MAX5065/MAX5067 Dual-Phase, +0.6V to +3.3V Output Parallelable, Average-Current-Mode Controllers General Description
... provide high-output-current capability in a compact package with a minimum number of external components. The MAX5065/MAX5067 utilize a dual-phase, average-current-mode control that enables optimal use of low RDS(ON) MOSFETs, eliminating the need for external heatsinks even when delivering high outp ...
... provide high-output-current capability in a compact package with a minimum number of external components. The MAX5065/MAX5067 utilize a dual-phase, average-current-mode control that enables optimal use of low RDS(ON) MOSFETs, eliminating the need for external heatsinks even when delivering high outp ...
05_transistordcbias1
... Using Kirchoff’s voltage law: VCE – VCC – IC RC Because: VCE = VC - VE Since VE = 0V, then: VC = VCE Also: VBE = VB - VE with VE = 0V, then: VB = VBE ...
... Using Kirchoff’s voltage law: VCE – VCC – IC RC Because: VCE = VC - VE Since VE = 0V, then: VC = VCE Also: VBE = VB - VE with VE = 0V, then: VB = VBE ...
ZXLD1374
... power MOSFET switch, load and ambient temperature conditions. To ensure best operation in Boost and Buck-boost modes with input voltages, VIN, between 6.5 and 12V a suitable boot-strap network on VAUX pin is recommended. Performance in Buck mode will be reduced at input voltages (VIN, VAUX) below 8V ...
... power MOSFET switch, load and ambient temperature conditions. To ensure best operation in Boost and Buck-boost modes with input voltages, VIN, between 6.5 and 12V a suitable boot-strap network on VAUX pin is recommended. Performance in Buck mode will be reduced at input voltages (VIN, VAUX) below 8V ...
Characterisation of Schottky Varactor Diodes for - An
... Figure 11 shows that device 1 has much larger current compared to device 2 because device 1 has larger area compared to device 2. The ideality factor (n) and the saturation current are extracted based on the procedures outlined in [10]. The ideality factor (n) for device 1 was 1.2 compared to 1.09 f ...
... Figure 11 shows that device 1 has much larger current compared to device 2 because device 1 has larger area compared to device 2. The ideality factor (n) and the saturation current are extracted based on the procedures outlined in [10]. The ideality factor (n) for device 1 was 1.2 compared to 1.09 f ...
Experiment 6 Transistors as amplifiers and switches
... Figure 6-2: Characteristic curves of a typical BJT. The 2N2219A is a general-purpose, NPN transistor similar to the PN2222. Each curve shows the variation in collector current with the voltage between the collector and emitter for a fixed base current; base current was stepped through a range of val ...
... Figure 6-2: Characteristic curves of a typical BJT. The 2N2219A is a general-purpose, NPN transistor similar to the PN2222. Each curve shows the variation in collector current with the voltage between the collector and emitter for a fixed base current; base current was stepped through a range of val ...
DRV8885 1.5-A Stepper Motor Driver With
... The DRV8885 is capable of driving up to 1.5 A full scale or 1.0 A rms output current (depending on proper PCB ground plane for thermal dissipation and at 24 V and TA = 25°C). The DRV8885 integrated current sense functionality eliminates the need for two external sense resistors. The STEP/DIR pins pr ...
... The DRV8885 is capable of driving up to 1.5 A full scale or 1.0 A rms output current (depending on proper PCB ground plane for thermal dissipation and at 24 V and TA = 25°C). The DRV8885 integrated current sense functionality eliminates the need for two external sense resistors. The STEP/DIR pins pr ...
LT1129/LT1129-3.3/LT1129-5 - Micropower Low Dropout Regulators with Shutdown
... pin will turn on and clamp the pin to approximately 7V or – 0.6V. This range allows the use of 5V logic devices to drive the pin directly. For high impedance sources or logic running on supply voltages greater than 5.5V, the maximum current driven into the shutdown pin must be limited to less than 2 ...
... pin will turn on and clamp the pin to approximately 7V or – 0.6V. This range allows the use of 5V logic devices to drive the pin directly. For high impedance sources or logic running on supply voltages greater than 5.5V, the maximum current driven into the shutdown pin must be limited to less than 2 ...
INVESTIGATION ON THE ROLE OF UPQC FOR POWER QUALITY
... mainly on the rating of the dc storage device. Chellali Benachaiba et al. [14] presents an application of DVR for the improvement of voltage quality. R.N.Bhargavi, et al. [15] presents causes of a poor power quality are harmonic currents, poor power factor, supply voltage variations, etc. Voltage s ...
... mainly on the rating of the dc storage device. Chellali Benachaiba et al. [14] presents an application of DVR for the improvement of voltage quality. R.N.Bhargavi, et al. [15] presents causes of a poor power quality are harmonic currents, poor power factor, supply voltage variations, etc. Voltage s ...
TRANSIENT RECOVERY VOLTAGE (TRV) FOR HIGH
... Even when overhead lines are present, it is possible for the recovery voltage to be oscillatory. To be oscillatory, the surge impedance of a source side line has to be such that the equivalent surge impedance Zeq is equal or higher than 0.5 Leq / Ceq (Leq = equivalent source inductance, Ceq = equiva ...
