Here
... (d) van der Waals equation is a relation between the pressure, temperature and volume of a gas that accounts for the non‐zero size of the gas molecules and the attractive forces between them. (e) Gibbs free energy, G = H − TS, combines enthalpy and entropy to give a quantity which must decreas ...
... (d) van der Waals equation is a relation between the pressure, temperature and volume of a gas that accounts for the non‐zero size of the gas molecules and the attractive forces between them. (e) Gibbs free energy, G = H − TS, combines enthalpy and entropy to give a quantity which must decreas ...
幻灯片 1
... opposed by electrostatic repulsion between protons. Electrostatic repulsion force: among the protons. Repulsion dominates as Z increases and there is only a limited number of stable elements. ...
... opposed by electrostatic repulsion between protons. Electrostatic repulsion force: among the protons. Repulsion dominates as Z increases and there is only a limited number of stable elements. ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... Element “X” is composed of the following naturally occurring isotopes: Isotope ...
... Element “X” is composed of the following naturally occurring isotopes: Isotope ...
Chemistry
... Chemistry is about the study of matter, its interactions and transformations. At a macroscopic level, we observe matter and its interactions everywhere in our daily life. The submicroscopic level looks at the structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O-Level, students have been i ...
... Chemistry is about the study of matter, its interactions and transformations. At a macroscopic level, we observe matter and its interactions everywhere in our daily life. The submicroscopic level looks at the structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O-Level, students have been i ...
Order date : 24-07-2010
... 4. S. Glasston, Source Book on Atomic Energy, 3rd Edn., East- West Press Pvt. Ltd., 1967. 5. Friedlander, J. W. Kennedy, Introduction to Radiochemistry, John Wiley and Sons, 1981. 6. Friedlander, J. W. Kennedy, J. M. Miller, Nuclear and Radiochemistry, 3rd Edn., John Wiley and Sons, 1981. MODULE V ( ...
... 4. S. Glasston, Source Book on Atomic Energy, 3rd Edn., East- West Press Pvt. Ltd., 1967. 5. Friedlander, J. W. Kennedy, Introduction to Radiochemistry, John Wiley and Sons, 1981. 6. Friedlander, J. W. Kennedy, J. M. Miller, Nuclear and Radiochemistry, 3rd Edn., John Wiley and Sons, 1981. MODULE V ( ...
The science of chemistry is concerned with the composition
... extremely toxic if breathed into the lungs. It has been responsible for many cases of human poisoning. In other respects mercury vapor behaves much like any gas. It is easily compressible. Even when quite modest pressures are applied, the volume decreases noticeably. It is also much less dense than ...
... extremely toxic if breathed into the lungs. It has been responsible for many cases of human poisoning. In other respects mercury vapor behaves much like any gas. It is easily compressible. Even when quite modest pressures are applied, the volume decreases noticeably. It is also much less dense than ...
The science of chemistry is concerned with the
... extremely toxic if breathed into the lungs. It has been responsible for many cases of human poisoning. In other respects mercury vapor behaves much like any gas. It is easily compressible. Even when quite modest pressures are applied, the volume decreases noticeably. It is also much less dense than ...
... extremely toxic if breathed into the lungs. It has been responsible for many cases of human poisoning. In other respects mercury vapor behaves much like any gas. It is easily compressible. Even when quite modest pressures are applied, the volume decreases noticeably. It is also much less dense than ...
Chem101 - Lecture 2 Elements Elements
... characteristic number of isotopes and relative abundance of each. • For example ...
... characteristic number of isotopes and relative abundance of each. • For example ...
Word - icho39.chem.msu.ru
... Of course, these results obtained by extrapolation are approximate. Moreover, bulk properties such as melting and boiling points can be measured only for significant amounts of an element, whereas only three atoms of the 118-th element were obtained and they decayed during milliseconds. For this rea ...
... Of course, these results obtained by extrapolation are approximate. Moreover, bulk properties such as melting and boiling points can be measured only for significant amounts of an element, whereas only three atoms of the 118-th element were obtained and they decayed during milliseconds. For this rea ...
