Ch. 4: Electron Configuration
... radiation is absorbed by matter only in whole numbers of photons. – Electron is knocked off metal surface only if struck by one photon with certain minimum energy. Mullis Chemistry Holt Ch.4 ...
... radiation is absorbed by matter only in whole numbers of photons. – Electron is knocked off metal surface only if struck by one photon with certain minimum energy. Mullis Chemistry Holt Ch.4 ...
Atoms, Ions, and Molecules File
... Atoms of different elements are different. • Atoms are not changed into different atoms in a chemical reaction. • Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. ...
... Atoms of different elements are different. • Atoms are not changed into different atoms in a chemical reaction. • Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. ...
CHEM 1305 - HCC Learning Web
... PART II – Show your work: (8 points each) 21a. Element X has natural isotopes; X-63 (62.940amu) and X-65 (64.928amu). Calculate the atomic mass of element X given the abundance of X-63 is 69.17% b. Which element corresponds to each of the following electron configuration? i. 1S2 2S2 2P5 ii. 1S2 2S2 ...
... PART II – Show your work: (8 points each) 21a. Element X has natural isotopes; X-63 (62.940amu) and X-65 (64.928amu). Calculate the atomic mass of element X given the abundance of X-63 is 69.17% b. Which element corresponds to each of the following electron configuration? i. 1S2 2S2 2P5 ii. 1S2 2S2 ...
Chemical Formulas
... Chemical formulas indicate the relative number of atoms of each kind element in a chemical compound (ionic and molecular) Ionic compound the number of atoms in a formula units Capital letter each element NaCl Subscript # atoms ...
... Chemical formulas indicate the relative number of atoms of each kind element in a chemical compound (ionic and molecular) Ionic compound the number of atoms in a formula units Capital letter each element NaCl Subscript # atoms ...
Student - Davison Chemistry Website
... 1. Improved Rutherford’s work by saying electrons do not lose energy in the atoms so they will stay in orbit. 2. Stated there are definite levels in which the electrons follow set paths without gaining or losing energy (Planetary Model). 3. Each level has a certain amount of energy associated with i ...
... 1. Improved Rutherford’s work by saying electrons do not lose energy in the atoms so they will stay in orbit. 2. Stated there are definite levels in which the electrons follow set paths without gaining or losing energy (Planetary Model). 3. Each level has a certain amount of energy associated with i ...
T1_The_Origins_Of_Quantum_Mechanics
... 1905: …“photons” (g), each of energy E = hf. Think of these now as individual photons instead of a smooth plane wave!! This is at the core of Einstein’s explanation. We now think of light as being made of photons. Each one carries a specific amount of energy, E = hf. It also has other particle prop ...
... 1905: …“photons” (g), each of energy E = hf. Think of these now as individual photons instead of a smooth plane wave!! This is at the core of Einstein’s explanation. We now think of light as being made of photons. Each one carries a specific amount of energy, E = hf. It also has other particle prop ...
Lecture. Photoelectric Effect
... “Although surely the correct description of the electromagnetic field is a quantum one, just as surely the vast majority of optical phenomena are equally well described by a semiclassical theory, with atoms quantized but with a classical field. ... The first experimental example of a manifestly quan ...
... “Although surely the correct description of the electromagnetic field is a quantum one, just as surely the vast majority of optical phenomena are equally well described by a semiclassical theory, with atoms quantized but with a classical field. ... The first experimental example of a manifestly quan ...
1.3.5 Spectroscopy Name Symbol Definition SI unit Notes total term
... The electronic states of molecules are labelled by the symmetry species label of the wavefunction in the molecular point group. These should be Latin or Greek upright capital letters. As for atoms, the spin multiplicity (2S + 1) may be indicated by a left superscript. For linear molecules the value ...
