Allowed and forbidden transitions in artificial hydrogen and helium
... knt l ¼ I p ðt l þ t h þ t m Þ=e: As the current measures the unrelaxed electron number, knt l ¼ A expð2t h =tS–T Þ for the condition G21 s & tS–T (no upper limit in principle), where A < 1 is approximately the ratio of Gs21 for the triplet to that for the singlet. Figure 3e shows a typical measurem ...
... knt l ¼ I p ðt l þ t h þ t m Þ=e: As the current measures the unrelaxed electron number, knt l ¼ A expð2t h =tS–T Þ for the condition G21 s & tS–T (no upper limit in principle), where A < 1 is approximately the ratio of Gs21 for the triplet to that for the singlet. Figure 3e shows a typical measurem ...
Chapter 12 - NCERT books
... the intense electric field there scatters it through a large angle. The atomic electrons, being so light, do not appreciably affect the α-particles. The scattering data shown in Fig. 12.3 can be analysed by employing Rutherford’s nuclear model of the atom. As the gold foil is very thin, it can be as ...
... the intense electric field there scatters it through a large angle. The atomic electrons, being so light, do not appreciably affect the α-particles. The scattering data shown in Fig. 12.3 can be analysed by employing Rutherford’s nuclear model of the atom. As the gold foil is very thin, it can be as ...
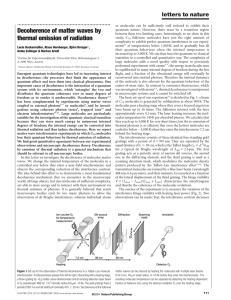
Decoherence of matter waves by thermal emission of radiation
... or molecules can be sufficiently well isolated to exhibit their quantum nature. However, there must be a transition region between these two limiting cases. Interestingly, as we show in this study, C70 fullerene molecules have just the right amount of complexity to exhibit perfect quantum interferen ...
... or molecules can be sufficiently well isolated to exhibit their quantum nature. However, there must be a transition region between these two limiting cases. Interestingly, as we show in this study, C70 fullerene molecules have just the right amount of complexity to exhibit perfect quantum interferen ...
Problem Set - Structures and Properties Unit v. 0914
... molecule? b) How many pi bonds are present in each molecule? c) Based on your analysis, what hybrid orbitals are found around each carbon? d) Based on your analysis, what molecular geometry (shape) is present around each carbon? ...
... molecule? b) How many pi bonds are present in each molecule? c) Based on your analysis, what hybrid orbitals are found around each carbon? d) Based on your analysis, what molecular geometry (shape) is present around each carbon? ...
Slides - Max-Planck
... We check the relative error between (1) and (2) with respect to the number of photons that are emitted. ...
... We check the relative error between (1) and (2) with respect to the number of photons that are emitted. ...
Problem Set 3: Solutions
... 9. Time delay in the photoelectric effect. A beam of ultraviolet light of intensity 1.6 × 10−12 W is suddenly turned on and falls on a metal surface, ejecting electrons through the photoelectric effect. The beam has a cross-sectional area of 1 cm2 , and the wavelength corresponds to a photon energy ...
... 9. Time delay in the photoelectric effect. A beam of ultraviolet light of intensity 1.6 × 10−12 W is suddenly turned on and falls on a metal surface, ejecting electrons through the photoelectric effect. The beam has a cross-sectional area of 1 cm2 , and the wavelength corresponds to a photon energy ...
Topic 1 Review - Capital High School
... period of the periodic table, and __________ as you go from the bottom to the top of a group in the table. 35. In general, as you go across a period in the periodic table from left to right: (1) the atomic radius __________; (2) the electron affinity becomes __________ negative; and (3) the first io ...
... period of the periodic table, and __________ as you go from the bottom to the top of a group in the table. 35. In general, as you go across a period in the periodic table from left to right: (1) the atomic radius __________; (2) the electron affinity becomes __________ negative; and (3) the first io ...
Implementations of Quantum Information
... systems and decoherence, but there are promising techniques such as quantum error correction to overcome these problems. Many candidates for physical quantum information processing, and we study some of these here. ...
... systems and decoherence, but there are promising techniques such as quantum error correction to overcome these problems. Many candidates for physical quantum information processing, and we study some of these here. ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.