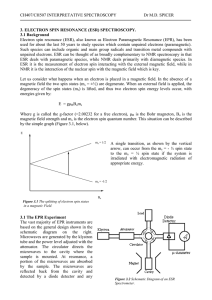
chapter02_part1_lecture - bloodhounds Incorporated
... • The first shell (closest to the nucleus) can contain two electrons • Each additional shell can contain eight electrons • Each lower shell is filled with electrons before the next higher level contains any electrons. ...
... • The first shell (closest to the nucleus) can contain two electrons • Each additional shell can contain eight electrons • Each lower shell is filled with electrons before the next higher level contains any electrons. ...
Chapter 2 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... C. I and II only D. I, II, and III A 92-2. How many atoms are in 12 molecules of glucose, C6H12O6? A. 24 B. 288 C. 7.22 x 1024 D. 1.73 x 1026 A 92-3. The simplest formula for an oxide of nitrogen that has 25.9 percentage nitrogen by mass is: A. N2O B. NO2 C. N2O3 D. N2O5 A 91-1. Which of the followi ...
... C. I and II only D. I, II, and III A 92-2. How many atoms are in 12 molecules of glucose, C6H12O6? A. 24 B. 288 C. 7.22 x 1024 D. 1.73 x 1026 A 92-3. The simplest formula for an oxide of nitrogen that has 25.9 percentage nitrogen by mass is: A. N2O B. NO2 C. N2O3 D. N2O5 A 91-1. Which of the followi ...
Chapter 9 - Fayetteville State University
... 6) Molecules: are made of atoms and form the ultimate particles of gaseous or liquid compounds 7) Periodic Law: States that elements arranged in order of the atomic number share similar chemical and physical properties. These arrangement are called groups, examples are the alkali metals (Li, Na, K, ...
... 6) Molecules: are made of atoms and form the ultimate particles of gaseous or liquid compounds 7) Periodic Law: States that elements arranged in order of the atomic number share similar chemical and physical properties. These arrangement are called groups, examples are the alkali metals (Li, Na, K, ...
Chapter 7 Quantum Theory of the Atom
... an atomic orbital (described by three quantum numbers—n, l, ml). It describes a region of space with a definite shape where there is a high probability of finding the electron. ...
... an atomic orbital (described by three quantum numbers—n, l, ml). It describes a region of space with a definite shape where there is a high probability of finding the electron. ...
Atomic Structure Electrons in Atoms
... • The lowest energy state of an atom is its ground state • When an atom gains energy (through heating for example) it is in an excited state – in an excited state the electron absorbs the energy & jumps to higher energy level when it jumps back down to its ground state it releases excess energy in t ...
... • The lowest energy state of an atom is its ground state • When an atom gains energy (through heating for example) it is in an excited state – in an excited state the electron absorbs the energy & jumps to higher energy level when it jumps back down to its ground state it releases excess energy in t ...
A mole - MSE125
... (a) Cite two important quantum mechanical concepts associated with the Bohr model of the atom. (b) Cite two important additional refinements that resulted from the wave-mechanical atomic model. ...
... (a) Cite two important quantum mechanical concepts associated with the Bohr model of the atom. (b) Cite two important additional refinements that resulted from the wave-mechanical atomic model. ...
Ionic and Covalent Compounds: Naming, Formulas, Properties 1
... For all of the Representative Elements, as you go down a group the radii of ions of equal charge increase. This is due primarily to the fact that as you go down the group the outermost electrons have a larger value of n. ...
... For all of the Representative Elements, as you go down a group the radii of ions of equal charge increase. This is due primarily to the fact that as you go down the group the outermost electrons have a larger value of n. ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.