STUDY MATERIAL 2015-16 CHEMISTRY CLASS XI
... This support material is one such effort by Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, an empirical endeavour to help students learn more effectively and efficiently. It is designed to give proper platform to students for better practice and understanding of the chapters. This can suitably be used during revisio ...
... This support material is one such effort by Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, an empirical endeavour to help students learn more effectively and efficiently. It is designed to give proper platform to students for better practice and understanding of the chapters. This can suitably be used during revisio ...
physical setting chemistry
... 60 Explain, in terms of bonding, why compound A is saturated. [1] 61 Explain, in terms of molecular structure, why the chemical properties of compound A are different from the chemical properties of compound B. [1] ...
... 60 Explain, in terms of bonding, why compound A is saturated. [1] 61 Explain, in terms of molecular structure, why the chemical properties of compound A are different from the chemical properties of compound B. [1] ...
Atomic Mass - HCC Learning Web
... EX. 4 Consider the reaction, 2NH3 + 5F2 → N2F4 + 6HF. If 25.0 g of NH3 are reacted with 150. g of F2, (a) What is the limiting reactant? (b) Calculate the theoretical yield of N2F4 in grams. (c) Calculate the percent yield if 56.8 g of N2F4 are actually obtained. (d) Calculate the actual yield of N ...
... EX. 4 Consider the reaction, 2NH3 + 5F2 → N2F4 + 6HF. If 25.0 g of NH3 are reacted with 150. g of F2, (a) What is the limiting reactant? (b) Calculate the theoretical yield of N2F4 in grams. (c) Calculate the percent yield if 56.8 g of N2F4 are actually obtained. (d) Calculate the actual yield of N ...
Problem 5. The Second Law of thermodynamics
... 1. As can be seen from the figure, there are many possible ways to go from point A (1 bar, 298 K) to point B (8 bar, 298 K) using only adiabatic and isobaric segments. The work W is equal to the area under the path. It is clear that W is minimal if we complete the process in two stages: isobaric coo ...
... 1. As can be seen from the figure, there are many possible ways to go from point A (1 bar, 298 K) to point B (8 bar, 298 K) using only adiabatic and isobaric segments. The work W is equal to the area under the path. It is clear that W is minimal if we complete the process in two stages: isobaric coo ...
CHEM 1405 Practice Exam #2 (2015)
... 7) Which fourth period transition element has the highest atomic number? A) Ca B) Cd C) Kr D) Zn C) Sb and Te D) Po and At C) Ca D) none of the above 8) Which of the following elements are fourth period metalloids? A) Si and Ge B) Ge and As 9) Which of the following is an alkali metal? A) Al B) Fe 1 ...
... 7) Which fourth period transition element has the highest atomic number? A) Ca B) Cd C) Kr D) Zn C) Sb and Te D) Po and At C) Ca D) none of the above 8) Which of the following elements are fourth period metalloids? A) Si and Ge B) Ge and As 9) Which of the following is an alkali metal? A) Al B) Fe 1 ...
Cleaning Up With Atom Economy
... Page 2 American Chemical Society --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------economy, Trost has developed a number of palladium and ruthenium catalysts. These catalysts enable chemical synthesis to proceed by simple addition rea ...
... Page 2 American Chemical Society --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------economy, Trost has developed a number of palladium and ruthenium catalysts. These catalysts enable chemical synthesis to proceed by simple addition rea ...
Problem 5. The Second Law of thermodynamics
... 1. As can be seen from the figure, there are many possible ways to go from point A (1 bar, 298 K) to point B (8 bar, 298 K) using only adiabatic and isobaric segments. The work W is equal to the area under the path. It is clear that W is minimal if we complete the process in two stages: isobaric coo ...
... 1. As can be seen from the figure, there are many possible ways to go from point A (1 bar, 298 K) to point B (8 bar, 298 K) using only adiabatic and isobaric segments. The work W is equal to the area under the path. It is clear that W is minimal if we complete the process in two stages: isobaric coo ...
