Chapter 2 - Chemistry
... - class of molecular substances that contain carbon combined with other elements, such as hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen hydrocarbon - simplest organic compounds - those compounds containing only hydrogen and carbon - extensively used as sources of energy - starting materials for plastics functional ...
... - class of molecular substances that contain carbon combined with other elements, such as hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen hydrocarbon - simplest organic compounds - those compounds containing only hydrogen and carbon - extensively used as sources of energy - starting materials for plastics functional ...
1. some basic concepts of chemistry
... Every experimental measurement has some amount of uncertainty associated with it. The uncertainty in the experimental or the calculated values is indicated by mentioning the number of significant figures. Significant figures are meaningful digits which are known with certainty. The uncertainty is in ...
... Every experimental measurement has some amount of uncertainty associated with it. The uncertainty in the experimental or the calculated values is indicated by mentioning the number of significant figures. Significant figures are meaningful digits which are known with certainty. The uncertainty is in ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... represent each. In the generalized equation, the letters A and B represent positive ions (elements that lose electrons). The letters X and Y will represent negative ions (elements that gain electrons). In a synthesis reaction, two or more reactants are combined to form one product. The generalized e ...
... represent each. In the generalized equation, the letters A and B represent positive ions (elements that lose electrons). The letters X and Y will represent negative ions (elements that gain electrons). In a synthesis reaction, two or more reactants are combined to form one product. The generalized e ...
Group II Elements - Innovative Education.org
... The first ionisation energy is the energy required to remove one electron from each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1+ ions. Electronegativity. Electronegativity measures the pull of an atom of an element on the electrons in a chemical bond (covalent). The stronger its ...
... The first ionisation energy is the energy required to remove one electron from each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1+ ions. Electronegativity. Electronegativity measures the pull of an atom of an element on the electrons in a chemical bond (covalent). The stronger its ...
AP Chemistry
... (D) always contain multiple covalent bonds (E) are packed tightly into a crystal lattice 1416. An example of a molecular compound that exists as a solid at STP is ...
... (D) always contain multiple covalent bonds (E) are packed tightly into a crystal lattice 1416. An example of a molecular compound that exists as a solid at STP is ...
9th class bridge course 74-112
... Atoms of different elements are different in all respects. Atoms combine in small whole numbers to form compound atoms (molecules). Atom is the smallest unit of matter which takes part in a chemical reaction. All the points put forward in Dalton’s atomic theory have been contradicted by modern resea ...
... Atoms of different elements are different in all respects. Atoms combine in small whole numbers to form compound atoms (molecules). Atom is the smallest unit of matter which takes part in a chemical reaction. All the points put forward in Dalton’s atomic theory have been contradicted by modern resea ...
CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2: Organic
... The energy required to promote the electron would be more than offset by the formation of two extra covalent bonds. However, whereas the others would involve 2p orbitals. Spectroscopic measurements show that all four bonds in methane are identical. Let's look at an alkane, ethane for example. Each c ...
... The energy required to promote the electron would be more than offset by the formation of two extra covalent bonds. However, whereas the others would involve 2p orbitals. Spectroscopic measurements show that all four bonds in methane are identical. Let's look at an alkane, ethane for example. Each c ...
The Chemistry of Global Warming
... – During years of warmer temperatures, more heavy water escapes to the atmosphere that return to Earth as snow or rainfall; hence, higher 2H/1H implies higher temperature. ...
... – During years of warmer temperatures, more heavy water escapes to the atmosphere that return to Earth as snow or rainfall; hence, higher 2H/1H implies higher temperature. ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... charged species at ROB3LYP level using a smaller basis and then by single point PCM calculations at the same level but using the larger basis set. 2.3 Thermal energy and molecular entropy Thermal energy and entropy contribution towards the free energy change of the reductive process are obtained for ...
... charged species at ROB3LYP level using a smaller basis and then by single point PCM calculations at the same level but using the larger basis set. 2.3 Thermal energy and molecular entropy Thermal energy and entropy contribution towards the free energy change of the reductive process are obtained for ...
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY
... One of the most fundamental characteristics of a specific body of matter is the quantity of it. In discussing the quantitative chemical characteristics of matter it is essential to have a way of expressing quantity in a way that is proportional to the number of individual entities of the substance- ...
... One of the most fundamental characteristics of a specific body of matter is the quantity of it. In discussing the quantitative chemical characteristics of matter it is essential to have a way of expressing quantity in a way that is proportional to the number of individual entities of the substance- ...
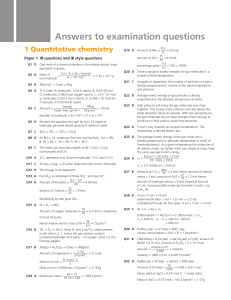
Answers to examination questions
... Q1 A Magnesium is a metal; chlorine is a non-metal. Typically, a metal and a non-metal react to form an ionic compound. Q2 A All four molecules are based upon a tetrahedral arrangement of four regions of high electron density. However, lone pairs cause more repulsion than bonding pairs. The ...
... Q1 A Magnesium is a metal; chlorine is a non-metal. Typically, a metal and a non-metal react to form an ionic compound. Q2 A All four molecules are based upon a tetrahedral arrangement of four regions of high electron density. However, lone pairs cause more repulsion than bonding pairs. The ...
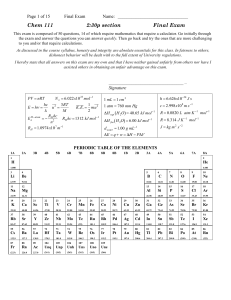
Final Exam - KFUPM Faculty List
... ClF3: electrons needed: 7 (Cl) + 3 x 7 (F) = 28 electrons Cl-F single bonds from Cl to each one of the F atoms to complete the octets each F atom gets 3 lone pairs 8 electrons/F: 3 x 8 = 24 electrons Cl can expand its octet, so the missing 4 electrons go as 2 lone pairs to Cl trigonal bipyramidal ar ...
