AQA Additional Sci C2 Revision Guide
... C2 Topic 2: Nanoscience Nanoscience is becoming increasingly important in today’s world. It involves the use and control of structures called nanoparticles that are very small (1 - 100 nanometres in size). A nanometre (nm) is one billionth of a metre (0.000 000 001m). Nanoparticles can occur natural ...
... C2 Topic 2: Nanoscience Nanoscience is becoming increasingly important in today’s world. It involves the use and control of structures called nanoparticles that are very small (1 - 100 nanometres in size). A nanometre (nm) is one billionth of a metre (0.000 000 001m). Nanoparticles can occur natural ...
Support material for lesson planning – AS content
... (g) the shapes of, and bond angles in, molecules and ions with up to six electron pairs (including lone pairs) surrounding the central atom as predicted by electron pair repulsion, including the relative repulsive strengths of bonded pairs and lone pairs of electrons (h) electron pair repulsion to e ...
... (g) the shapes of, and bond angles in, molecules and ions with up to six electron pairs (including lone pairs) surrounding the central atom as predicted by electron pair repulsion, including the relative repulsive strengths of bonded pairs and lone pairs of electrons (h) electron pair repulsion to e ...
Complete the following equations
... (a) Does the formation of ammonia favor high temperature or low temperature? Explain. (b) Does the formation of ammonia favor high pressure of low pressure? Explain. (c) Industrial production of ammonia is normally carried out at temperature 250 – 300oC and pressure 150 – 200 atm. Discuss the advant ...
... (a) Does the formation of ammonia favor high temperature or low temperature? Explain. (b) Does the formation of ammonia favor high pressure of low pressure? Explain. (c) Industrial production of ammonia is normally carried out at temperature 250 – 300oC and pressure 150 – 200 atm. Discuss the advant ...
Midterm Practice Exam Key
... Aqueous Reactions (5 marks) 1. A substance is considered ____________ if it will dissolve in a specific solvent. 2. An ____________ in the oxidation number of an atom signifies oxidation, while a ____________ in the oxidation number signifies reduction. 3. A ____________ reaction is one in which ...
... Aqueous Reactions (5 marks) 1. A substance is considered ____________ if it will dissolve in a specific solvent. 2. An ____________ in the oxidation number of an atom signifies oxidation, while a ____________ in the oxidation number signifies reduction. 3. A ____________ reaction is one in which ...
Final Exam Review 2010 UbD
... 76. Define “limiting reactants” _______________________________________________________________ How do you determine the limiting reactant for a chemical reaction? ____________________________ 77. Define “ percent yield” ___________________________________________________________________ What is the ...
... 76. Define “limiting reactants” _______________________________________________________________ How do you determine the limiting reactant for a chemical reaction? ____________________________ 77. Define “ percent yield” ___________________________________________________________________ What is the ...
Chemistry
... Chemistry is about the study of matter, its interactions and transformations. At a macroscopic level, we observe matter and its interactions everywhere in our daily life. The submicroscopic level looks at the structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O-Level, students have been i ...
... Chemistry is about the study of matter, its interactions and transformations. At a macroscopic level, we observe matter and its interactions everywhere in our daily life. The submicroscopic level looks at the structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O-Level, students have been i ...
CFE Higher Chemistry in Society Homework EB
... A piece of lithium with a mass of 1.50 g is placed in an aqueous solution containing 6.00 g of copper (II) sulphate. The reaction that occurs is: 2Li(s) + CuSO4(aq) Cu + Li2SO4 (aq) (a) Determine which reactant is in excess. (b) Calculate how many grams of copper will be formed. ...
... A piece of lithium with a mass of 1.50 g is placed in an aqueous solution containing 6.00 g of copper (II) sulphate. The reaction that occurs is: 2Li(s) + CuSO4(aq) Cu + Li2SO4 (aq) (a) Determine which reactant is in excess. (b) Calculate how many grams of copper will be formed. ...
KEY
... was originally. correct 2. there is less ammonia present than there was originally. 3. there is the same amount of ammonia present as there was originally. 4. the nitrogen is used up completely. Explanation: LeChatelier’s Principle states that if a change occurs in a system at equilibruim, the syste ...
... was originally. correct 2. there is less ammonia present than there was originally. 3. there is the same amount of ammonia present as there was originally. 4. the nitrogen is used up completely. Explanation: LeChatelier’s Principle states that if a change occurs in a system at equilibruim, the syste ...
Document
... • we can simplify the equation for the formation of AgCl by omitting all ions that do not participate in the reaction Net ionic equation: ...
... • we can simplify the equation for the formation of AgCl by omitting all ions that do not participate in the reaction Net ionic equation: ...
Matter and Measurement
... In order to compare the enthalpies of different reactions, it is necessary to define a set of conditions called the standard state. The standard state of a substance is its pure form at atmospheric pressure of 1 atm and the temperature of interest (usually 298 K). The most stable form of an element ...
... In order to compare the enthalpies of different reactions, it is necessary to define a set of conditions called the standard state. The standard state of a substance is its pure form at atmospheric pressure of 1 atm and the temperature of interest (usually 298 K). The most stable form of an element ...
