Jaynes-Cummings model
... First, we note that we already have a basis of energy eigenstates for the harmonic oscillator Hamiltonian Ĥfield , being the number states {|ni, n = 0, 1, 2, . . .} with eigenvalues ~ω(n + 1/2). We also have a basis of energy eigenstates for the 2-level atom Hamiltonian Ĥatom , being the states |g ...
... First, we note that we already have a basis of energy eigenstates for the harmonic oscillator Hamiltonian Ĥfield , being the number states {|ni, n = 0, 1, 2, . . .} with eigenvalues ~ω(n + 1/2). We also have a basis of energy eigenstates for the 2-level atom Hamiltonian Ĥatom , being the states |g ...
Document
... Any nucleus in the environment of a unpaired spin will feel a magnectic field Be coming from the isotropic and dipolar fields. Depending on the orientation of the electron, the fields felt by the nucleus can be termed Be+ and Be- which in turn will orient with respect to the applied field. The resul ...
... Any nucleus in the environment of a unpaired spin will feel a magnectic field Be coming from the isotropic and dipolar fields. Depending on the orientation of the electron, the fields felt by the nucleus can be termed Be+ and Be- which in turn will orient with respect to the applied field. The resul ...
24 Sept 08 - Seattle Central College
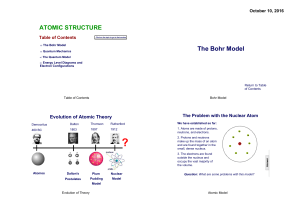
... • It was known that atoms were neutrally-charged, but that they contained negatively-charged particles called electrons. • Lord Kelvin (yes, that Lord Kelvin) proposed the “PlumPudding” Model (we will call it the “Chocolate-Chip Cookie” Model) of atomic structure. • In this model, the atom is compos ...
... • It was known that atoms were neutrally-charged, but that they contained negatively-charged particles called electrons. • Lord Kelvin (yes, that Lord Kelvin) proposed the “PlumPudding” Model (we will call it the “Chocolate-Chip Cookie” Model) of atomic structure. • In this model, the atom is compos ...
CECAM Meeting “Development of Methods for
... extended model systems. Simulations in smaller clusters are affected by surface states that speed up the electron injection process, and periodic boundary conditions often introduce artificial recurrencies. • Reaction mechanisms and characteristic times for electron ...
... extended model systems. Simulations in smaller clusters are affected by surface states that speed up the electron injection process, and periodic boundary conditions often introduce artificial recurrencies. • Reaction mechanisms and characteristic times for electron ...
Chapter 3
... 62. Allicin is the compound responsible for the characteristic smell of garlic. An analysis of the compound gives the following percent composition by mass: C: 44.4 percent; H: 6.21 percent; S: 39.5 percent; O: 9.86 percent. What is its molecular formula given that its molar mass is about 162 g? A) ...
... 62. Allicin is the compound responsible for the characteristic smell of garlic. An analysis of the compound gives the following percent composition by mass: C: 44.4 percent; H: 6.21 percent; S: 39.5 percent; O: 9.86 percent. What is its molecular formula given that its molar mass is about 162 g? A) ...
lesson 5
... • Atoms of most metals have fewer than 4 outer-shell electrons. • Atoms of nonmetals have 4 or more outer-shell electrons. When forming a compound: • The metal transfers or lends outer-ring electrons to the nonmetal. • The nonmetal borrows these electrons. Here is an easy way to remember this: M E T ...
... • Atoms of most metals have fewer than 4 outer-shell electrons. • Atoms of nonmetals have 4 or more outer-shell electrons. When forming a compound: • The metal transfers or lends outer-ring electrons to the nonmetal. • The nonmetal borrows these electrons. Here is an easy way to remember this: M E T ...
Quantum Disentanglement Eraser
... which path or both paths choice is made randomly by photon 2 • When photon 1 triggers D0, photon 2 is still on its way to BSA, BSB • After registering of photon 1 at D0, we look at the subsequent detection events at D1, D2, D3, D4 with appropriate time delay • Joint detection events at D0 and Di mus ...
... which path or both paths choice is made randomly by photon 2 • When photon 1 triggers D0, photon 2 is still on its way to BSA, BSB • After registering of photon 1 at D0, we look at the subsequent detection events at D1, D2, D3, D4 with appropriate time delay • Joint detection events at D0 and Di mus ...
Two-dimensional momentum imaging of Rydberg states using half-cycle pulse ionization
... direction and y direction兲, can ionize. The final momentum distribution is influenced by the focussing effect of the combined Coulomb potential and external static electric field. We will show that at high kick strengths, where the strength of the HCP suffices that 100% of the excited Rydberg state ...
... direction and y direction兲, can ionize. The final momentum distribution is influenced by the focussing effect of the combined Coulomb potential and external static electric field. We will show that at high kick strengths, where the strength of the HCP suffices that 100% of the excited Rydberg state ...
Path Integrals from meV to MeV: Tutzing `92
... The classical motion of the collinear helium atom with the electrons on different sides of the nucleus turns out to be fully chaotic, even though we cannot rigorously prove this. A system is called "chaotic" if all PO are linearly unstable and their number proliferates exponentially with the action ...
... The classical motion of the collinear helium atom with the electrons on different sides of the nucleus turns out to be fully chaotic, even though we cannot rigorously prove this. A system is called "chaotic" if all PO are linearly unstable and their number proliferates exponentially with the action ...
Modern Physics 342
... Show that the average value of x is L/2, for a particle in a box of length L, independent of the quantum state (not quantized). Since the wave function is ...
... Show that the average value of x is L/2, for a particle in a box of length L, independent of the quantum state (not quantized). Since the wave function is ...
Chem 1 Worksheets WSHEET 1: Working with Numbers Practice
... 1. Calcium fluoride, CaF2, is a source of fluorine and is used to fluoridate drinking water. Calculate its molar mass. 2. Calculate the molar mass of Ca(BO2)2·6H2O. 3. Calculate the number of moles in 17.8 g of the antacid magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2. 4. Calculate the number of oxygen atoms in 29.3 ...
... 1. Calcium fluoride, CaF2, is a source of fluorine and is used to fluoridate drinking water. Calculate its molar mass. 2. Calculate the molar mass of Ca(BO2)2·6H2O. 3. Calculate the number of moles in 17.8 g of the antacid magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2. 4. Calculate the number of oxygen atoms in 29.3 ...
sp0103_32-36 Gaughan
... number and spin quantum number, where the angular momentum depends on orbital characteristics, while spin refers to the intrinsic magnetic moment of the respective particles. In the initial orbit, the antiproton’s angular momentum is on the order of 38, while its spin is 1⁄2, as indeed is that of th ...
... number and spin quantum number, where the angular momentum depends on orbital characteristics, while spin refers to the intrinsic magnetic moment of the respective particles. In the initial orbit, the antiproton’s angular momentum is on the order of 38, while its spin is 1⁄2, as indeed is that of th ...
FREE Sample Here
... Chemicals used as reagents, such as bromthymol blue or sodium iodide, may permanently stain clothing. Use with caution. ...
... Chemicals used as reagents, such as bromthymol blue or sodium iodide, may permanently stain clothing. Use with caution. ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.