Preview Sample 1
... A) there is the loss of one or more electrons from one atom to another atom of the same molecule. B) there is the gain of one or more electrons from one atom to another atom of the same molecule. C) one of the atoms has a greater affinity for electrons than the other atom of the same molecule. D) on ...
... A) there is the loss of one or more electrons from one atom to another atom of the same molecule. B) there is the gain of one or more electrons from one atom to another atom of the same molecule. C) one of the atoms has a greater affinity for electrons than the other atom of the same molecule. D) on ...
Document
... Iterative procedure with initial set of trial orbitals. Equations are solved until energy obtained in 2 successive iterations is identical, within some specified tolerance limit. • Restricted HF: spin-orbitals have same spatial part for spin up and spin down • Unrestricted HF: spin-orbitals can have ...
... Iterative procedure with initial set of trial orbitals. Equations are solved until energy obtained in 2 successive iterations is identical, within some specified tolerance limit. • Restricted HF: spin-orbitals have same spatial part for spin up and spin down • Unrestricted HF: spin-orbitals can have ...
Element Approx.
... of years for Earth to produce but humans are taking minerals out of Earth’s crust at a fast rate ...
... of years for Earth to produce but humans are taking minerals out of Earth’s crust at a fast rate ...
Ordinal Explanation of the Periodic System of Chemical Elements
... to provide a reasonably successful theoretical explanation for the periodic system. This was followed by more accurate versions by himself and Stoner in 1922 and 1924 respectively. The emergence of quantum mechanics in 1925{26 rather interestingly did not provide any improved qualitative explanation ...
... to provide a reasonably successful theoretical explanation for the periodic system. This was followed by more accurate versions by himself and Stoner in 1922 and 1924 respectively. The emergence of quantum mechanics in 1925{26 rather interestingly did not provide any improved qualitative explanation ...
atomic structure sm
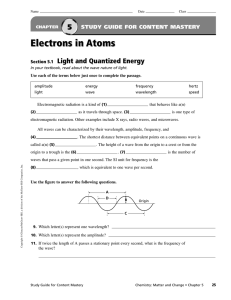
... Recall that Quantization was used to explain the “Ultraviolet Catastrophe” (Planck) Einstein’s work on the “Photoelectric Effect” also contributed to the concept of quantization. When light strikes the surface of certain metals, electrons may be ejected. The light must be of a certain frequency (col ...
... Recall that Quantization was used to explain the “Ultraviolet Catastrophe” (Planck) Einstein’s work on the “Photoelectric Effect” also contributed to the concept of quantization. When light strikes the surface of certain metals, electrons may be ejected. The light must be of a certain frequency (col ...
Few-Body Systems
... 1 Introduction Some simple atomic or molecular systems consisting of a small number of positively and negatively charged particles present unusual properties and are extremely fragile, as compared to species most commonly encountered in Nature. In the case of only two particles, in a very highly-exc ...
... 1 Introduction Some simple atomic or molecular systems consisting of a small number of positively and negatively charged particles present unusual properties and are extremely fragile, as compared to species most commonly encountered in Nature. In the case of only two particles, in a very highly-exc ...
CHM 103 Lecture 11 S07
... Last Time: Polar Molecules • contain polar bonds. • have a separation of positive and negative charge called a dipole indicated with + and -. ...
... Last Time: Polar Molecules • contain polar bonds. • have a separation of positive and negative charge called a dipole indicated with + and -. ...
Language of chemistry
... Among these the first three states are found on earth naturally. The plasma state is present in the stars. Plasma state is similar to gaseous state but in which some of the particles are in an ...
... Among these the first three states are found on earth naturally. The plasma state is present in the stars. Plasma state is similar to gaseous state but in which some of the particles are in an ...
Question 2
... Indicate if you would expect the following compounds to be electrolytes or non-electrolytes when in aqueous solution. In each case very briefly explain your answer. Use equations if appropriate. (6) a) Sodium chloride ...
... Indicate if you would expect the following compounds to be electrolytes or non-electrolytes when in aqueous solution. In each case very briefly explain your answer. Use equations if appropriate. (6) a) Sodium chloride ...
Chemistry Final Exam Study Guide
... ____ 75. Who was the man who lived from 460B.C.–370B.C. and was among the first to suggest the idea of atoms? a. Atomos c. Democritus b. Dalton d. Thomson ____ 76. Dalton's atomic theory included which idea? a. All atoms of all elements are the same size. b. Atoms of different elements always combin ...
... ____ 75. Who was the man who lived from 460B.C.–370B.C. and was among the first to suggest the idea of atoms? a. Atomos c. Democritus b. Dalton d. Thomson ____ 76. Dalton's atomic theory included which idea? a. All atoms of all elements are the same size. b. Atoms of different elements always combin ...
Lecture 03B - Balancing Redox
... -Halogens usually -1, unless combine with more EN element (dichlorine monoxide, ClO-Cl, Cl is +1; F is always -1) Rule 4: The algebraic sum of all O.N.s of all atoms in a neutral compound or polyatomic ion is equal to the net charge. - For neutral compounds, the sum of the O.N.s is 0 - For a charged ...
... -Halogens usually -1, unless combine with more EN element (dichlorine monoxide, ClO-Cl, Cl is +1; F is always -1) Rule 4: The algebraic sum of all O.N.s of all atoms in a neutral compound or polyatomic ion is equal to the net charge. - For neutral compounds, the sum of the O.N.s is 0 - For a charged ...
