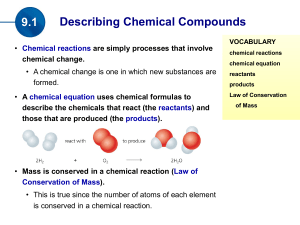
(the products). Mass is conserved in a chemical reaction
... • Reaction rate is explained by the collision theory, which states that molecules must collide in order to react. • Collisions must also be effective, which means that they must have sufficient energy for a reaction to occur. ...
... • Reaction rate is explained by the collision theory, which states that molecules must collide in order to react. • Collisions must also be effective, which means that they must have sufficient energy for a reaction to occur. ...
Chemistry 116: General Chemistry
... 7. A closed system of three gases is governed by the reversible reaction shown. Kp = 4 10-7 at the current temperature of the mixture, PNO2 = 4.1 10-2 atm, PNO = 8.9 10-4 atm, and PO2 = 8.5 10-3 atm. In order to reach equilibrium, how must the system adjust? ...
... 7. A closed system of three gases is governed by the reversible reaction shown. Kp = 4 10-7 at the current temperature of the mixture, PNO2 = 4.1 10-2 atm, PNO = 8.9 10-4 atm, and PO2 = 8.5 10-3 atm. In order to reach equilibrium, how must the system adjust? ...
Test 2
... 13. A sample of limestone (containing calcium carbonate, CaCO3) weighing 413mg is treated with oxalic acid (H2C2O4) to give 472mg calcium oxalate (CaC2O4). CaCO3(s) + H2C2O4(aq) CaC2O4(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(l). What is the percentage of calcium carbonate in the limestone? ...
... 13. A sample of limestone (containing calcium carbonate, CaCO3) weighing 413mg is treated with oxalic acid (H2C2O4) to give 472mg calcium oxalate (CaC2O4). CaCO3(s) + H2C2O4(aq) CaC2O4(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(l). What is the percentage of calcium carbonate in the limestone? ...
Slide 1
... 94.4 NO3- + “OM” → 13.6 CO2 + 92.4 HCO3- + 55.3 N2 + 84.8 H2O + HPO42Manganese Oxide Reduction 236 MnO2 + “OM” + 364 CO2 + 104 H2O → 470 HCO3- + 8N2 + 236 Mn2+ + HPO42Iron Oxide Reduction 212 Fe2O3 + “OM” + 742 CO2 + 318 H2O → 848 HCO3- + 16 NH3 + 424 Fe2+ + HPO42Sulfate Reduction 53 SO42- + “OM” → ...
... 94.4 NO3- + “OM” → 13.6 CO2 + 92.4 HCO3- + 55.3 N2 + 84.8 H2O + HPO42Manganese Oxide Reduction 236 MnO2 + “OM” + 364 CO2 + 104 H2O → 470 HCO3- + 8N2 + 236 Mn2+ + HPO42Iron Oxide Reduction 212 Fe2O3 + “OM” + 742 CO2 + 318 H2O → 848 HCO3- + 16 NH3 + 424 Fe2+ + HPO42Sulfate Reduction 53 SO42- + “OM” → ...
Solution
... = 1.83 x 1083, this is a very large K indicating that the products are strongly favored. This is consistent with the negative free energy of part (c). e) The pressure of oxygen is 5 atm and the pressure of hydrogen is 10 atm at 25°C. In which direction will the reaction shift in order to regain equi ...
... = 1.83 x 1083, this is a very large K indicating that the products are strongly favored. This is consistent with the negative free energy of part (c). e) The pressure of oxygen is 5 atm and the pressure of hydrogen is 10 atm at 25°C. In which direction will the reaction shift in order to regain equi ...
review sheet
... 14. Where will water boil at a lower temperature 250 feet or 10,000 feet above sea level? _____________________________________________ Why?_____________________ 15. Explain on the molecular level how solids, liquids and gases compare. Which has the most kinetic energy? ...
... 14. Where will water boil at a lower temperature 250 feet or 10,000 feet above sea level? _____________________________________________ Why?_____________________ 15. Explain on the molecular level how solids, liquids and gases compare. Which has the most kinetic energy? ...
Chemistry of Life - juan-roldan
... ◦Are two or more forms of atoms of the same element ◦Contain the same number of protons and electrons, but the number of neutrons ...
... ◦Are two or more forms of atoms of the same element ◦Contain the same number of protons and electrons, but the number of neutrons ...
C1a - Mr Corfe
... down in the group (not including groups 3-8) TYPES OF REACTIONS PHYSICAL – changing of states EXOTHERMIC – gives out heat ENDOTHERMIC – take in heat from it surrounding THERMAL DECOMPOSITION – is a chemical reaction where a single compound breaks up into two or more simpler compounds or elements whe ...
... down in the group (not including groups 3-8) TYPES OF REACTIONS PHYSICAL – changing of states EXOTHERMIC – gives out heat ENDOTHERMIC – take in heat from it surrounding THERMAL DECOMPOSITION – is a chemical reaction where a single compound breaks up into two or more simpler compounds or elements whe ...
AP Chemistry 2013 Semester 1 Final Exam Review Problems
... oxalic acid, H2C2O4, to give solid calcium oxalate, CaC2O4, carbon dioxide and water. The mass of the calcium oxalate produced is 472mg. Write a balanced equation for this reaction. What is the mass percentage of calcium carbonate in this limestone? 8. Potassium superoxide, KO2, is employed in a sel ...
... oxalic acid, H2C2O4, to give solid calcium oxalate, CaC2O4, carbon dioxide and water. The mass of the calcium oxalate produced is 472mg. Write a balanced equation for this reaction. What is the mass percentage of calcium carbonate in this limestone? 8. Potassium superoxide, KO2, is employed in a sel ...
2 (aq)
... Designates a reactant or product in the liquid state: placed after the formula Designates a reactant or product in the gaseous state; placed after the formula Designates an aqueous solution; the substance is dissolved in water; placed after the formula Indicates that heat is supplied to the reaction ...
... Designates a reactant or product in the liquid state: placed after the formula Designates a reactant or product in the gaseous state; placed after the formula Designates an aqueous solution; the substance is dissolved in water; placed after the formula Indicates that heat is supplied to the reaction ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.