Exam 2 Fall 2005 Chemsitry 1211
... 23.) If 20 mL of 0.010 M H3PO4 solution is completely neutralized by 60.0 mL of Ca(OH)2 solution, what is the molarity of the Ca(OH)2 solution? a.) b.) c.) d.) e.) ...
... 23.) If 20 mL of 0.010 M H3PO4 solution is completely neutralized by 60.0 mL of Ca(OH)2 solution, what is the molarity of the Ca(OH)2 solution? a.) b.) c.) d.) e.) ...
PDF(343KB)
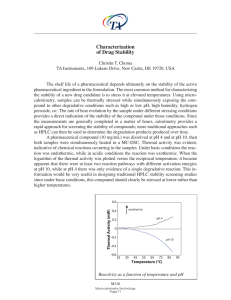
... the stability of a new drug candidate is to stress it at elevated temperatures. Using microcalorimetry, samples can be thermally stressed while simultaneously exposing the compound to other degradative conditions such as high or low pH, high humidity, hydrogen peroxide, etc. The rate of heat evoluti ...
... the stability of a new drug candidate is to stress it at elevated temperatures. Using microcalorimetry, samples can be thermally stressed while simultaneously exposing the compound to other degradative conditions such as high or low pH, high humidity, hydrogen peroxide, etc. The rate of heat evoluti ...
CHM 2045C - State College of Florida
... CHM 1025C with a grade of “C” or better or one year of high school college preparatory honors or AP chemistry within last three years. This course meets Area V for the A.A./A.S. general education requirements. A rigorous study of chemistry principles for students who have already studied basic conce ...
... CHM 1025C with a grade of “C” or better or one year of high school college preparatory honors or AP chemistry within last three years. This course meets Area V for the A.A./A.S. general education requirements. A rigorous study of chemistry principles for students who have already studied basic conce ...
Biochemistry Introduction day 1
... Isotopes: Atoms of an element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Ex: Oxygen usually has 8 neutrons but 9 and 10 neutrons can be found in some oxygen atoms. Some isotopes are unstable in the nucleus which makes it more likely to decay and release energy. This i ...
... Isotopes: Atoms of an element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Ex: Oxygen usually has 8 neutrons but 9 and 10 neutrons can be found in some oxygen atoms. Some isotopes are unstable in the nucleus which makes it more likely to decay and release energy. This i ...
Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions
... Combustion means oxygen in reactants – complete combustion of hydrocarbon means water and carbon dioxide are formed 3. Iron (III) oxide is formed when Iron is oxidized. 4. pure copper and sulfur dioxide are produced by heating copper( II) sulfide in the presence of oxygen 5, Water is formed by the e ...
... Combustion means oxygen in reactants – complete combustion of hydrocarbon means water and carbon dioxide are formed 3. Iron (III) oxide is formed when Iron is oxidized. 4. pure copper and sulfur dioxide are produced by heating copper( II) sulfide in the presence of oxygen 5, Water is formed by the e ...
CH. 15 Notes
... Chemical ReactionsThe process by which 1 or more substances undergo change to produce 1 or more different substances Reactions occur when chemical bonds are broken. The atoms rearranged and form new bonds ...
... Chemical ReactionsThe process by which 1 or more substances undergo change to produce 1 or more different substances Reactions occur when chemical bonds are broken. The atoms rearranged and form new bonds ...
Slide 1
... reaction; it shows the complete formulas of all reactants and products. • However, although this equation shows the reactants and products of the reaction, it does not give a very clear picture of what actually occurs in solution. • The complete ionic equation, better represents the actual forms of ...
... reaction; it shows the complete formulas of all reactants and products. • However, although this equation shows the reactants and products of the reaction, it does not give a very clear picture of what actually occurs in solution. • The complete ionic equation, better represents the actual forms of ...
Key To T2 Review For Final Study Guide File - District 196 e
... 8. What is a limiting reactant? Why is this reactant so important? The limiting reactant is the reactant that runs out first in a chemical reaction, therefore determining the amount of product produced. 9. What is an excess reactant? The reactant that there is more than enough of to complete the lim ...
... 8. What is a limiting reactant? Why is this reactant so important? The limiting reactant is the reactant that runs out first in a chemical reaction, therefore determining the amount of product produced. 9. What is an excess reactant? The reactant that there is more than enough of to complete the lim ...
Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
... Chemical reactions involve the formation, breaking, or rearrangement of chemical bonds. There are 4 general types: Dehydration synthesis: A + B → AB + water Decomposition (or hydrolysis): AB + water → A + B Exchange: AB + CD → AD + CB Reversible: A + B < - - - > AB ...
... Chemical reactions involve the formation, breaking, or rearrangement of chemical bonds. There are 4 general types: Dehydration synthesis: A + B → AB + water Decomposition (or hydrolysis): AB + water → A + B Exchange: AB + CD → AD + CB Reversible: A + B < - - - > AB ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.