... ClF3: electrons needed: 7 (Cl) + 3 x 7 (F) = 28 electrons Cl-F single bonds from Cl to each one of the F atoms to complete the octets each F atom gets 3 lone pairs 8 electrons/F: 3 x 8 = 24 electrons Cl can expand its octet, so the missing 4 electrons go as 2 lone pairs to Cl trigonal bipyramidal ar ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... Basically, noble gases (e.g. helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon) are the only atoms with minimum energy per shell. Then, atoms must satisfy a chemical rule that states atoms in ground-state which do not have an entire outer shell (there are some valence electrons but not all of them) need mo ...
... Basically, noble gases (e.g. helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon) are the only atoms with minimum energy per shell. Then, atoms must satisfy a chemical rule that states atoms in ground-state which do not have an entire outer shell (there are some valence electrons but not all of them) need mo ...
Chemical Changes and Structure Homework Booklet
... b. During the experiment, the test tube becomes warm. What term is used to describe a reaction which gives out heat? c. Calculate the average rate at which gas is given off between 10 and 40s of the reaction. d. Why would increasing the concentration of the acid increase the rate of the reaction? ...
... b. During the experiment, the test tube becomes warm. What term is used to describe a reaction which gives out heat? c. Calculate the average rate at which gas is given off between 10 and 40s of the reaction. d. Why would increasing the concentration of the acid increase the rate of the reaction? ...
1411_lecture_ch2
... showed the signatures of hydrogen nuclei. Rutherford determined that the only place this hydrogen could have come from was the nitrogen, and therefore nitrogen must contain hydrogen nuclei. He thus suggested that the hydrogen nucleus, which was known to have an atomic number of 1, was an elementary ...
... showed the signatures of hydrogen nuclei. Rutherford determined that the only place this hydrogen could have come from was the nitrogen, and therefore nitrogen must contain hydrogen nuclei. He thus suggested that the hydrogen nucleus, which was known to have an atomic number of 1, was an elementary ...
2.ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS
... b. You recognize the fact that whenever a cation can have multiple oxidation states (1+, 2+, and 5+ in this case) the name of the compound must indicate the charge. Therefore, the names of the compounds in part (a) would be exy(I) sulfate, exy(II) sulfate, and exy(V) sulfate, respectively. 2.26 a. T ...
... b. You recognize the fact that whenever a cation can have multiple oxidation states (1+, 2+, and 5+ in this case) the name of the compound must indicate the charge. Therefore, the names of the compounds in part (a) would be exy(I) sulfate, exy(II) sulfate, and exy(V) sulfate, respectively. 2.26 a. T ...
AP CHEMISTRY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT
... The Law of Conservation of Mass: mass is neither lost nor gained during an ordinary chemical reaction. In other words, the products of a reaction must have the same number of type of atoms as the reactants. Law of Definite Proportion: a given compound always contains exactly proportions of elements ...
... The Law of Conservation of Mass: mass is neither lost nor gained during an ordinary chemical reaction. In other words, the products of a reaction must have the same number of type of atoms as the reactants. Law of Definite Proportion: a given compound always contains exactly proportions of elements ...
Shape
... ‣ We often describe the shape of a molecule with terms that relate to geometric figures. ‣ These geometric figures have characteristic “corners” that indicate the positions of the surrounding atoms around a central atom in the center of the geometric figure. ‣ The geometric figures also have charact ...
... ‣ We often describe the shape of a molecule with terms that relate to geometric figures. ‣ These geometric figures have characteristic “corners” that indicate the positions of the surrounding atoms around a central atom in the center of the geometric figure. ‣ The geometric figures also have charact ...
Answer key
... C-Matter-201. I can explain what physical and chemical properties are, and list examples. C-Matter-202. I can describe how density relates to mass and volume for matter. C-Matter-203. I can calculate density given the mass and volume, or calculate relationships between density, mass and volume C-Mat ...
... C-Matter-201. I can explain what physical and chemical properties are, and list examples. C-Matter-202. I can describe how density relates to mass and volume for matter. C-Matter-203. I can calculate density given the mass and volume, or calculate relationships between density, mass and volume C-Mat ...
Questions - SMK Raja Perempuan Ipoh
... Hydrogen peroxide decomposes accordin to the following equation: 2 H 2O2 (l) 2 H 2O (l) + O2 (g) 1. Calculate the volume of oxygen gas, O2 measured at STP that can be obtained from the decomposition of 34 g of hydrogen peroxide, H 2O2 . [Relative atomic mass : H, 1 ; O, 16. Molar volume : 22.4 dm ...
... Hydrogen peroxide decomposes accordin to the following equation: 2 H 2O2 (l) 2 H 2O (l) + O2 (g) 1. Calculate the volume of oxygen gas, O2 measured at STP that can be obtained from the decomposition of 34 g of hydrogen peroxide, H 2O2 . [Relative atomic mass : H, 1 ; O, 16. Molar volume : 22.4 dm ...
File
... C-Matter-201. I can explain what physical and chemical properties are, and list examples. C-Matter-202. I can describe how density relates to mass and volume for matter. C-Matter-203. I can calculate density given the mass and volume, or calculate relationships between density, mass and volume C-Mat ...
... C-Matter-201. I can explain what physical and chemical properties are, and list examples. C-Matter-202. I can describe how density relates to mass and volume for matter. C-Matter-203. I can calculate density given the mass and volume, or calculate relationships between density, mass and volume C-Mat ...