Chapter 2 - The Chemical Context of Life
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... 2. All ______________of a given ______________are ___________but atoms of any one element are __________________ from the atoms of every other element. 3. ___________________are formed when _____________of different elements unite in ...
... 2. All ______________of a given ______________are ___________but atoms of any one element are __________________ from the atoms of every other element. 3. ___________________are formed when _____________of different elements unite in ...
Introduction to Chemistry for Coach Keith`s Biology
... Neutrons are neutral or have no electrical charge (n), have a mass of 1 amu, are found in the nucleus, and when added to the number of protons, determine the atomic mass of the element Example: Sodium has 11 protons and 12 neutrons so its atomic mass is 11+12=23 amu Electrons (e-) are negatively ch ...
... Neutrons are neutral or have no electrical charge (n), have a mass of 1 amu, are found in the nucleus, and when added to the number of protons, determine the atomic mass of the element Example: Sodium has 11 protons and 12 neutrons so its atomic mass is 11+12=23 amu Electrons (e-) are negatively ch ...
R E V I E W -- P R A C T I C E E X A
... 74. The difference between an electron affinity value of –47 and one of –329 is that with a value of –47: a. the more difficult it is for an atom to take on an extra electron b. the more easily the atom can take on an extra electron. c. the greater effect there is on the atomic radii d. the more ele ...
... 74. The difference between an electron affinity value of –47 and one of –329 is that with a value of –47: a. the more difficult it is for an atom to take on an extra electron b. the more easily the atom can take on an extra electron. c. the greater effect there is on the atomic radii d. the more ele ...
Atoms - ChemConnections
... chloride ions is one to one. However, a macroscopic sample of a sodium chloride (table salt) crystal contains billions and billions of sodium ions and chloride ions. Molecules Compounds such as water, H2O, ammonia, NH3, and buckminsterfullerene, C60, are molecules. They are molecular rather than ion ...
... chloride ions is one to one. However, a macroscopic sample of a sodium chloride (table salt) crystal contains billions and billions of sodium ions and chloride ions. Molecules Compounds such as water, H2O, ammonia, NH3, and buckminsterfullerene, C60, are molecules. They are molecular rather than ion ...
AP Semestar Exam REVIEW
... ____ 42. Place the following atoms in order of increasing size: Al, Cl, Mg, O, and P. a. Cl < O < P < Al < Mg b. Cl < P < Al < Mg < O c. O < Cl < P < Al < Mg d. O < Mg < Al < P < Cl e. none of the above ____ 43. A pair of electrons that is shared between two atoms is a. a covalent bond. b. a lone pa ...
... ____ 42. Place the following atoms in order of increasing size: Al, Cl, Mg, O, and P. a. Cl < O < P < Al < Mg b. Cl < P < Al < Mg < O c. O < Cl < P < Al < Mg d. O < Mg < Al < P < Cl e. none of the above ____ 43. A pair of electrons that is shared between two atoms is a. a covalent bond. b. a lone pa ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... 2. All ______________of a given ______________are ___________but atoms of any one element are __________________ from the atoms of every other element. 3. ___________________are formed when _____________of different elements unite in ...
... 2. All ______________of a given ______________are ___________but atoms of any one element are __________________ from the atoms of every other element. 3. ___________________are formed when _____________of different elements unite in ...
AP Chemistry Summer Packet More Chapter Two and Chapter
... with the same sign of charge are brought near each other, a repulsive force occurs. These forces are electrostatic in nature. In chemistry, the force of attraction or repulsion is given by a. The electrostatic Law b. The Chrystaline Law c. Coulomb’s Law d. Dalton’s Law 77. In the solid state, ionic ...
... with the same sign of charge are brought near each other, a repulsive force occurs. These forces are electrostatic in nature. In chemistry, the force of attraction or repulsion is given by a. The electrostatic Law b. The Chrystaline Law c. Coulomb’s Law d. Dalton’s Law 77. In the solid state, ionic ...
Atomic Theories- Part I - Tenafly Public Schools
... chemically combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Example: CO2 ...
... chemically combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Example: CO2 ...
Chapters 6, 8
... Step 2: Start balancing metal first. Continue with any nonmetal other than O or H. Step 3: When all atoms other than O and H are balanced, start balancing either O or H. if there is either O2 or H2 on the left side, balance it last. Predict the products, making sure that the charges within the molec ...
... Step 2: Start balancing metal first. Continue with any nonmetal other than O or H. Step 3: When all atoms other than O and H are balanced, start balancing either O or H. if there is either O2 or H2 on the left side, balance it last. Predict the products, making sure that the charges within the molec ...
specimen
... The non-metals chlorine and carbon have very different boiling points. Chlorine is a gas at room temperature but carbon does not boil until well over 4500 oC. ...
... The non-metals chlorine and carbon have very different boiling points. Chlorine is a gas at room temperature but carbon does not boil until well over 4500 oC. ...
GEO143_activity_2_at..
