Practice Test Packet
... What would happen to the system if the pressure were decreased? [A] The water vapor would become liquid water. [B] The NO concentration would increase. [C] Nothing would happen. [D] More oxygen would be produced. [E] The ammonia concentration would increase. 2. The following questions refer to the e ...
... What would happen to the system if the pressure were decreased? [A] The water vapor would become liquid water. [B] The NO concentration would increase. [C] Nothing would happen. [D] More oxygen would be produced. [E] The ammonia concentration would increase. 2. The following questions refer to the e ...
Semester 2 Review WS
... b. When nickel (II) chlorate is heated, it breaks down into nickel (II) chloride and oxygen gas. ...
... b. When nickel (II) chlorate is heated, it breaks down into nickel (II) chloride and oxygen gas. ...
C4C5C6
... • Three factors affect the position of the equilibrium: Changing Equilibrium Temperature For all reversible reactions, one direction is an exothermic reaction and the reverse direction is endothermic. • decrease temperature - rate of endothermic reaction decreases •equilibrium will shift towards th ...
... • Three factors affect the position of the equilibrium: Changing Equilibrium Temperature For all reversible reactions, one direction is an exothermic reaction and the reverse direction is endothermic. • decrease temperature - rate of endothermic reaction decreases •equilibrium will shift towards th ...
Atoms and Molecules
... THIS SUMMER ASSIGNMENT IS VOLUNTARY!!! This assignment is a voluntary activity for those who wish for a bit of review or want to polish off the rust. We will conduct a general review of first-year chemistry material during the first one or two class meetings (typically the first week of school). We ...
... THIS SUMMER ASSIGNMENT IS VOLUNTARY!!! This assignment is a voluntary activity for those who wish for a bit of review or want to polish off the rust. We will conduct a general review of first-year chemistry material during the first one or two class meetings (typically the first week of school). We ...
AP Chem Test 5-7 Practice Exam - mvhs
... 1. The value of ∆H0 for the reaction below is -126 kJ. The amount of heat that is released by the reaction of 25.0 g of Na2O2 with water is __________ kJ. 2 Na2O2 (s) + 2 H2O(l) 4 NaOH(s) + O2(g) A) 20.2 B) 40.4 C) 67.5 D) 80.8 E) -126 2. The ΔH for the exothermic solution process when solid sodiu ...
... 1. The value of ∆H0 for the reaction below is -126 kJ. The amount of heat that is released by the reaction of 25.0 g of Na2O2 with water is __________ kJ. 2 Na2O2 (s) + 2 H2O(l) 4 NaOH(s) + O2(g) A) 20.2 B) 40.4 C) 67.5 D) 80.8 E) -126 2. The ΔH for the exothermic solution process when solid sodiu ...
Biochemistry Assessment
... are changed by the reactions they catalyze increase the activation energy strengthen the chemical bonds are sensitive to changes in temperature and pH ...
... are changed by the reactions they catalyze increase the activation energy strengthen the chemical bonds are sensitive to changes in temperature and pH ...
Thermochemistry
... Changes in matter are accompanied by a change in energy. Remember, nature is lazy!! Physical and chemical changes occur because that is the path of least resistance. The production and usage of energy that occurs in reactions have enormous impacts on society. People are making big bucks as they try ...
... Changes in matter are accompanied by a change in energy. Remember, nature is lazy!! Physical and chemical changes occur because that is the path of least resistance. The production and usage of energy that occurs in reactions have enormous impacts on society. People are making big bucks as they try ...
Atomic Theory (2
... f. 24.6 L of CH4 g. 75.3 L of NO2 2.) Convert the following to particles (atoms, compounds, molecules, etc): a. 3.5 moles of Aluminum Phosphide b. 7.9 moles of diphosphorus pentoxide c. 1.5 moles of Carbon tetrachloride d. 5 L of Chlorine e. 15 L of Hydrogen gas f. 32 g of O2 g. 62 g of P h. 132 g o ...
... f. 24.6 L of CH4 g. 75.3 L of NO2 2.) Convert the following to particles (atoms, compounds, molecules, etc): a. 3.5 moles of Aluminum Phosphide b. 7.9 moles of diphosphorus pentoxide c. 1.5 moles of Carbon tetrachloride d. 5 L of Chlorine e. 15 L of Hydrogen gas f. 32 g of O2 g. 62 g of P h. 132 g o ...
Chemistry - Bourbon County Schools
... twice/week) Reading and analysis of “real life” chemical research situation (weekly) Common assessment (end of unit) ...
... twice/week) Reading and analysis of “real life” chemical research situation (weekly) Common assessment (end of unit) ...
Redox Reactions C12-1-10
... electrons are partially transferred from hydrogen to oxygen. Oxygen is a more electronegative element than hydrogen. The electron pair in the covalent bond is shifted toward oxygen resulting in a partial negative charge on oxygen and partial positive charge on hydrogen. Both reactions above are exam ...
... electrons are partially transferred from hydrogen to oxygen. Oxygen is a more electronegative element than hydrogen. The electron pair in the covalent bond is shifted toward oxygen resulting in a partial negative charge on oxygen and partial positive charge on hydrogen. Both reactions above are exam ...
Test-tube Reactions - University of Manitoba
... electrons are partially transferred from hydrogen to oxygen. Oxygen is a more electronegative element than hydrogen. The electron pair in the covalent bond is shifted toward oxygen resulting in a partial negative charge on oxygen and partial positive charge on hydrogen. Both reactions above are exam ...
... electrons are partially transferred from hydrogen to oxygen. Oxygen is a more electronegative element than hydrogen. The electron pair in the covalent bond is shifted toward oxygen resulting in a partial negative charge on oxygen and partial positive charge on hydrogen. Both reactions above are exam ...
Practice Exam 3
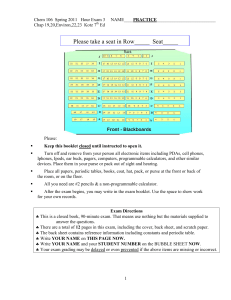
... This is a closed book, 90-minute exam. That means use nothing but the materials supplied to answer the questions. There are a total of 12 pages in this exam, including the cover, back sheet, and scratch paper. The back sheet contains reference information including constants and periodic table ...
... This is a closed book, 90-minute exam. That means use nothing but the materials supplied to answer the questions. There are a total of 12 pages in this exam, including the cover, back sheet, and scratch paper. The back sheet contains reference information including constants and periodic table ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.