... Even when overhead lines are present, it is possible for the recovery voltage to be oscillatory. To be oscillatory, the surge impedance of a source side line has to be such that the equivalent surge impedance Zeq is equal or higher than 0.5 Leq / Ceq (Leq = equivalent source inductance, Ceq = equiva ...
to get the file - Caltech Optical Observatories
... away. This step increase in detector bias is the electrical equivalent of resetting and reading after a fixed photogenerated charge has been left on the diode for a very long period. The voltage drift observed is the equivalent of image persistence. ...
... away. This step increase in detector bias is the electrical equivalent of resetting and reading after a fixed photogenerated charge has been left on the diode for a very long period. The voltage drift observed is the equivalent of image persistence. ...
BDTIC www.BDTIC.com/infineon Ballast Design for 54W T5 Fluorescent Lamp
... Ballast Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... Ballast Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Document
... a) Half –controlled bridge, a 90°, source of e.m.f. in load c) Full-controlled bridge, a > 90°, source of e.m.f. in load d) Full-controlled bridge, a 90°, source of e.m.f. in load4. Which is the most suitable power device for high frequency ( more 100 kHz) switching application? a) Power MOSFET b) B ...
... a) Half –controlled bridge, a 90°, source of e.m.f. in load c) Full-controlled bridge, a > 90°, source of e.m.f. in load d) Full-controlled bridge, a 90°, source of e.m.f. in load4. Which is the most suitable power device for high frequency ( more 100 kHz) switching application? a) Power MOSFET b) B ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE)
... units in each of its three phases. Each H-bridge unit has its own dc source, and for an induction motor it would be a battery unit, fuel cell or solar cell. Each SDC (separate D.C. source) is associated with a single-phase fullbridge inverter. The ac voltage sources of different level inverters are ...
... units in each of its three phases. Each H-bridge unit has its own dc source, and for an induction motor it would be a battery unit, fuel cell or solar cell. Each SDC (separate D.C. source) is associated with a single-phase fullbridge inverter. The ac voltage sources of different level inverters are ...
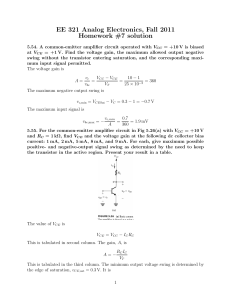
EE 321 Analog Electronics, Fall 2011 Homework #7 solution
... 5.56. Consider the CE amplifier circuit of Fig 5.26(a) when operated with a dc supply VCC = +5 V. It is required to find the point at which the transistor should be biased; that is, find the value of VCE so that the output sine-wave signal vce resulting from an input sine-wave signal vbe of 5 mV pea ...
... 5.56. Consider the CE amplifier circuit of Fig 5.26(a) when operated with a dc supply VCC = +5 V. It is required to find the point at which the transistor should be biased; that is, find the value of VCE so that the output sine-wave signal vce resulting from an input sine-wave signal vbe of 5 mV pea ...
Generator Installation Problem Solvers Compatable with ANY Generator or Transfer Switch
... Push to save adjustment ...
... Push to save adjustment ...
The world’s best seller WT300E Series Digital Power Meter
... WT310E (or another WT series instrument) provides a trustworthy power measurement solutions for testing the standby and off mode power of household products and office equipment. The solution enables testing to be performed according to the IEC62301 Ed1.0 and Ed2.0 standards which specify the use of ...
... WT310E (or another WT series instrument) provides a trustworthy power measurement solutions for testing the standby and off mode power of household products and office equipment. The solution enables testing to be performed according to the IEC62301 Ed1.0 and Ed2.0 standards which specify the use of ...
Dual 28V Input Voltage Charger with Linear
... is optimized for an AC/DC adapter power source. The charger has two 28 V power devices, to eliminate the need of any external power source selection and input over-voltage protection circuitry. Each of the power devices independently controls the charge current from the input, and performs as an ind ...
... is optimized for an AC/DC adapter power source. The charger has two 28 V power devices, to eliminate the need of any external power source selection and input over-voltage protection circuitry. Each of the power devices independently controls the charge current from the input, and performs as an ind ...
TPS43330-Q1,332-Q1 - Texas Instruments
... High-impedance differential-voltage inputs from the current-sense element (sense resistor or inductor DCR) for each buck controller. Choose the current-sense element to set the maximum current through the inductor based on the current-limit threshold (subject to tolerances) and considering the typic ...
... High-impedance differential-voltage inputs from the current-sense element (sense resistor or inductor DCR) for each buck controller. Choose the current-sense element to set the maximum current through the inductor based on the current-limit threshold (subject to tolerances) and considering the typic ...
NVT2001; NVT2002 1. General description Bidirectional voltage level translator for open-drain and
... The pull-up resistor value needs to limit the current through the pass transistor when it is in the ON state to about 15 mA. This ensures a pass voltage of 260 mV to 350 mV. If the current through the pass transistor is higher than 15 mA, the pass voltage also is higher in the ON state. To set the c ...
... The pull-up resistor value needs to limit the current through the pass transistor when it is in the ON state to about 15 mA. This ensures a pass voltage of 260 mV to 350 mV. If the current through the pass transistor is higher than 15 mA, the pass voltage also is higher in the ON state. To set the c ...
Josephson voltage standard

A Josephson voltage standard is a complex system that uses a superconductive integrated circuit chip operating at 4 K to generate stable voltages that depend only on an applied frequency and fundamental constants. It is an intrinsic standard in the sense that it does not depend on any physical artifact. It is the most accurate method to generate or measure voltage and, by international agreement, is the basis for voltage standards around the World.