Assignment 6
... polymers, where dimerization of this type occurs in essentially all cases. Find an example of a polymer where the molecular structure is known, sketch a picture of the structure and indicate on your sketch where the dimerizaton occurs. Comment on the likely conduction properties of most polymeric ma ...
... polymers, where dimerization of this type occurs in essentially all cases. Find an example of a polymer where the molecular structure is known, sketch a picture of the structure and indicate on your sketch where the dimerizaton occurs. Comment on the likely conduction properties of most polymeric ma ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... Base your answers to questions 75 through 77 on the information below. Litharge, PbO, is an ore that can be roasted (heated) in the presence of carbon monoxide, CO, to produce elemental lead. The reaction that takes place during this roasting process is represented by the balanced equation below. Pb ...
... Base your answers to questions 75 through 77 on the information below. Litharge, PbO, is an ore that can be roasted (heated) in the presence of carbon monoxide, CO, to produce elemental lead. The reaction that takes place during this roasting process is represented by the balanced equation below. Pb ...
$doc.title
... propagation of a wave group? Establish particle position to an uncertainty Δxo at time zero: what is uncertainty Δxt at later time t? ...
... propagation of a wave group? Establish particle position to an uncertainty Δxo at time zero: what is uncertainty Δxt at later time t? ...
Department of Physical Sciences (Physics)
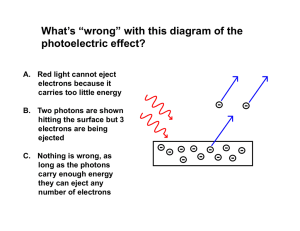
... (iv) Orbiting satellites and spacecraft can become charged because the light from the sun ejects electrons from their outer surface and they must be designed to minimise this effect. If the skin is coated with Ni which has a work function of 4.87eV, calculate the longest wavelength of the incident s ...
... (iv) Orbiting satellites and spacecraft can become charged because the light from the sun ejects electrons from their outer surface and they must be designed to minimise this effect. If the skin is coated with Ni which has a work function of 4.87eV, calculate the longest wavelength of the incident s ...
n - Egloos
... 27. When an excited atom emits a photon, the linear momentum of the photon must be balanced by the recoil momentum of the atom. As a result, some of the excitation energy of the atom goes into the kinetic energy of its recoil. (a) Modify Eq. (4.16) to include this effect. (b) Find the ratio between ...
... 27. When an excited atom emits a photon, the linear momentum of the photon must be balanced by the recoil momentum of the atom. As a result, some of the excitation energy of the atom goes into the kinetic energy of its recoil. (a) Modify Eq. (4.16) to include this effect. (b) Find the ratio between ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... A negatively charged atom is called an Anion – it has more electrons than protons. ...
... A negatively charged atom is called an Anion – it has more electrons than protons. ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... 19. His model of the atom has been called the “plum pudding” Model. 20. His model of the atom has been called the “billiard ball” model. 21. He studied matter in cathode ray tubes. 22. His philosophical idea included the term “atomos”. 23. He added to the atomic theory the idea that atoms had positi ...
... 19. His model of the atom has been called the “plum pudding” Model. 20. His model of the atom has been called the “billiard ball” model. 21. He studied matter in cathode ray tubes. 22. His philosophical idea included the term “atomos”. 23. He added to the atomic theory the idea that atoms had positi ...
Spring 2009 Final Exam Review – Part 2
... 2. Find the % of each element in each substance in #1. 3. How many molecules are there in 24 grams of FeF3? 4. How many molecules are there in 450 grams of Na2SO4? 5. How many grams are there in 2.3 x 1024 atoms of silver? 6. How many grams are there in 7.4 x 1023 molecules of AgNO3? 7. ...
... 2. Find the % of each element in each substance in #1. 3. How many molecules are there in 24 grams of FeF3? 4. How many molecules are there in 450 grams of Na2SO4? 5. How many grams are there in 2.3 x 1024 atoms of silver? 6. How many grams are there in 7.4 x 1023 molecules of AgNO3? 7. ...
Measuring and Calculating
... freeze solid then the entropy would decrease. 5 th realize that every time the temp increases or decreases the entropy of the system increases or decrease. ...
... freeze solid then the entropy would decrease. 5 th realize that every time the temp increases or decreases the entropy of the system increases or decrease. ...
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
... Determine the wavelength of light emitted when a hydrogen atom makes a transition from the n = 6 to the n = 2 energy level according to the Bohr ...
... Determine the wavelength of light emitted when a hydrogen atom makes a transition from the n = 6 to the n = 2 energy level according to the Bohr ...
the principle quantum number
... • Map to determine location of the electrons….. • (Methods for denoting earrangement for an atom: orbital notation) ...
... • Map to determine location of the electrons….. • (Methods for denoting earrangement for an atom: orbital notation) ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy

X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a surface-sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the elemental composition at the parts per thousand range, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements that exist within a material. XPS spectra are obtained by irradiating a material with a beam of X-rays while simultaneously measuring the kinetic energy and number of electrons that escape from the top 0 to 10 nm of the material being analyzed. XPS requires high vacuum (P ~ 10−8 millibar) or ultra-high vacuum (UHV; P < 10−9 millibar) conditions, although a current area of development is ambient-pressure XPS, in which samples are analyzed at pressures of a few tens of millibar.XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its as-received state, or after some treatment, for example: fracturing, cutting or scraping in air or UHV to expose the bulk chemistry, ion beam etching to clean off some or all of the surface contamination (with mild ion etching) or to intentionally expose deeper layers of the sample (with more extensive ion etching) in depth-profiling XPS, exposure to heat to study the changes due to heating, exposure to reactive gases or solutions, exposure to ion beam implant, exposure to ultraviolet light.XPS is also known as ESCA (Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis), an abbreviation introduced by Kai Siegbahn's research group to emphasize the chemical (rather than merely elemental) information that the technique provides.In principle XPS detects all elements. In practice, using typical laboratory-scale X-ray sources, XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot easily detect hydrogen (Z = 1) or helium (Z = 2).Detection limits for most of the elements (on a modern instrument) are in the parts per thousand range. Detection limits of parts per million (ppm) are possible, but require special conditions: concentration at top surface or very long collection time (overnight).XPS is routinely used to analyze inorganic compounds, metal alloys, semiconductors, polymers, elements, catalysts, glasses, ceramics, paints, papers, inks, woods, plant parts, make-up, teeth, bones, medical implants, bio-materials, viscous oils, glues, ion-modified materials and many others.XPS is less routinely used to analyze the hydrated forms of some of the above materials by freezing the samples in their hydrated state in an ultra pure environment, and allowing or causing multilayers of ice to sublime away prior to analysis. Such hydrated XPS analysis allows hydrated sample structures, which may be different from vacuum-dehydrated sample structures, to be studied in their more relevant as-used hydrated structure. Many bio-materials such as hydrogels are examples of such samples.