Scientific Jury of the 30th International
... your students need to show in Melbourne. We have tried to highlight the procedures in each exercise that need some particular caution, even for students of Olympiad level but our warnings cannot be comprehensive - your students will still need your careful supervision. We have also not included spec ...
... your students need to show in Melbourne. We have tried to highlight the procedures in each exercise that need some particular caution, even for students of Olympiad level but our warnings cannot be comprehensive - your students will still need your careful supervision. We have also not included spec ...
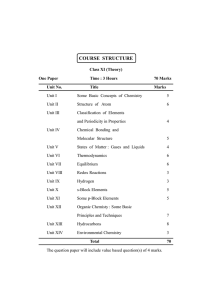
COURSE STRUCTURE
... as well as by the photoelectric effect. Heisenberg’s uncertainty Principle states that ‘‘It is impossible to measure simultaneously the position and momentum of a microscopic particle with absolute accuracy. If one of them is measured with greater accuracy, the other becomes less accurate. The produ ...
... as well as by the photoelectric effect. Heisenberg’s uncertainty Principle states that ‘‘It is impossible to measure simultaneously the position and momentum of a microscopic particle with absolute accuracy. If one of them is measured with greater accuracy, the other becomes less accurate. The produ ...
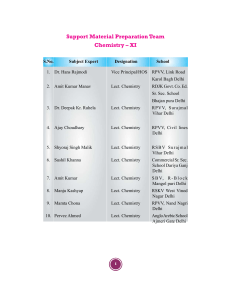
Support Material
... Law of Multiple Proportions (John Dalton) : When two elements combine to form two or more compounds, then the different masses of one element, which combine with a ®xed mass of the other, bear a simple ratio to one another. Gay Lussac’s Law : When gases combine or are produced in a chemical reac ...
... Law of Multiple Proportions (John Dalton) : When two elements combine to form two or more compounds, then the different masses of one element, which combine with a ®xed mass of the other, bear a simple ratio to one another. Gay Lussac’s Law : When gases combine or are produced in a chemical reac ...
chemistry writing team
... The wave nature of electron has been confirmed by Davisson and Germer’s experiment whereas the particle nature is confirmed by scintillation method as well as by the photoelectric effect. Heisenberg’s uncertainty Principle states that ‘‘It is impossible to measure simultaneously the position and mom ...
... The wave nature of electron has been confirmed by Davisson and Germer’s experiment whereas the particle nature is confirmed by scintillation method as well as by the photoelectric effect. Heisenberg’s uncertainty Principle states that ‘‘It is impossible to measure simultaneously the position and mom ...
Holt Modern Chemistry Workbook
... Br atom. a. What type of bond is expected between K and Br? b. Which ion in the compound KBr is larger? ...
... Br atom. a. What type of bond is expected between K and Br? b. Which ion in the compound KBr is larger? ...
Some basic concepts of chemistry
... Discovery of isotopes indicated that all atoms of the same elements are not perfectly identical. They may differ in their masses. Atoms of different elements may posses the same mass (isobar) but they always have different atomic numbers and differ in chemical properties. It could not explain why ce ...
... Discovery of isotopes indicated that all atoms of the same elements are not perfectly identical. They may differ in their masses. Atoms of different elements may posses the same mass (isobar) but they always have different atomic numbers and differ in chemical properties. It could not explain why ce ...
BalanceEquationsetc
... • A mole is defined as the number of atoms in exactly 12 grams of carbon- 12 • The number is called Avogadro’s Number • One mole of carbon atoms has a mass of 12 grams ...
... • A mole is defined as the number of atoms in exactly 12 grams of carbon- 12 • The number is called Avogadro’s Number • One mole of carbon atoms has a mass of 12 grams ...
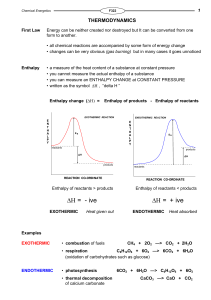
Enthalpy change
... change will depend on the difference between the energy required to break the bonds and that released as bonds are made. energy released making bonds > energy used to break bonds ... EXOTHERMIC energy used to break bonds > energy released making bonds ... ENDOTHERMIC ...