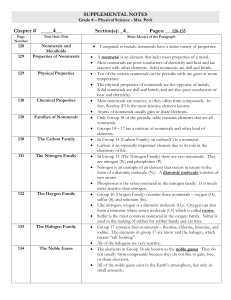
Practice Test Material - Directorate of Education
... What is kinetic gas equation? Deduce (i) Boyle‘s law (ii) Charle‘s law from kinetic gas equation. OR ...
... What is kinetic gas equation? Deduce (i) Boyle‘s law (ii) Charle‘s law from kinetic gas equation. OR ...
X012/12/02
... 8. Which of the following graphs could represent the change in the rate of reaction when magnesium ribbon reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid? ...
... 8. Which of the following graphs could represent the change in the rate of reaction when magnesium ribbon reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid? ...
the Language of Chemistry
... He was the first person to make the distinction between organic and inorganic compounds. He introduced the classical system of chemical symbols in 1811, in which elements are abbreviated by one or two letters to make a distinct abbreviation from their Latin names. He developed the radical theory of ...
... He was the first person to make the distinction between organic and inorganic compounds. He introduced the classical system of chemical symbols in 1811, in which elements are abbreviated by one or two letters to make a distinct abbreviation from their Latin names. He developed the radical theory of ...
Solutions (DOC format, upgraded July 20)
... 1. As can be seen from the figure, there are many possible ways to go from point A (1 bar, 298 K) to point B (8 bar, 298 K) using only adiabatic and isobaric segments. The work W is equal to the area under the path. It is clear that W is minimal if we complete the process in two stages: isobaric coo ...
... 1. As can be seen from the figure, there are many possible ways to go from point A (1 bar, 298 K) to point B (8 bar, 298 K) using only adiabatic and isobaric segments. The work W is equal to the area under the path. It is clear that W is minimal if we complete the process in two stages: isobaric coo ...
The Copper Cycle
... Acids are usually easy to recognize since their formulas start with H—e.g. HCl(aq), HNO3(aq), and H2SO4(aq) are all acids. Note that the physical state aqueous, (aq), must be included to distinguish an acid from other forms of a substance. For example, the formula “HCl” can also be used for hydrogen ...
... Acids are usually easy to recognize since their formulas start with H—e.g. HCl(aq), HNO3(aq), and H2SO4(aq) are all acids. Note that the physical state aqueous, (aq), must be included to distinguish an acid from other forms of a substance. For example, the formula “HCl” can also be used for hydrogen ...
Effect of an external electric field on the dissociation energy and the
... the opposite direction to the dipole moment of the system strengthens the interaction due to a larger mutual polarization between both molecules and increases the covalent character of the hydrogen bond, while an external field in the opposite direction has the inverse effect. The properties of the ...
... the opposite direction to the dipole moment of the system strengthens the interaction due to a larger mutual polarization between both molecules and increases the covalent character of the hydrogen bond, while an external field in the opposite direction has the inverse effect. The properties of the ...
Here`s - Sonlight
... Compare this incredibly logical system of units to the chaotic English system. If we want to measure something short, we use the inch unit, which is equal to one-twelfth of a foot. On the other hand, if we want to measure something with small volume, we might use the quart unit, which is equal to on ...
... Compare this incredibly logical system of units to the chaotic English system. If we want to measure something short, we use the inch unit, which is equal to one-twelfth of a foot. On the other hand, if we want to measure something with small volume, we might use the quart unit, which is equal to on ...
File - Varsity Field
... Q7. Ammonium sulphate reacts with sodium hydroxide: Q8. Rhodocrosite, a red mineral, consists largely of manganese II carbonate. Write an equation for the reaction of the mineral with hydrochloric acid. Name the products. Q9. Sodium sulphite and acetic acid react. Q10. Write a balanced, net ionic eq ...
... Q7. Ammonium sulphate reacts with sodium hydroxide: Q8. Rhodocrosite, a red mineral, consists largely of manganese II carbonate. Write an equation for the reaction of the mineral with hydrochloric acid. Name the products. Q9. Sodium sulphite and acetic acid react. Q10. Write a balanced, net ionic eq ...
Chemistry 2014 - SC3210 IC Scope and Sequence
... Explain that energy can be transformed from one form to another. Science Practice: Integrate concepts from both chemistry and physics to analyze energy transformations and the conservation of energy. Heat Describe heat flow in terms of the motion of atoms or molecules. Distinguish between exothermic ...