... The electronic states of molecules are labelled by the symmetry species label of the wavefunction in the molecular point group. These should be Latin or Greek upright capital letters. As for atoms, the spin multiplicity (2S + 1) may be indicated by a left superscript. For linear molecules the value ...
electron
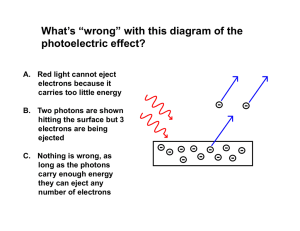
... What’s “wrong” with this diagram of the photoelectric effect? A. Red light cannot eject electrons because it carries too little energy B. Two photons are shown hitting the surface but 3 electrons are being ejected C. Nothing is wrong, as long as the photons carry enough energy they can eject any ...
... What’s “wrong” with this diagram of the photoelectric effect? A. Red light cannot eject electrons because it carries too little energy B. Two photons are shown hitting the surface but 3 electrons are being ejected C. Nothing is wrong, as long as the photons carry enough energy they can eject any ...
Electron Configurations
... • energy levels are labeled by a quantum number, n. • lowest energy level n=1 • Called ground state ...
... • energy levels are labeled by a quantum number, n. • lowest energy level n=1 • Called ground state ...
Atom (A) or Ion
... 82. What is pH and how is it measured? 83. What factors affect solubility? 84. What is molarity? 85. If I have 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate in .3 L of solution, what is the molarity? 86. If I have 700 mL of a 5 M NaOH solution, how many grams of NaOH were used to make the solution? 87. What are coll ...
... 82. What is pH and how is it measured? 83. What factors affect solubility? 84. What is molarity? 85. If I have 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate in .3 L of solution, what is the molarity? 86. If I have 700 mL of a 5 M NaOH solution, how many grams of NaOH were used to make the solution? 87. What are coll ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 82. What is pH and how is it measured? 83. What factors affect solubility? 84. What is molarity? 85. If I have 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate in .3 L of solution, what is the molarity? 86. If I have 700 mL of a 5 M NaOH solution, how many grams of NaOH were used to make the solution? 87. What are coll ...
... 82. What is pH and how is it measured? 83. What factors affect solubility? 84. What is molarity? 85. If I have 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate in .3 L of solution, what is the molarity? 86. If I have 700 mL of a 5 M NaOH solution, how many grams of NaOH were used to make the solution? 87. What are coll ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 82. What is pH and how is it measured? 83. What factors affect solubility? 84. What is molarity? 85. If I have 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate in .3 L of solution, what is the molarity? 86. If I have 700 mL of a 5 M NaOH solution, how many grams of NaOH were used to make the solution? 87. What are coll ...
... 82. What is pH and how is it measured? 83. What factors affect solubility? 84. What is molarity? 85. If I have 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate in .3 L of solution, what is the molarity? 86. If I have 700 mL of a 5 M NaOH solution, how many grams of NaOH were used to make the solution? 87. What are coll ...
PIB and HH - Unit 4 - Chemical Names and Formulas
... 1. Restate in one or two words: “The amount of energy required to remove one electron from the valence shell of a neutral atom.” 2. Restate in one or two words: “The tendency of an atom to hold on to its valence electrons while engaged in a chemical bond.” 3. Restate in one or two words: “The action ...
... 1. Restate in one or two words: “The amount of energy required to remove one electron from the valence shell of a neutral atom.” 2. Restate in one or two words: “The tendency of an atom to hold on to its valence electrons while engaged in a chemical bond.” 3. Restate in one or two words: “The action ...
namimg compounds
... • Transition metals have a variety of ionic charges, but most form ions with a +2 charge. • If a metal has more than one common ion, the charge it takes is shown with Roman numerals. For example, copper(I) = Cu+, copper(II) = Cu2+, iron(II) =FeZ+, iron(III) = Fe3+. • The metals in Groups V and VI al ...
... • Transition metals have a variety of ionic charges, but most form ions with a +2 charge. • If a metal has more than one common ion, the charge it takes is shown with Roman numerals. For example, copper(I) = Cu+, copper(II) = Cu2+, iron(II) =FeZ+, iron(III) = Fe3+. • The metals in Groups V and VI al ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.