of volume compared with the nuclei, and this volume occupied by the electrons keeps the atomic nuclei relatively far apart, as compared with the size of the nuclei themselves. This phenomenon limits the distance between nuclei and atoms in a bond.In general, strong chemical bonding is associated with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules, crystals, metals and diatomic gases—indeed most of the physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure and the bulk properties of matter.All bonds can be explained by quantum theory, but, in practice, simplification rules allow chemists to predict the strength, directionality, and polarity of bonds. The octet rule and VSEPR theory are two examples. More sophisticated theories are valence bond theory which includes orbital hybridization and resonance, and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method which includes ligand field theory. Electrostatics are used to describe bond polarities and the effects they have on chemical substances.