Heat capacity - Department of Chemistry and Physics
... Common examples of this are: - A mirror shatters when dropped and does not reform - It is easy to scramble an egg and difficult to unscramble it - Food dye when dropped into water disperses ...
... Common examples of this are: - A mirror shatters when dropped and does not reform - It is easy to scramble an egg and difficult to unscramble it - Food dye when dropped into water disperses ...
Honors Chemistry Unit 4 Student Packet: Honors Chemistry Problem
... When electricity is applied to liquid water, it decomposes into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. Mercury(II) oxide is heated to produce solid mercury and gaseous oxygen. Aqueous potassium iodide and aqueous lead(II) nitrate react to produce solid lead(II) iodide and a solution of potassium nitrate. Soli ...
... When electricity is applied to liquid water, it decomposes into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. Mercury(II) oxide is heated to produce solid mercury and gaseous oxygen. Aqueous potassium iodide and aqueous lead(II) nitrate react to produce solid lead(II) iodide and a solution of potassium nitrate. Soli ...
thermdyn - chemmybear.com
... (a) What is the value of the equilibrium constant for For the reaction above, H, G, and S are all negative. Which of the substances would predominate in the system represented above? an equilibrium mixture of copper, sulfur, and copper(I) (b) Calculate S at 25C for the reaction indicated by ...
... (a) What is the value of the equilibrium constant for For the reaction above, H, G, and S are all negative. Which of the substances would predominate in the system represented above? an equilibrium mixture of copper, sulfur, and copper(I) (b) Calculate S at 25C for the reaction indicated by ...
Combined
... The average rate of decrease in mass of sodium carbonate was 15.9 g min1 The average rate of decrease in concentration of the acid was 0.0125 mol dm3 s1 The average rate of increase in volume of carbon dioxide was 60 cm3 s1 Sodium carbonate and sulphuric acid just reacted completely. To be conti ...
... The average rate of decrease in mass of sodium carbonate was 15.9 g min1 The average rate of decrease in concentration of the acid was 0.0125 mol dm3 s1 The average rate of increase in volume of carbon dioxide was 60 cm3 s1 Sodium carbonate and sulphuric acid just reacted completely. To be conti ...
_______1. solution a. capable of being dissolved _______2. solute
... 117. Catalysts ________________ the rate of a reaction without being _________________. This means that catalysts are neither a __________________ nor a __________________. 118. List three ways to increase the rate at which a reactions proceeds: _________________________________________________ ____ ...
... 117. Catalysts ________________ the rate of a reaction without being _________________. This means that catalysts are neither a __________________ nor a __________________. 118. List three ways to increase the rate at which a reactions proceeds: _________________________________________________ ____ ...
Principles of Chemical Thermodynamics and Kinetics
... The induced fit model is used to explain the mechanism of action for enzyme function seen in Figure 10-2. Once a substrate binds loosely to the active site of an enzyme, a conformational change in shape occurs to cause tight binding between the enzyme and the substrate. This tight binding allows the ...
... The induced fit model is used to explain the mechanism of action for enzyme function seen in Figure 10-2. Once a substrate binds loosely to the active site of an enzyme, a conformational change in shape occurs to cause tight binding between the enzyme and the substrate. This tight binding allows the ...
Chapter 3: Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... heat of formation, molar heat of combustion, entropy, free energy, reaction rate, chemical kinetics, rate law, calorimeter, thermochemistry, reaction mechanism, intermediates, collision theory, activation energy, activated complex, catalyst,, ratedetermining step Essential Questions and Content: D ...
... heat of formation, molar heat of combustion, entropy, free energy, reaction rate, chemical kinetics, rate law, calorimeter, thermochemistry, reaction mechanism, intermediates, collision theory, activation energy, activated complex, catalyst,, ratedetermining step Essential Questions and Content: D ...
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry
... Thermochemistry: study of heat flow Thermodynamics: deals with all kinds of energy effects in all kinds of process; deals with heat and work (w) Work includes all forms of energy except heat. Remember energy (E) can either be neither created nor destroyed. E system = - ΔE surroundings 1st Law of The ...
... Thermochemistry: study of heat flow Thermodynamics: deals with all kinds of energy effects in all kinds of process; deals with heat and work (w) Work includes all forms of energy except heat. Remember energy (E) can either be neither created nor destroyed. E system = - ΔE surroundings 1st Law of The ...
Unit 2:
... At 25ºC the solubility product constant, Ksp, for strontium sulfate, SrSO4, is 7.610-7. The solubility product constant for strontium fluoride, SrF2, is 7.910-10. (a) What is the molar solubility of SrSO4 in pure water at 25ºC? (b) What is the molar solubility of SrF2 in pure water at 25ºC? (c) An ...
... At 25ºC the solubility product constant, Ksp, for strontium sulfate, SrSO4, is 7.610-7. The solubility product constant for strontium fluoride, SrF2, is 7.910-10. (a) What is the molar solubility of SrSO4 in pure water at 25ºC? (b) What is the molar solubility of SrF2 in pure water at 25ºC? (c) An ...