Sec 5.8 - 5.11 notes
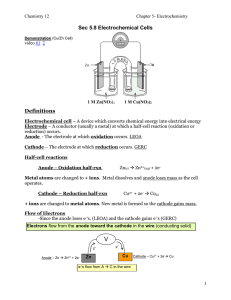
... 9) Electrons do not travel through the ______ _______, only through the _______. 10) Ions (cations & anions) do not travel through the wire but only through the _____________. 11) The salt bridge can contain any ______________. 12) The anode will ________(gains/loses) mass as it is __________(oxidiz ...
... 9) Electrons do not travel through the ______ _______, only through the _______. 10) Ions (cations & anions) do not travel through the wire but only through the _____________. 11) The salt bridge can contain any ______________. 12) The anode will ________(gains/loses) mass as it is __________(oxidiz ...
Chapter 4
... Similarly, when a sulfite reacts with an acid, the products are a salt, sulfur dioxide, and water. ...
... Similarly, when a sulfite reacts with an acid, the products are a salt, sulfur dioxide, and water. ...
Chemistry II Exams and Answer Keys 2015 Season
... 5. Concentrated hydrochloric acid is 36.5 % (w/w) and has a density of 1.20 g/mL. What is the molar concentration of this solution? A. 36.5 M B. 12.0 M C. 1.20 M D. 3.65 M ...
... 5. Concentrated hydrochloric acid is 36.5 % (w/w) and has a density of 1.20 g/mL. What is the molar concentration of this solution? A. 36.5 M B. 12.0 M C. 1.20 M D. 3.65 M ...
File
... AP Thermodynamics Packet Unit 9 Thermodynamics Review Students should be able to demonstrate an understanding of the following essential knowledge: 3.C.2 Net changes in energy for a chemical reaction can be endothermic or exothermic. 5.A.1 Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy ...
... AP Thermodynamics Packet Unit 9 Thermodynamics Review Students should be able to demonstrate an understanding of the following essential knowledge: 3.C.2 Net changes in energy for a chemical reaction can be endothermic or exothermic. 5.A.1 Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy ...
name chemistry final review
... a. 200.0 g C3H6 and 200.0 g of O2 2 C3H6 + 9 O2 → 6 H2O + 6 CO2 O2 is the LR, C3H6 is in excess. There is 141.5g of C3H6 left over and 75.08g H2O and 183.4g CO2 produced. b. 45.9 g CuSO4 and 67.3 g of Fe(C2H3O2)3 3 CuSO4 + 2 Fe(C2H3O2)3 → 3 Cu(C2H3O2)2 + Fe2(SO4)3 CuSO4 is the LR, Fe(C2H3O2)3 is in ...
... a. 200.0 g C3H6 and 200.0 g of O2 2 C3H6 + 9 O2 → 6 H2O + 6 CO2 O2 is the LR, C3H6 is in excess. There is 141.5g of C3H6 left over and 75.08g H2O and 183.4g CO2 produced. b. 45.9 g CuSO4 and 67.3 g of Fe(C2H3O2)3 3 CuSO4 + 2 Fe(C2H3O2)3 → 3 Cu(C2H3O2)2 + Fe2(SO4)3 CuSO4 is the LR, Fe(C2H3O2)3 is in ...
Chapter 4 Solution Chemistry
... • Much of the chemistry (both biological and nonbiological) that takes place on Earth involves water in some fashion: – Almost 75% of the Earth’s surface is covered by water or ice. – About 66% of the human body consists of water. – A lot of important chemistry takes place in aqueous solution, in wh ...
... • Much of the chemistry (both biological and nonbiological) that takes place on Earth involves water in some fashion: – Almost 75% of the Earth’s surface is covered by water or ice. – About 66% of the human body consists of water. – A lot of important chemistry takes place in aqueous solution, in wh ...
The Oxidation States of Tin
... tends to form bonds with two ligands. There is however, one more configuration that can be obtained under special conditions. If the tin were to absorb some energy from its surroundings, it would have enough force to promote one of the s electrons to the p energy level, thus half filling it. This ar ...
... tends to form bonds with two ligands. There is however, one more configuration that can be obtained under special conditions. If the tin were to absorb some energy from its surroundings, it would have enough force to promote one of the s electrons to the p energy level, thus half filling it. This ar ...
Combustion
... A combustion reaction always involves oxygen as one of the reactants. Often the other reactant in a combustion reaction is a hydrocarbon. Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that are made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms (General formula of a hydrocarbon: CxHy). The combustion of hydrocarbons can be ...
... A combustion reaction always involves oxygen as one of the reactants. Often the other reactant in a combustion reaction is a hydrocarbon. Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that are made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms (General formula of a hydrocarbon: CxHy). The combustion of hydrocarbons can be ...
Chapter 9 – Reaction Energetics
... determining how much energy must be supplied to break all of the interactions that had to be broken and subtracting the energy that is released when all of the new interactions form. Bond energies give us estimates of these energies, but tabulated bond energies are averages. For example, a C-Cl bond ...
... determining how much energy must be supplied to break all of the interactions that had to be broken and subtracting the energy that is released when all of the new interactions form. Bond energies give us estimates of these energies, but tabulated bond energies are averages. For example, a C-Cl bond ...