Holt Modern Chemistry Workbook: intro - ch 5
... The goal of basic research is to increase knowledge. In chemistry, basic research includes the study of the properties of a chemical. It also includes the study of what happens when two chemicals are mixed. Sometimes, scientists do basic r esearch simply to satisfy their curiosity about a chemical ...
... The goal of basic research is to increase knowledge. In chemistry, basic research includes the study of the properties of a chemical. It also includes the study of what happens when two chemicals are mixed. Sometimes, scientists do basic r esearch simply to satisfy their curiosity about a chemical ...
chapter twenty-one transition metals and coordination chemistry
... is an anion, the –ate suffix ending is added to the name of the metal. Also, the ligands were not in alphabetical order (a in aqua comes before c in chloro). d. The correct name is sodium tetracyanooxalatocobaltate(II). The only error is that tetra should be omitted in front of sodium. That four sod ...
... is an anion, the –ate suffix ending is added to the name of the metal. Also, the ligands were not in alphabetical order (a in aqua comes before c in chloro). d. The correct name is sodium tetracyanooxalatocobaltate(II). The only error is that tetra should be omitted in front of sodium. That four sod ...
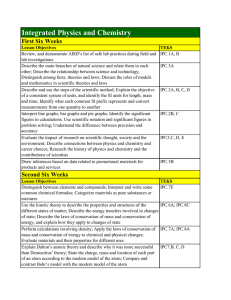
Organic Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
... compounds through both ionic and covalent bonding. Anchor: CHEM.A.1.1 – Identify and describe how observable and measureable properties can be used to classify and describe matter and energy. Eligible Content CHEM.A.1.1.4 – Relate the physical properties of matter to its atomic or molecular struct ...
... compounds through both ionic and covalent bonding. Anchor: CHEM.A.1.1 – Identify and describe how observable and measureable properties can be used to classify and describe matter and energy. Eligible Content CHEM.A.1.1.4 – Relate the physical properties of matter to its atomic or molecular struct ...
Mechanistic and Computational Studies of Ferroin, Simple Organic
... scrutiny and perhaps try to prove what they may find intriguing themselves. That being said, most potential inadequacies have already been identified and discussed. The initial goal of this study was to model the oxidation of bromomalonic acid (BMA) by Fe(1,10-phenanthroline)33+ (a.k.a. ferriin) and ...
... scrutiny and perhaps try to prove what they may find intriguing themselves. That being said, most potential inadequacies have already been identified and discussed. The initial goal of this study was to model the oxidation of bromomalonic acid (BMA) by Fe(1,10-phenanthroline)33+ (a.k.a. ferriin) and ...
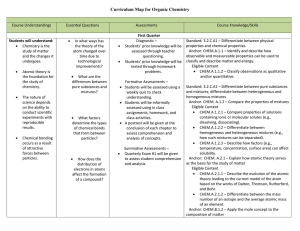
Integrated Physics and Chemistry
... Name simple ionic and covalent compounds; Predict the charge of a transition metal cation in an ionic compound; Write chemical formulas for simple ionic compounds; Distinguish a covalent compound’s empirical formula from its molecular formula Describe how carbon atoms bond covalently to form organic ...
... Name simple ionic and covalent compounds; Predict the charge of a transition metal cation in an ionic compound; Write chemical formulas for simple ionic compounds; Distinguish a covalent compound’s empirical formula from its molecular formula Describe how carbon atoms bond covalently to form organic ...
For metals
... Are completely nonreactive since they have eight valence electrons, making a stable octet. Kr and Xe can be forced, in the laboratory, to give up some valence electrons to react with fluorine. Since noble gases do not naturally bond to any other elements, one atom of noble gas is considered to be a ...
... Are completely nonreactive since they have eight valence electrons, making a stable octet. Kr and Xe can be forced, in the laboratory, to give up some valence electrons to react with fluorine. Since noble gases do not naturally bond to any other elements, one atom of noble gas is considered to be a ...
2 Atoms and Molecules
... that a minimum of 115 different kinds of atoms exist. Eighty-eight of the elements are naturally occurring and therefore are found in Earth’s crust, oceans, or atmosphere. The others are synthetic elements produced in the laboratory. Each element can be characterized and identified by its unique set ...
... that a minimum of 115 different kinds of atoms exist. Eighty-eight of the elements are naturally occurring and therefore are found in Earth’s crust, oceans, or atmosphere. The others are synthetic elements produced in the laboratory. Each element can be characterized and identified by its unique set ...
