review by Alicea
... fermions’: particles that, unlike electrons and positrons, constitute their own antiparticles.1 The monumental significance of this development required many intervening decades to fully appreciate, and despite being an ‘old’ idea Majorana fermions remain central to diverse problems across modern ph ...
... fermions’: particles that, unlike electrons and positrons, constitute their own antiparticles.1 The monumental significance of this development required many intervening decades to fully appreciate, and despite being an ‘old’ idea Majorana fermions remain central to diverse problems across modern ph ...
Scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy
... (or dry N2 jet for cleaner processing) unto a substrate, typically a highly doped Si substrate capped with 300nm of SiO2, which enables detection under an optical microscope [1] as described in detail in the next section on optical characterization [24-26]. Often one follows up this step with an AFM ...
... (or dry N2 jet for cleaner processing) unto a substrate, typically a highly doped Si substrate capped with 300nm of SiO2, which enables detection under an optical microscope [1] as described in detail in the next section on optical characterization [24-26]. Often one follows up this step with an AFM ...
theories of intramolecular vibrational energy transfer
... coupled oscillator systems were sometimes found to relax nonstatistically, and sometimes not at all. In this context it is worth noting that statistical theories of chemical reactions have always allowed for the presence of nonstatistical effects, by, for instance, excluding certain “inactive” modes ...
... coupled oscillator systems were sometimes found to relax nonstatistically, and sometimes not at all. In this context it is worth noting that statistical theories of chemical reactions have always allowed for the presence of nonstatistical effects, by, for instance, excluding certain “inactive” modes ...
Stoichiometry - Social Circle City Schools
... As you learned in Unit 1, atoms are so small and have such small masses that any amount of atoms we would work with would be very hard to count. For example, a piece of aluminum about the size of a pencil eraser contains approximately 2 × 1022 aluminum atoms! The mole (abbreviated mol) is the unit c ...
... As you learned in Unit 1, atoms are so small and have such small masses that any amount of atoms we would work with would be very hard to count. For example, a piece of aluminum about the size of a pencil eraser contains approximately 2 × 1022 aluminum atoms! The mole (abbreviated mol) is the unit c ...
Resolution-of-identity approach to Hartree–Fock, hybrid
... implementation with compact and efficient NAO basis sets. Our specific implementation is based on the ‘Fritz Haber Institute ab initio molecular simulations’ (FHI-aims) [64] program package. While we make reference to FHI-aims basis sets throughout much of this work, the numerical foundation present ...
... implementation with compact and efficient NAO basis sets. Our specific implementation is based on the ‘Fritz Haber Institute ab initio molecular simulations’ (FHI-aims) [64] program package. While we make reference to FHI-aims basis sets throughout much of this work, the numerical foundation present ...
FREE Sample Here
... 7. The most significant contribution to modern science made by alchemists was A) their fundamental work in the transmutation of the elements. B) their widespread acceptance of observation and experimentation. C) their systematic method of naming substances. D) their understanding of the nature of ch ...
... 7. The most significant contribution to modern science made by alchemists was A) their fundamental work in the transmutation of the elements. B) their widespread acceptance of observation and experimentation. C) their systematic method of naming substances. D) their understanding of the nature of ch ...
Multiple Choice
... Both are non-polar, but CCl4 has more electrons ( more polarizable) stronger dispersion force. Hydrogen bonding occurs when H is bonded to N, O or F. Only N2H4 has that arrangement. Farthest from each other in the gaseous phase, which is at t5. Melting occurs along 1st plateau (t2) and boiling alo ...
... Both are non-polar, but CCl4 has more electrons ( more polarizable) stronger dispersion force. Hydrogen bonding occurs when H is bonded to N, O or F. Only N2H4 has that arrangement. Farthest from each other in the gaseous phase, which is at t5. Melting occurs along 1st plateau (t2) and boiling alo ...
Chapter 6: Thermochemistry
... A) Energy is neither lost nor gained in any energy transformations. B) Perpetual motion is possible. C) Energy is conserved in quality but not in quantity. D) Energy is being created as time passes. We have more energy in the universe now than when time began. Ans: A Category: Easy Section: 6.3 58. ...
... A) Energy is neither lost nor gained in any energy transformations. B) Perpetual motion is possible. C) Energy is conserved in quality but not in quantity. D) Energy is being created as time passes. We have more energy in the universe now than when time began. Ans: A Category: Easy Section: 6.3 58. ...
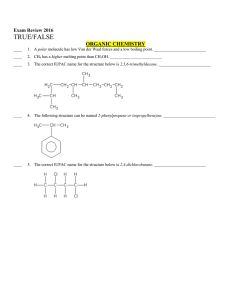
Multiple Choice Exam Review June 2016
... ____ 11. The 2p orbitals in oxygen have three unpaired electrons. ____________________ ____ 12. The shape of SO2 is trigonal planar. ____________________ ____ 13. The valence p orbitals in phosphorus, P, are half-filled. ____________________ ____ 14. All of the valence electrons in Fe2+ must have th ...