... Explain that energy can be transformed from one form to another. Science Practice: Integrate concepts from both chemistry and physics to analyze energy transformations and the conservation of energy. Heat Describe heat flow in terms of the motion of atoms or molecules. Distinguish between exothermic ...
Discussion 9, Mahaffy et al., Chapter 15
... a. Oxidation is loss of electrons (acts as a reducing agent) b.Reduction is gain of electrons (acts as a oxidizing agent) Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to the total charge. e. In compo ...
... a. Oxidation is loss of electrons (acts as a reducing agent) b.Reduction is gain of electrons (acts as a oxidizing agent) Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to the total charge. e. In compo ...
atoms - HCC Learning Web
... • If we know the molecular formula of a compound, we can determine its empirical formula. The converse is not true! Atoms, Molecules, and Ions © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • If we know the molecular formula of a compound, we can determine its empirical formula. The converse is not true! Atoms, Molecules, and Ions © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Bohr, Niels Henrik David
... their atoms and that only the atomic weight and possible radioactive behaviour are determined by the small but massive nucleus itself. Rutherford's nuclear atom was both mechanically and electromagnetically unstable, but Bohr imposed stability on it by introducing the new and not yet clarified idea ...
... their atoms and that only the atomic weight and possible radioactive behaviour are determined by the small but massive nucleus itself. Rutherford's nuclear atom was both mechanically and electromagnetically unstable, but Bohr imposed stability on it by introducing the new and not yet clarified idea ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... The physical properties of nonmetals are the opposite of metals. Solid nonmetals are dull and brittle, and are also poor conductors of heat and electricity. Most nonmetals are reactive, so they often form compounds. In fact, fluorine (F) is the most reactive element known. Atoms of nonmetals usually ...
... The physical properties of nonmetals are the opposite of metals. Solid nonmetals are dull and brittle, and are also poor conductors of heat and electricity. Most nonmetals are reactive, so they often form compounds. In fact, fluorine (F) is the most reactive element known. Atoms of nonmetals usually ...
Mole Intro - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 2. What is the mass in grams of the following: a. 0.00100 mol of K2CO3 b. 3.50 mol of iron (II) chloride c. 5 x 10-4 mol of hydrogen sulfide 3. Make the following conversions: a. 1.00 mol of ammonium chloride to formula units b. 2.5 mol of O3 to molecules c. 0.003 mol of cadmium to atoms 4. Make th ...
... 2. What is the mass in grams of the following: a. 0.00100 mol of K2CO3 b. 3.50 mol of iron (II) chloride c. 5 x 10-4 mol of hydrogen sulfide 3. Make the following conversions: a. 1.00 mol of ammonium chloride to formula units b. 2.5 mol of O3 to molecules c. 0.003 mol of cadmium to atoms 4. Make th ...
THE MOLE - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... a. 25.0 g of carbon b. 0.353 g of MgO c. 400.2 g of water 2. What is the mass in grams of the following: a. 0.00100 mol of K2CO3 b. 3.50 mol of iron (II) chloride c. 5 x 10-4 mol of hydrogen sulfide 3. Make the following conversions: a. 1.00 mol of ammonium chloride to formula units b. 2.5 mol of O3 ...
... a. 25.0 g of carbon b. 0.353 g of MgO c. 400.2 g of water 2. What is the mass in grams of the following: a. 0.00100 mol of K2CO3 b. 3.50 mol of iron (II) chloride c. 5 x 10-4 mol of hydrogen sulfide 3. Make the following conversions: a. 1.00 mol of ammonium chloride to formula units b. 2.5 mol of O3 ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... Element “X” is composed of the following naturally occurring isotopes: Isotope ...
... Element “X” is composed of the following naturally occurring isotopes: Isotope ...
O usually has oxidation number of -2, except in peroxides where it is
... element increases (like a big Ox) Na Na+ + 1eIn Reduction half reactions, the oxidation number (value) gets smaller (this is what reduction means) ...
... element increases (like a big Ox) Na Na+ + 1eIn Reduction half reactions, the oxidation number (value) gets smaller (this is what reduction means) ...