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry
... order to achieve its ends. This means that a good chemist is one who not only has a mastery of chemical theory, but also a good knowledge of chemical facts. With such a knowledge, he can direct a trial and error approach to practical problems in the most promising directions. Inorganic Chemistry Org ...
... order to achieve its ends. This means that a good chemist is one who not only has a mastery of chemical theory, but also a good knowledge of chemical facts. With such a knowledge, he can direct a trial and error approach to practical problems in the most promising directions. Inorganic Chemistry Org ...
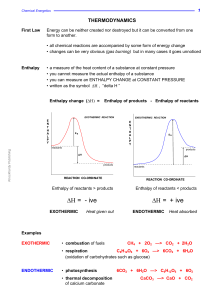
Η - Knockhardy
... the individual atoms join up again but in the form of products. The overall energy change will depend on the difference between the energy required to break the bonds and that released as bonds are made. energy released making bonds > energy used to break bonds ... EXOTHERMIC energy used to break bo ...
... the individual atoms join up again but in the form of products. The overall energy change will depend on the difference between the energy required to break the bonds and that released as bonds are made. energy released making bonds > energy used to break bonds ... EXOTHERMIC energy used to break bo ...
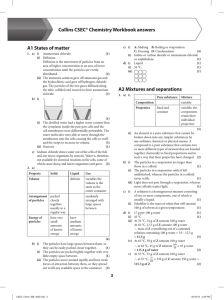
Collins CSEC® Chemistry Workbook answers A1 States of matter
... ii) Their chemical properties are the same because they are both made of the same element, carbon. Their physical properties are different because the atoms are bonded differently in each of them. (2) iii) Diamond has a high melting point: The strong covalent bonds between the carbon atoms throughou ...
... ii) Their chemical properties are the same because they are both made of the same element, carbon. Their physical properties are different because the atoms are bonded differently in each of them. (2) iii) Diamond has a high melting point: The strong covalent bonds between the carbon atoms throughou ...
Wilhelm Ostwald, the Father of Physical Chemistry
... a weak electrolyte (CH3COOH). Ostwald’s dilution law holds good only for weak electrolytes. For weak electrolytes, the degree of dissociation is governed by (2). Hence, the decrease in α with increase in concentration is because of partial dissociation. The theory of Arrhenius was based on the assum ...
... a weak electrolyte (CH3COOH). Ostwald’s dilution law holds good only for weak electrolytes. For weak electrolytes, the degree of dissociation is governed by (2). Hence, the decrease in α with increase in concentration is because of partial dissociation. The theory of Arrhenius was based on the assum ...
Module 29: General Chemistry Instructor Guide – Answer Key
... Compound – a substance that is composed of two or more elements that are chemically combined in fixed proportions. Mixture – a material that can be separated by physical means into two or more substances. ...
... Compound – a substance that is composed of two or more elements that are chemically combined in fixed proportions. Mixture – a material that can be separated by physical means into two or more substances. ...
Chapter 3: Ionic and Covalent Compounds Chapter 3: Ionic and
... 80. Anions are formed when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons. A) True B) False Ans: A Difficulty: Easy 81. The (II) in the name of the ionic compound lead (II) acetate specifically indicates that there are two lead ions present in the compound. A) True B) False Ans: B Difficulty: Medium 82. ...
... 80. Anions are formed when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons. A) True B) False Ans: A Difficulty: Easy 81. The (II) in the name of the ionic compound lead (II) acetate specifically indicates that there are two lead ions present in the compound. A) True B) False Ans: B Difficulty: Medium 82. ...
PDF - mockies – Mockiesgateacademy
... aims of alchemy that emerged with time were the quest for the elixir of life (the drinking of which would endue the alchemist with immortality), and the search for the philosopher’s stone, which would turn base metals into gold. Improbable as these ideas might seem today, the alchemists continued th ...
... aims of alchemy that emerged with time were the quest for the elixir of life (the drinking of which would endue the alchemist with immortality), and the search for the philosopher’s stone, which would turn base metals into gold. Improbable as these ideas might seem today, the alchemists continued th ...
Study Guide for Chapter 22 - Hydrocarbon Compounds
... of rotation about a carbon-carbon double bond leads to geometric isomers. 68. Most cyclic hydrocarbons have higher boiling ...
... of rotation about a carbon-carbon double bond leads to geometric isomers. 68. Most cyclic hydrocarbons have higher boiling ...
Chem 2A Final Review
... 11. The number of lone pairs of electrons in CF3- is 12. The molecular arrangement of atoms around H3O+ is: ...
... 11. The number of lone pairs of electrons in CF3- is 12. The molecular arrangement of atoms around H3O+ is: ...