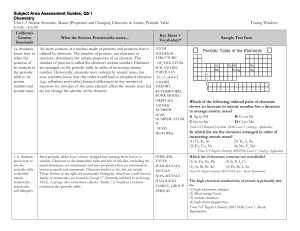
Subject Area Assessment Guides
... atomic orbitals. Atoms (usually nonmetals) of similar electronegativities can form covalent bonds to become molecules. In a covalent bond, therefore, bonding electron pairs are localized in the region between the bonded atoms. In metals valence electrons are not localized to individual atoms but are ...
... atomic orbitals. Atoms (usually nonmetals) of similar electronegativities can form covalent bonds to become molecules. In a covalent bond, therefore, bonding electron pairs are localized in the region between the bonded atoms. In metals valence electrons are not localized to individual atoms but are ...
Introduction to elementary quantum mechanics
... system is invariant under some symmetry operation then the corresponding Hamiltonian is also invariant and there exists an operator representing this symmetry operation, which commutes with the Hamiltonian, [H,S]=0, i.e., the order of the product of both operators acting on any wave function is unim ...
... system is invariant under some symmetry operation then the corresponding Hamiltonian is also invariant and there exists an operator representing this symmetry operation, which commutes with the Hamiltonian, [H,S]=0, i.e., the order of the product of both operators acting on any wave function is unim ...
1 mole
... the number of atoms in 16 g of oxygen, in 4 grams of He, in 32 g of sulfur, etc. the number of molecules in the molecular weight, in grams, of any compound. the number of molecules in 18 g of water, in 40 g of lithium carbide. Much later, a mole, that equal number, was found to be 6.022 x 1023(repre ...
... the number of atoms in 16 g of oxygen, in 4 grams of He, in 32 g of sulfur, etc. the number of molecules in the molecular weight, in grams, of any compound. the number of molecules in 18 g of water, in 40 g of lithium carbide. Much later, a mole, that equal number, was found to be 6.022 x 1023(repre ...
IB Chemistry Online EQ_Ans
... 1 Sodium, magnesium and aluminium are metallic and hence are good electrical conductors due to the presence of delocalized valence electrons. From sodium, magnesium to aluminium, the atomic and ionic size decrease and the number of valence electrons available for delocalization increases from one t ...
... 1 Sodium, magnesium and aluminium are metallic and hence are good electrical conductors due to the presence of delocalized valence electrons. From sodium, magnesium to aluminium, the atomic and ionic size decrease and the number of valence electrons available for delocalization increases from one t ...
Chemistry 201 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... Which of the following pairs of elements will form an ionic compound? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
... Which of the following pairs of elements will form an ionic compound? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... 8.5D recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing substances 8.5F recognize whether a chemical equation containing coefficients is balanced or not and how that relates to the law of conservation of ...
... 8.5D recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing substances 8.5F recognize whether a chemical equation containing coefficients is balanced or not and how that relates to the law of conservation of ...
Review Worksheet
... e) There are no _________ forces between gas molecules or between molecules and the sides of the container with which they collide. In a real gas, there actually is attraction between the molecules of a gas. Once again, this attraction WILL BE IGNORED when discussing ideal gases. f) Molecules collid ...
... e) There are no _________ forces between gas molecules or between molecules and the sides of the container with which they collide. In a real gas, there actually is attraction between the molecules of a gas. Once again, this attraction WILL BE IGNORED when discussing ideal gases. f) Molecules collid ...
Balancing ANY chemical Equation
... • Electrolytes: Substances that form ions when dissolved in solution. Electrolytes can be weak or strong. • Strong Electrolytes: Substances that completely separate into their component ions when dissolved. (All soluble ionic compounds and strong acids are strong electrolytes.) • Weak Electrolytes: ...
... • Electrolytes: Substances that form ions when dissolved in solution. Electrolytes can be weak or strong. • Strong Electrolytes: Substances that completely separate into their component ions when dissolved. (All soluble ionic compounds and strong acids are strong electrolytes.) • Weak Electrolytes: ...
August 2010 Regents Exam part 1
... 9 The percent composition by mass of nitrogen in NH4OH (gram-formula mass = 35 grams/mole) is equal to Nitrogen is 14 g out of 35 g molar mass ...
... 9 The percent composition by mass of nitrogen in NH4OH (gram-formula mass = 35 grams/mole) is equal to Nitrogen is 14 g out of 35 g molar mass ...
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are ""strong bonds"" such as covalent or ionic bonds and ""weak bonds"" such as Dipole-dipole interaction, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.Since opposite charges attract via a simple electromagnetic force, the negatively charged electrons that are orbiting the nucleus and the positively charged protons in the nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitutes the chemical bond. Due to the matter wave nature of electrons and their smaller mass, they must occupy a much larger amount of volume compared with the nuclei, and this volume occupied by the electrons keeps the atomic nuclei relatively far apart, as compared with the size of the nuclei themselves. This phenomenon limits the distance between nuclei and atoms in a bond.In general, strong chemical bonding is associated with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules, crystals, metals and diatomic gases—indeed most of the physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure and the bulk properties of matter.All bonds can be explained by quantum theory, but, in practice, simplification rules allow chemists to predict the strength, directionality, and polarity of bonds. The octet rule and VSEPR theory are two examples. More sophisticated theories are valence bond theory which includes orbital hybridization and resonance, and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method which includes ligand field theory. Electrostatics are used to describe bond polarities and the effects they have on chemical substances.