... change will depend on the difference between the energy required to break the bonds and that released as bonds are made. energy released making bonds > energy used to break bonds ... EXOTHERMIC energy used to break bonds > energy released making bonds ... ENDOTHERMIC ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical
... • Most often involve hydrocarbons reacting with oxygen in the air ...
... • Most often involve hydrocarbons reacting with oxygen in the air ...
231. - Department of Chemistry
... cyclopentadienyl ligand has a dramatic effect on the reactivity of Fe⫹. For example, we have shown that the rate of ligation with N2 [14], N2O [15], CO [15], and NH3 [16] is enhanced by a factor of ⬎103, ⬃10, ⬎104, and ⬃102, respectively, in helium bath gas at 0.35 Torr. We have also investigated th ...
... cyclopentadienyl ligand has a dramatic effect on the reactivity of Fe⫹. For example, we have shown that the rate of ligation with N2 [14], N2O [15], CO [15], and NH3 [16] is enhanced by a factor of ⬎103, ⬃10, ⬎104, and ⬃102, respectively, in helium bath gas at 0.35 Torr. We have also investigated th ...
Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
... substances can result in physical and/or chemical changes. Standard: 3.2.C.A4 – Interpret and apply the Laws of Conservation of Mass, Constant Composition (Definite Proportions), and Multiple Proportions. Anchor: CHEM.B.1.2 – Apply the mole concept to the composition of matter Eligible Content CHEM. ...
... substances can result in physical and/or chemical changes. Standard: 3.2.C.A4 – Interpret and apply the Laws of Conservation of Mass, Constant Composition (Definite Proportions), and Multiple Proportions. Anchor: CHEM.B.1.2 – Apply the mole concept to the composition of matter Eligible Content CHEM. ...
File
... 8 Positive ions are formed when the vaporised atom or molecule is bombarded with fast-moving electrons. The kinetic energy of these electrons is great enough to cause the removal of an electron from the outermost orbital of the atom or of one of the bonding electrons in the molecule. e ...
... 8 Positive ions are formed when the vaporised atom or molecule is bombarded with fast-moving electrons. The kinetic energy of these electrons is great enough to cause the removal of an electron from the outermost orbital of the atom or of one of the bonding electrons in the molecule. e ...
Appendices and Glossary
... element’s atomic weight. It represents the “average atomic weight” or “average atomic mass” of the element because it is determined from the masses and abundance of the different isotopes of the element. Although there is a technical difference between weight and mass (weight depends on the gravitat ...
... element’s atomic weight. It represents the “average atomic weight” or “average atomic mass” of the element because it is determined from the masses and abundance of the different isotopes of the element. Although there is a technical difference between weight and mass (weight depends on the gravitat ...
Chapter 3 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations q
... - hold atoms together to form compounds - are forces of attraction between atoms. - the bonding g attraction comes from attractions between protons and electrons. i.) Ionic bonds - result when electrons have been transferred between atoms, resulting in oppositely charged ions that attract each other ...
... - hold atoms together to form compounds - are forces of attraction between atoms. - the bonding g attraction comes from attractions between protons and electrons. i.) Ionic bonds - result when electrons have been transferred between atoms, resulting in oppositely charged ions that attract each other ...
Electron attachment to molecular clusters by collisional charge transfer
... A) were observed, but extensive signal averaging was required to detect any other positive ion species (for which typical signals are E A). Thus,here we present only observations of negative ions. As seen in Figure 2, the chlorine cluster system yields negative ions corresponding to electron attachm ...
... A) were observed, but extensive signal averaging was required to detect any other positive ion species (for which typical signals are E A). Thus,here we present only observations of negative ions. As seen in Figure 2, the chlorine cluster system yields negative ions corresponding to electron attachm ...
Ions
... Karen C. Timberlake General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake ...
... Karen C. Timberlake General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.