chemistry module p
... Molecules Molecules are formed in many substances when small groups of atoms join together with a unique structural conformation. The atoms can be all the same or there can be several different types. A chemical formula gives information about the types and numbers of atoms present in each of these ...
... Molecules Molecules are formed in many substances when small groups of atoms join together with a unique structural conformation. The atoms can be all the same or there can be several different types. A chemical formula gives information about the types and numbers of atoms present in each of these ...
Unit 6- Math of Chemistry
... combustion of 3 mol of C2H6 according to the equation? mol C2H6 = 3 mol mol water = x mol ratio ethane to water = 2:6 3mol C2H6/ 2 mol C2H6 = x/6mol water X=9mol water ...
... combustion of 3 mol of C2H6 according to the equation? mol C2H6 = 3 mol mol water = x mol ratio ethane to water = 2:6 3mol C2H6/ 2 mol C2H6 = x/6mol water X=9mol water ...
chemistry-subject test5 w. solutions
... dispersion forces (in the order of decreasing strength). For the ideal gas law to give an accurate prediction of the volume, then, we are looking for gases that do not have ahttp://doc.guandang.net/bbca35c11081d34250955e480.html strong dipole moment. Methane, CH4, does not have a dipole moment: What ...
... dispersion forces (in the order of decreasing strength). For the ideal gas law to give an accurate prediction of the volume, then, we are looking for gases that do not have ahttp://doc.guandang.net/bbca35c11081d34250955e480.html strong dipole moment. Methane, CH4, does not have a dipole moment: What ...
Unit 7 Homework and Lab Packet
... 3. What mass of sodium nitrate will be obtained from the reaction of 4.97 grams of lead (II) nitrate with sodium iodide? Pb(NO3)2 + 2 NaI PbI2 + 2 NaNO3 ...
... 3. What mass of sodium nitrate will be obtained from the reaction of 4.97 grams of lead (II) nitrate with sodium iodide? Pb(NO3)2 + 2 NaI PbI2 + 2 NaNO3 ...
3-A
... (C9H8O4) and acetic acid (CH3CO2H). Use this information to determine the mass of acetic anhydride required to react with 4.50 g of salicylic acid. How many ...
... (C9H8O4) and acetic acid (CH3CO2H). Use this information to determine the mass of acetic anhydride required to react with 4.50 g of salicylic acid. How many ...
laman web smk raja perempuan, ipoh
... 2. calculate the quantities present at equilibrium from given appropriate data 3. deduce expressions for equilibrium constants in terms of concentrations Kc, and partial pressures, Kp 4. calculate the value of the equilibrium constants in terms of concentrations or partial pressures from appropriate ...
... 2. calculate the quantities present at equilibrium from given appropriate data 3. deduce expressions for equilibrium constants in terms of concentrations Kc, and partial pressures, Kp 4. calculate the value of the equilibrium constants in terms of concentrations or partial pressures from appropriate ...
OCR Gateway Science
... (c) The synthesis of ammonia is carried out in a closed system. What is meant by the term closed system? (d) At the start of the reaction only hydrogen and nitrogen are present. Describe how the rate of the forward and back reactions change as equilibrium is established. ...
... (c) The synthesis of ammonia is carried out in a closed system. What is meant by the term closed system? (d) At the start of the reaction only hydrogen and nitrogen are present. Describe how the rate of the forward and back reactions change as equilibrium is established. ...
Chapter 5 ppt
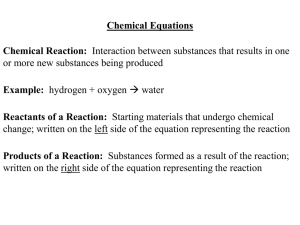
... change; written on the left side of the equation representing the reaction Products of a Reaction: Substances formed as a result of the reaction; written on the right side of the equation representing the reaction ...
... change; written on the left side of the equation representing the reaction Products of a Reaction: Substances formed as a result of the reaction; written on the right side of the equation representing the reaction ...
Chemical Reactivity as Described by Quantum Chemical Methods
... local softness over various domains in space [38] (Other concepts introduced in this framework are reviewed in [39, 40]) In this way it is shown that DFT gave the possibility to sharply define concepts known for a long time in chemistry, but to which inadequate precision could be given to use them w ...
... local softness over various domains in space [38] (Other concepts introduced in this framework are reviewed in [39, 40]) In this way it is shown that DFT gave the possibility to sharply define concepts known for a long time in chemistry, but to which inadequate precision could be given to use them w ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... Once equilibrium is established, the reaction is over, right? Not exactly. An experimenter has some ability to affect the equilibrium. Chemical equilibria can be shifted by changing the conditions that the system experiences. We say that we “stress” the equilibrium. When we stress the equilibrium, th ...
... Once equilibrium is established, the reaction is over, right? Not exactly. An experimenter has some ability to affect the equilibrium. Chemical equilibria can be shifted by changing the conditions that the system experiences. We say that we “stress” the equilibrium. When we stress the equilibrium, th ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.










2)](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015968611_1-56df287e8435abc2be6b0a2948d2417f-300x300.png)