OXIDATION NUMBERS
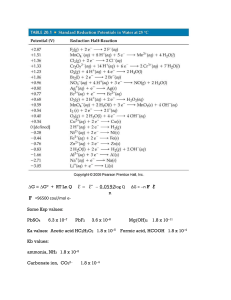
... so that eventually an equilibrium is established; the rate of formation of the ions is equal to the rate of deposition: Zn2+(aq) + 2eZn(s) The formation of the electric double layer causes a potential difference between the surface of the metal and the liquid; this is called the electrode potential. ...
... so that eventually an equilibrium is established; the rate of formation of the ions is equal to the rate of deposition: Zn2+(aq) + 2eZn(s) The formation of the electric double layer causes a potential difference between the surface of the metal and the liquid; this is called the electrode potential. ...
SrF 2(s)
... composition and decomposition do NOT happen in solutions so ionic compounds are (s) Example: 1. potassium iodide solution is added to lead(II) nitrate solution ...
... composition and decomposition do NOT happen in solutions so ionic compounds are (s) Example: 1. potassium iodide solution is added to lead(II) nitrate solution ...
Redox Introduction
... led chemists to formulate a more generalized definition of reduction. By definition, reduction is the process by which electrons are apparently added to atoms or ions. ...
... led chemists to formulate a more generalized definition of reduction. By definition, reduction is the process by which electrons are apparently added to atoms or ions. ...
Energy
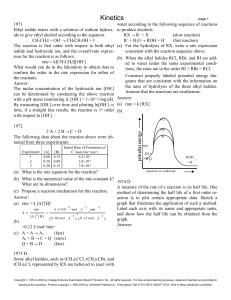
... Units of Energy All forms of energy can be expressed in the same units. To find the MKS unit for energy, it is convenient to use the equation for kinetic energy. EK = 1/2mv2 So units are (kg) (m/s)2 = kg.m2 = 1 Joule = 1 J s2 Since 1 J is a small amount of energy, we often express energy in terms o ...
... Units of Energy All forms of energy can be expressed in the same units. To find the MKS unit for energy, it is convenient to use the equation for kinetic energy. EK = 1/2mv2 So units are (kg) (m/s)2 = kg.m2 = 1 Joule = 1 J s2 Since 1 J is a small amount of energy, we often express energy in terms o ...
Document
... substituted compounds carry great importance in pharmaceutical chemistry, material science and healthcare ...
... substituted compounds carry great importance in pharmaceutical chemistry, material science and healthcare ...
Physical Chemistry Problems. ©Mike Lyons 2009
... Answer either : part (a) and part (b) or part (c) and part (d). a. What is the internal energy U and the enthalpy H of a system? Write down an expression for the First Law of Thermodynamics which relates the change in internal energy of a system to the work done on the system and the heat absorbed b ...
... Answer either : part (a) and part (b) or part (c) and part (d). a. What is the internal energy U and the enthalpy H of a system? Write down an expression for the First Law of Thermodynamics which relates the change in internal energy of a system to the work done on the system and the heat absorbed b ...
3.0 Properties of Phosgene
... temperatures above 250oC (482oF), phosgene decomposes to form mixtures of carbon monoxide (CO), chlorine (CI2) carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbon tetrachloride (CCI4). Phosgene reacts slowly with water to form carbon dioxide and hydrochloric acid. Phosgene reacts readily with caustic solution and even ...
... temperatures above 250oC (482oF), phosgene decomposes to form mixtures of carbon monoxide (CO), chlorine (CI2) carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbon tetrachloride (CCI4). Phosgene reacts slowly with water to form carbon dioxide and hydrochloric acid. Phosgene reacts readily with caustic solution and even ...
AP Chemistry
... a. when energy required to break bonds > energy released to form new bonds, +H (endothermic) 1. products at a higher energy state than reactants (weaker bonds) 2. surroundings lose energy (cool down) b. when energy required to break bonds < energy released to form new bonds, –H (exothermic) 1. pro ...
... a. when energy required to break bonds > energy released to form new bonds, +H (endothermic) 1. products at a higher energy state than reactants (weaker bonds) 2. surroundings lose energy (cool down) b. when energy required to break bonds < energy released to form new bonds, –H (exothermic) 1. pro ...
9791/02 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL
... Carbon readily forms multiple bonds with itself, while silicon does not form these bonds so easily. The first compound containing a Si=Si double bond was synthesised in 1972. One such compound contains the following percentages by mass. C 41.3% ...
... Carbon readily forms multiple bonds with itself, while silicon does not form these bonds so easily. The first compound containing a Si=Si double bond was synthesised in 1972. One such compound contains the following percentages by mass. C 41.3% ...
高雄醫學大學九十二學年度學士後醫學系招生考試試題 科目:化學 考試
... 65. Body temperature is about 308 K. On a cold day, what volume of air at 273 K must a person with a lung capacity of 2.00 L breathe in to fill up the lungs? (A) 1.13 L (B) 1.77 L (C) 2.26 L (D) 3.08 L (E) 3.54 L 66. Calculate the temperature at which the average kinetic energy of O2 gas is twice th ...
... 65. Body temperature is about 308 K. On a cold day, what volume of air at 273 K must a person with a lung capacity of 2.00 L breathe in to fill up the lungs? (A) 1.13 L (B) 1.77 L (C) 2.26 L (D) 3.08 L (E) 3.54 L 66. Calculate the temperature at which the average kinetic energy of O2 gas is twice th ...
17.2.3 Interhalogen compounds(65-67)
... or Br, substitution is mainly or exclusively pura, whereas with deactivating substituents (X = -C02Et, -CHO, -N02) exclusively metubromination occurs.(72) A similar interpretation explains why IBr almost invariably brominates rather than iodinates aromatic compounds due to its appreciable dissociati ...
... or Br, substitution is mainly or exclusively pura, whereas with deactivating substituents (X = -C02Et, -CHO, -N02) exclusively metubromination occurs.(72) A similar interpretation explains why IBr almost invariably brominates rather than iodinates aromatic compounds due to its appreciable dissociati ...
AP 2005 Chemistry Free-Response Questions
... 2005 AP® CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS Your responses to the rest of the questions in this part of the examination will be graded on the basis of the accuracy and relevance of the information cited. Explanations should be clear and well organized. Examples and equations may be included in your ...
... 2005 AP® CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS Your responses to the rest of the questions in this part of the examination will be graded on the basis of the accuracy and relevance of the information cited. Explanations should be clear and well organized. Examples and equations may be included in your ...
Chemistry Standardized Test Practice: Student Edition
... Chapter 3: Matter—Properties and Changes .......................................5 Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom .................................................7 Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms .............................................................9 Chapter 6: The Periodic Table and Per ...
... Chapter 3: Matter—Properties and Changes .......................................5 Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom .................................................7 Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms .............................................................9 Chapter 6: The Periodic Table and Per ...
7.1 Describing Reactions
... Describing Ionic Compounds 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. Answer: H2 + Cl2 2HCl ...
... Describing Ionic Compounds 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. Answer: H2 + Cl2 2HCl ...
Slide 1
... Describing Ionic Compounds 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. Answer: H2 + Cl2 2HCl ...
... Describing Ionic Compounds 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. Answer: H2 + Cl2 2HCl ...
7.1 Describing Reactions
... Describing Ionic Compounds 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. Answer: H2 + Cl2 2HCl ...
... Describing Ionic Compounds 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. Answer: H2 + Cl2 2HCl ...