... what governs how elements combine with one another. Form groups of two and choose an element: Li, B, N, F, Mg, Si, S, Ar • Step 1: Write down the name of the element you chose. • Step 2: Determine the Atomic number, Atomic mass (rounded), and the number of protons, neutrons and electrons for the ele ...
... what governs how elements combine with one another. Form groups of two and choose an element: Li, B, N, F, Mg, Si, S, Ar • Step 1: Write down the name of the element you chose. • Step 2: Determine the Atomic number, Atomic mass (rounded), and the number of protons, neutrons and electrons for the ele ...
Ch03 1 VSEPR
... Electrons in a Free Atom Consider the arrangement of electrons in space in a free atom with eight valence electrons (e.g., Ne, F–, O2–, N3–). Electrons in each set (4α and 4β) will have a tetrahedral average arrangement relative to each other, owing to the Pauli Principle. Each tetrahedron has no o ...
... Electrons in a Free Atom Consider the arrangement of electrons in space in a free atom with eight valence electrons (e.g., Ne, F–, O2–, N3–). Electrons in each set (4α and 4β) will have a tetrahedral average arrangement relative to each other, owing to the Pauli Principle. Each tetrahedron has no o ...
Chapter 07 and 08 Chemical Bonding and Molecular
... • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell which is LOWER IN E ...
... • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell which is LOWER IN E ...
VSEPR Theory - Mr. Walsh`s AP Chemistry
... *Note: Even though tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal, and bent can have four electron groups (tetrahedral EG), they experience different bond angles because unbonded pairs repel more strongly than bonded electrons. Use this space for additional notes. ...
... *Note: Even though tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal, and bent can have four electron groups (tetrahedral EG), they experience different bond angles because unbonded pairs repel more strongly than bonded electrons. Use this space for additional notes. ...
HyperChem® MOLECULAR MODELING
... electron volts, eV. (To put this in perspective, the energy of an electron in a single hydrogen atom is –13.6 eV. So, it would take 13.6 eV to remove the electron completely from a hydrogen atom.) f) HOMO stands for highest occupied molecular orbital, and LUMO stands for lowest unoccupied molecular ...
... electron volts, eV. (To put this in perspective, the energy of an electron in a single hydrogen atom is –13.6 eV. So, it would take 13.6 eV to remove the electron completely from a hydrogen atom.) f) HOMO stands for highest occupied molecular orbital, and LUMO stands for lowest unoccupied molecular ...
Class Notes 2
... – backbone N-H group i+4 forms hydrogen bonding with backbone C = O group i – 3.6 residues per turn (5.4 Å, 1.5 Å per residue) • Variations, with chain more loosely or tightly coiled are possible (i+3 or i+5 instead of i+4) but not often ...
... – backbone N-H group i+4 forms hydrogen bonding with backbone C = O group i – 3.6 residues per turn (5.4 Å, 1.5 Å per residue) • Variations, with chain more loosely or tightly coiled are possible (i+3 or i+5 instead of i+4) but not often ...
Chemistry 127 – Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... • The mass spectrometer separates matter based on its mass and charge. • This data can be used to determine the abundance and mass of each isotope in a naturally occurring sample of that element. ...
... • The mass spectrometer separates matter based on its mass and charge. • This data can be used to determine the abundance and mass of each isotope in a naturally occurring sample of that element. ...
AP Chemistry Test Review
... 30) Remember that K doesn’t change unless the temperature changes! 31) Le Chatlier’s principle…(+) or (-) heat; ∆P; ∆V; (+) or (-) reactants and products; inert gases have no effect. 32) Q>K…the reaction goes backwards to the reactants 33) for Ksp, Q>K means a precipitate will form (see topic #45) ...
... 30) Remember that K doesn’t change unless the temperature changes! 31) Le Chatlier’s principle…(+) or (-) heat; ∆P; ∆V; (+) or (-) reactants and products; inert gases have no effect. 32) Q>K…the reaction goes backwards to the reactants 33) for Ksp, Q>K means a precipitate will form (see topic #45) ...
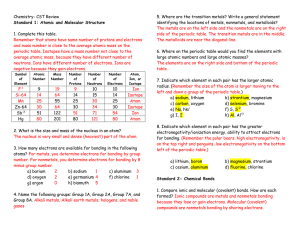
Chemistry- CST Review
... 2. Amino acids are building blocks for ___proteins___. 3. How many bonds does the carbon atom form? Carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds. ...
... 2. Amino acids are building blocks for ___proteins___. 3. How many bonds does the carbon atom form? Carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds. ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... 7. a. What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds? b. How does electronegativity difference determine bond type? 8. Write the electron configurations for a. Al+3 b. O-2 c. Ti+2. 9. Draw Lewis structures for the following; a. K2O b. MgCl2 c. KI d. Na3P 10. Which of the following compounds ...
... 7. a. What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds? b. How does electronegativity difference determine bond type? 8. Write the electron configurations for a. Al+3 b. O-2 c. Ti+2. 9. Draw Lewis structures for the following; a. K2O b. MgCl2 c. KI d. Na3P 10. Which of the following compounds ...