T-Shaped Molecular Building Units in the Porous Structure of Ag(4,4
... molecular building units has yielded a remarkable class of materials having diverse architecture and functions.1 These include metal-organic solids with open frameworks having zeolite-like attributes2 and others having important electronic3 and magnetic4 properties. One of the simplest strategies em ...
... molecular building units has yielded a remarkable class of materials having diverse architecture and functions.1 These include metal-organic solids with open frameworks having zeolite-like attributes2 and others having important electronic3 and magnetic4 properties. One of the simplest strategies em ...
AP Ch 3 Stoichiometry
... 2 Al + 3 Cl2 2 AlCl3 • We found that chlorine is the limiting reactant, and 43.8 g of aluminum chloride are produced. 35.0 g Cl2 1 mol Cl2 2 mol Al 71 g Cl2 ...
... 2 Al + 3 Cl2 2 AlCl3 • We found that chlorine is the limiting reactant, and 43.8 g of aluminum chloride are produced. 35.0 g Cl2 1 mol Cl2 2 mol Al 71 g Cl2 ...
Energy and Chemical Reactions
... resulting from the motion of an object is called kinetic energy, KE. The particle with the higher velocity will move another object (such as another atom) farther, so it can do more work. It must therefore have more energy. In short, an argon atom with a velocity of 456 m/s has greater kinetic energ ...
... resulting from the motion of an object is called kinetic energy, KE. The particle with the higher velocity will move another object (such as another atom) farther, so it can do more work. It must therefore have more energy. In short, an argon atom with a velocity of 456 m/s has greater kinetic energ ...
CHAPTER 19 TRANSITION METALS AND COORDINATION
... Most transition metals have unfilled d orbitals, which creates a large number of other electrons that can be removed. Stable ions of the representative metals are determined by how many s and p valence electrons can be removed. In general, representative metals lose all of the s and p valence electr ...
... Most transition metals have unfilled d orbitals, which creates a large number of other electrons that can be removed. Stable ions of the representative metals are determined by how many s and p valence electrons can be removed. In general, representative metals lose all of the s and p valence electr ...
The mole and calculations
... Think about the size of this number. 109 is a billion. 1018 is a billion billion. 1023 is one hundred thousand billion billion. If you had 6.022 x 1023 dollars you could spend a billion dollars a second for your entire lifetime and still have used less than 0.001% of your money. If C atoms were ...
... Think about the size of this number. 109 is a billion. 1018 is a billion billion. 1023 is one hundred thousand billion billion. If you had 6.022 x 1023 dollars you could spend a billion dollars a second for your entire lifetime and still have used less than 0.001% of your money. If C atoms were ...
chemistry - Textbooks Online
... aims of alchemy that emerged with time were the quest for the elixir of life (the drinking of which would endue the alchemist with immortality), and the search for the philosopher’s stone, which would turn base metals into gold. Improbable as these ideas might seem today, the alchemists continued th ...
... aims of alchemy that emerged with time were the quest for the elixir of life (the drinking of which would endue the alchemist with immortality), and the search for the philosopher’s stone, which would turn base metals into gold. Improbable as these ideas might seem today, the alchemists continued th ...
Chapter 3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions
... 29. The molecular formula of aspirin is C9H8O4. How many aspirin molecules are present in one 500-milligram tablet? A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 29. The molecular formula of aspirin is C9H8O4. How many aspirin molecules are present in one 500-milligram tablet? A. B. C. D. E. ...
advanced placement chemistry workbook and note set
... The average atomic mass of an element is the weighted-average mass of all of the naturally-occurring isotopes of an element. As an analogy, consider a class where your grade is made up of several categories. For example, perhaps tests are 70% of your grade, homework is 10% and laboratory work is 20 ...
... The average atomic mass of an element is the weighted-average mass of all of the naturally-occurring isotopes of an element. As an analogy, consider a class where your grade is made up of several categories. For example, perhaps tests are 70% of your grade, homework is 10% and laboratory work is 20 ...
chemistry - Ethiopian Ministry of Education
... 1.1.2 Major Fields of Chemistry The universe is just like a very big chemical laboratory, rearranging atoms and subatomic particles to produce elements and compounds. While planets are made up of rocks which are nothing but arrangement of compounds, an atmosphere is a mixture of compounds separated ...
... 1.1.2 Major Fields of Chemistry The universe is just like a very big chemical laboratory, rearranging atoms and subatomic particles to produce elements and compounds. While planets are made up of rocks which are nothing but arrangement of compounds, an atmosphere is a mixture of compounds separated ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.