Program Review - Austin Community College
... Assistant Program. In this program, students interested in science education can work as peer teachers for students at ACC. More full-time professors are needed. We would also like to have more technical lab support. Lab safety and ease of operation would be greatly improved with a larger technical ...
... Assistant Program. In this program, students interested in science education can work as peer teachers for students at ACC. More full-time professors are needed. We would also like to have more technical lab support. Lab safety and ease of operation would be greatly improved with a larger technical ...
Bioorganic chemistry-a scientific endeavour in continuous
... combinatory procedures; the polymerase chain reaction (PCR); all of the latest separation and spectroscopic methodology with computer analysis; and the generous use -as reagents -- of bacteria, fungi, enzymes, whole cells, and ground liver microsomes, inter alia. A graduate course in bioorganic chem ...
... combinatory procedures; the polymerase chain reaction (PCR); all of the latest separation and spectroscopic methodology with computer analysis; and the generous use -as reagents -- of bacteria, fungi, enzymes, whole cells, and ground liver microsomes, inter alia. A graduate course in bioorganic chem ...
1. Explain electrophile and nucleophile. 2. Explain
... 68 Why alkyl groups act as donors when attached to a π System? 69. Draw the resonance structures for the following compounds. Show the electron shift using curved arrow rotation. (i) C6H5OH (2) C6H5NO2 (3) C6H5C+H2 (4) CH3CH=CHCHO (5) CH3CH=CHC+H2 (6)C6H5CHO (7) CH2=CHOCH3. 70. Write chemical equat ...
... 68 Why alkyl groups act as donors when attached to a π System? 69. Draw the resonance structures for the following compounds. Show the electron shift using curved arrow rotation. (i) C6H5OH (2) C6H5NO2 (3) C6H5C+H2 (4) CH3CH=CHCHO (5) CH3CH=CHC+H2 (6)C6H5CHO (7) CH2=CHOCH3. 70. Write chemical equat ...
Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions
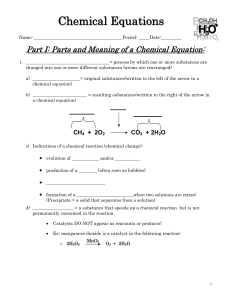
... 1. Write the correct formula(s) for the reactants on the left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. Ethane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water ...
... 1. Write the correct formula(s) for the reactants on the left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. Ethane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water ...
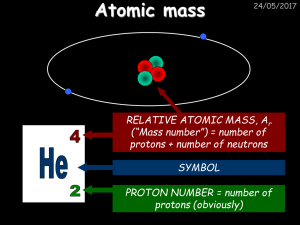
Atomic mass - drseemaljelani
... nothing can escape), equilibrium is reached when both reactions occur at exactly the same rate in each direction. The relative amounts of all the reacting substances at equilibrium depend on the conditions of the reaction. ...
... nothing can escape), equilibrium is reached when both reactions occur at exactly the same rate in each direction. The relative amounts of all the reacting substances at equilibrium depend on the conditions of the reaction. ...
Chemistry - Onslow College
... Writing word equations and balanced chemical equations for inorganic reactions By the end of this topic students will be able to 1. use solubility rules to predict precipitation and identify the precipitate. 2. carry out precipitation reactions and report experimental observations 3. from experime ...
... Writing word equations and balanced chemical equations for inorganic reactions By the end of this topic students will be able to 1. use solubility rules to predict precipitation and identify the precipitate. 2. carry out precipitation reactions and report experimental observations 3. from experime ...
Question paper - Unit A173/02 - Module C7 - Higher tier
... Scientists are investigating a new catalyst. The new catalyst is an enzyme. Here is some information about both catalysts. ...
... Scientists are investigating a new catalyst. The new catalyst is an enzyme. Here is some information about both catalysts. ...
2005 - NESACS
... 16. The first ionization potential of Cs is 3.894 electron volts. The minimum wavelength of electromagnetic radiation in nanometers required to ionize gaseous Cs is: 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J, c = 3.00 x 108 m/s, h = 6.62 x 10-34 J/s (A) (B) (C) (D) ...
... 16. The first ionization potential of Cs is 3.894 electron volts. The minimum wavelength of electromagnetic radiation in nanometers required to ionize gaseous Cs is: 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J, c = 3.00 x 108 m/s, h = 6.62 x 10-34 J/s (A) (B) (C) (D) ...
Chem 1A Practice Final
... b) FePO4 iron(III) phosphate c) HF hydrogen fluoride d) N2O nitrogen dioxide e) Mg3N2 magnesium nitride 2. A metal oxide contains 83.0% metal by mass. Determine the identity of the metal. a) Na b) Ca c) K d) Rb e) Sr 3. How many atoms of nitrogen are present in 3.52 g of calcium nitrate? a) 1.29 × 1 ...
... b) FePO4 iron(III) phosphate c) HF hydrogen fluoride d) N2O nitrogen dioxide e) Mg3N2 magnesium nitride 2. A metal oxide contains 83.0% metal by mass. Determine the identity of the metal. a) Na b) Ca c) K d) Rb e) Sr 3. How many atoms of nitrogen are present in 3.52 g of calcium nitrate? a) 1.29 × 1 ...