File - Mrs. Hille`s FunZone
... described the energy and position of the electrons in an atom Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle – it is impossible to know both the position and energy (momentum) of an electron at the same time. Photons – light particles that allow us to make observations ...
... described the energy and position of the electrons in an atom Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle – it is impossible to know both the position and energy (momentum) of an electron at the same time. Photons – light particles that allow us to make observations ...
Midterm Review Answers
... Questions 52-53nrefer to the following types of energy A) Activation energy B) Free energy C) Ionization energy D) Kinetic energy E) Lattice energy 52. The energy required to convert a ground-state atom in the gas phase to a gaseous positive ion. C 53. The energy released when gas phase ions bond t ...
... Questions 52-53nrefer to the following types of energy A) Activation energy B) Free energy C) Ionization energy D) Kinetic energy E) Lattice energy 52. The energy required to convert a ground-state atom in the gas phase to a gaseous positive ion. C 53. The energy released when gas phase ions bond t ...
CP Chemistry Final Exam Review Sheet
... 50. What is the octet rule? The octet rule states that atoms will gain, lose, or share electrons in order to get a full octet (8 e-) in the valence (outermost) shell of an atom. 51. An ion is a particle with an electrical charge created by the transfer (loss or gaining) of electrons. 52. What is a c ...
... 50. What is the octet rule? The octet rule states that atoms will gain, lose, or share electrons in order to get a full octet (8 e-) in the valence (outermost) shell of an atom. 51. An ion is a particle with an electrical charge created by the transfer (loss or gaining) of electrons. 52. What is a c ...
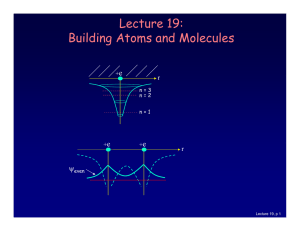
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
... It’s more like filling a bucket with water. • They are distributed among the energy levels according to the Exclusion Principle. • Particles that obey this principle are called “fermions”. Protons and neutrons are also fermions, but photons are not. Lecture 19, p 10 ...
... It’s more like filling a bucket with water. • They are distributed among the energy levels according to the Exclusion Principle. • Particles that obey this principle are called “fermions”. Protons and neutrons are also fermions, but photons are not. Lecture 19, p 10 ...
Unit 6 Study Guide – Chemical Bonding 1. A _ chemical
... c. SiCl3Br tetrahedral d. NO3 trigonal planar e. SO42tetrahedral ...
... c. SiCl3Br tetrahedral d. NO3 trigonal planar e. SO42tetrahedral ...
Pdf
... Although the variational calculations presented above are admittedly crude and are restricted to two-electron atomic ground states, it is reasonable to suppose that they present qualitatively correct patterns. In particular they lead to the proposition that the Mo” ller–Plesset series for W(), Eq. ...
... Although the variational calculations presented above are admittedly crude and are restricted to two-electron atomic ground states, it is reasonable to suppose that they present qualitatively correct patterns. In particular they lead to the proposition that the Mo” ller–Plesset series for W(), Eq. ...
orbital quantum number
... Note how Table 6.1 is set up. For n=1, the only allowed possibilities are ℓ=mℓ=0. For this case, Beiser lists the three solutions R, , and . For n=2, ℓ can be either 0 or 1. If ℓ=0 then mℓ=0. If ℓ=1 then mℓ=0 and mℓ=1 are allowed. The solutions for mℓ=1 are the same. Beiser tabulates the three ...
... Note how Table 6.1 is set up. For n=1, the only allowed possibilities are ℓ=mℓ=0. For this case, Beiser lists the three solutions R, , and . For n=2, ℓ can be either 0 or 1. If ℓ=0 then mℓ=0. If ℓ=1 then mℓ=0 and mℓ=1 are allowed. The solutions for mℓ=1 are the same. Beiser tabulates the three ...
particles - Prof.Dr.Ümit Demir
... Compton directed an x-ray beam of wavelength 0 toward a block of graphite. He found that the scattered x-rays had a slightly longer wavelength than the incident x-rays, and hence the energies of the scattered rays were lower. The amount of energy reduction depended on the angle at which the x-rays w ...
... Compton directed an x-ray beam of wavelength 0 toward a block of graphite. He found that the scattered x-rays had a slightly longer wavelength than the incident x-rays, and hence the energies of the scattered rays were lower. The amount of energy reduction depended on the angle at which the x-rays w ...
Wave Props of Particles - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... 1. The highest achievable resolving power of a microscope is limited only by the wavelength used; that is, the smallest item that can be distinguished has dimensions about equal to the wavelength. Suppose one wishes to “see” inside an atom. Assuming the atom to have a diameter of 100 pm, this mean ...
... 1. The highest achievable resolving power of a microscope is limited only by the wavelength used; that is, the smallest item that can be distinguished has dimensions about equal to the wavelength. Suppose one wishes to “see” inside an atom. Assuming the atom to have a diameter of 100 pm, this mean ...
Tunneling spectroscopy of disordered two
... of each such potential dip (here, cm,σ , cm,σ , and nD m,σ are the creation, annihilation, and number operators for these states, respectively). The energy associated with occupying such states arises from the local disorder potential VDm , and the ...
... of each such potential dip (here, cm,σ , cm,σ , and nD m,σ are the creation, annihilation, and number operators for these states, respectively). The energy associated with occupying such states arises from the local disorder potential VDm , and the ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE Chapter 7
... of a certain minimum E is used. Number of e- ejected does NOT depend on frequency, rather it depends on light intensity. ...
... of a certain minimum E is used. Number of e- ejected does NOT depend on frequency, rather it depends on light intensity. ...
希臘 - 中正大學化生系
... 1. His experiments suggested not only that cathode rays were over 1000 times lighter than the hydrogen atom, but also that their mass was the same whatever type of atom they came from. 2. He concluded that the rays were composed of very light, negatively charged particles which were a universal buil ...
... 1. His experiments suggested not only that cathode rays were over 1000 times lighter than the hydrogen atom, but also that their mass was the same whatever type of atom they came from. 2. He concluded that the rays were composed of very light, negatively charged particles which were a universal buil ...
Part 3: Quantum numbers and orbitals
... With this basic knowledge of quantum numbers and orbitals, we can now begin to develop a picture of the atom and to write electron configurations; this is a very important skill in chemistry. Based on the electron configuration of each element, we can explain and predict the behavior of that elemen ...
... With this basic knowledge of quantum numbers and orbitals, we can now begin to develop a picture of the atom and to write electron configurations; this is a very important skill in chemistry. Based on the electron configuration of each element, we can explain and predict the behavior of that elemen ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.