... ____ 11. The 2p orbitals in oxygen have three unpaired electrons. ____________________ ____ 12. The shape of SO2 is trigonal planar. ____________________ ____ 13. The valence p orbitals in phosphorus, P, are half-filled. ____________________ ____ 14. All of the valence electrons in Fe2+ must have th ...
Transition Metal-Modified Zirconium Phosphate Electrocatalysts for
... intercalated systems and that the metal‐adsorbed catalyst had retained α‐ZrP characteristics. In the metal-intercalated systems and that the metal-adsorbed catalyst had retained α-ZrP characteristics. case of pure α‐ZrP (Figure 3) two weight losses are observed, dehydration of water w ...
... intercalated systems and that the metal‐adsorbed catalyst had retained α‐ZrP characteristics. In the metal-intercalated systems and that the metal-adsorbed catalyst had retained α-ZrP characteristics. case of pure α‐ZrP (Figure 3) two weight losses are observed, dehydration of water w ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry
... In This Chapter… As you have learned in previous chapters, much of chemistry involves using macroscopic measurements to deduce what happens between atoms and molecules. We will now explore the chemical counting unit that links the atomic and macroscopic scales, the mole. The mole will allow us to ...
... In This Chapter… As you have learned in previous chapters, much of chemistry involves using macroscopic measurements to deduce what happens between atoms and molecules. We will now explore the chemical counting unit that links the atomic and macroscopic scales, the mole. The mole will allow us to ...
Graphene and its Interaction with Different Substrates
... graphene [12]. The reason this rather simple phenomenon was not understood earlier, was the lack of interest by the scientific community. In 1937 Landau had theoretically demonstrated that strictly two-dimensional crystals were thermodynamically unstable [13], and thus scientific interest in a clear ...
... graphene [12]. The reason this rather simple phenomenon was not understood earlier, was the lack of interest by the scientific community. In 1937 Landau had theoretically demonstrated that strictly two-dimensional crystals were thermodynamically unstable [13], and thus scientific interest in a clear ...
- UCL Discovery
... I, Nelson Yaw Dzade, hereby declare that this thesis titled “Computational study of the interactions of small molecules with the surfaces of iron-bearing minerals” is my own work and that all materials from other sources have been properly and fully acknowledged. ...
... I, Nelson Yaw Dzade, hereby declare that this thesis titled “Computational study of the interactions of small molecules with the surfaces of iron-bearing minerals” is my own work and that all materials from other sources have been properly and fully acknowledged. ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy

X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a surface-sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the elemental composition at the parts per thousand range, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements that exist within a material. XPS spectra are obtained by irradiating a material with a beam of X-rays while simultaneously measuring the kinetic energy and number of electrons that escape from the top 0 to 10 nm of the material being analyzed. XPS requires high vacuum (P ~ 10−8 millibar) or ultra-high vacuum (UHV; P < 10−9 millibar) conditions, although a current area of development is ambient-pressure XPS, in which samples are analyzed at pressures of a few tens of millibar.XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its as-received state, or after some treatment, for example: fracturing, cutting or scraping in air or UHV to expose the bulk chemistry, ion beam etching to clean off some or all of the surface contamination (with mild ion etching) or to intentionally expose deeper layers of the sample (with more extensive ion etching) in depth-profiling XPS, exposure to heat to study the changes due to heating, exposure to reactive gases or solutions, exposure to ion beam implant, exposure to ultraviolet light.XPS is also known as ESCA (Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis), an abbreviation introduced by Kai Siegbahn's research group to emphasize the chemical (rather than merely elemental) information that the technique provides.In principle XPS detects all elements. In practice, using typical laboratory-scale X-ray sources, XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot easily detect hydrogen (Z = 1) or helium (Z = 2).Detection limits for most of the elements (on a modern instrument) are in the parts per thousand range. Detection limits of parts per million (ppm) are possible, but require special conditions: concentration at top surface or very long collection time (overnight).XPS is routinely used to analyze inorganic compounds, metal alloys, semiconductors, polymers, elements, catalysts, glasses, ceramics, paints, papers, inks, woods, plant parts, make-up, teeth, bones, medical implants, bio-materials, viscous oils, glues, ion-modified materials and many others.XPS is less routinely used to analyze the hydrated forms of some of the above materials by freezing the samples in their hydrated state in an ultra pure environment, and allowing or causing multilayers of ice to sublime away prior to analysis. Such hydrated XPS analysis allows hydrated sample structures, which may be different from vacuum-dehydrated sample structures, to be studied in their more relevant as-used hydrated structure. Many bio-materials such as hydrogels are examples of such samples.







![Stoichiometry Chapter 3 CHEMA1301 [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014247793_1-84b4b6fe6fa37d77afbf7eb657ee347a-300x300.png)