Modern Atomic Structure
... Further they fall, more energy, higher frequency. This is simplified the orbitals also have different energies inside energy levels All the electrons can move around. ...
... Further they fall, more energy, higher frequency. This is simplified the orbitals also have different energies inside energy levels All the electrons can move around. ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
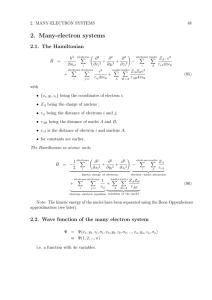
... states at lattice sites i and j. The electrons interact only when they meet on the same lattice site i. (The Pauli principle requires them to have opposite spin.) The kinetic energy and the interaction energy are characterized by the hopping term tij and the local Coulomb repulsion U, respectively. ...
... states at lattice sites i and j. The electrons interact only when they meet on the same lattice site i. (The Pauli principle requires them to have opposite spin.) The kinetic energy and the interaction energy are characterized by the hopping term tij and the local Coulomb repulsion U, respectively. ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. 3. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. 4. Atoms of one elemen ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. 3. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. 4. Atoms of one elemen ...
O O O O BF3 BF3 C N C N C O C O C N BF C N BF C N F3B
... neutral lone pair). Protic solvents strongly favor the ionization by H-bonding to both the proton and the anion. Aprotic solvents are less favorable, even if polar, because there is no H-bond donation to stabilize the anion, less ionization. DMSO is a polar aprotic solvent, gives less dissociation o ...
... neutral lone pair). Protic solvents strongly favor the ionization by H-bonding to both the proton and the anion. Aprotic solvents are less favorable, even if polar, because there is no H-bond donation to stabilize the anion, less ionization. DMSO is a polar aprotic solvent, gives less dissociation o ...
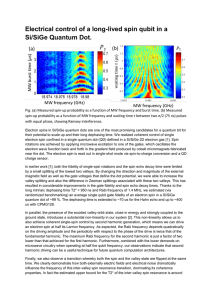
Electrical control of a long-lived spin qubit in a
... by a small splitting of the lowest two valleys. By changing the direction and magnitude of the external magnetic field as well as the gate voltages that define the dot potential, we were able to increase the valley splitting and also the difference in Zeeman splittings associated with these two vall ...
... by a small splitting of the lowest two valleys. By changing the direction and magnitude of the external magnetic field as well as the gate voltages that define the dot potential, we were able to increase the valley splitting and also the difference in Zeeman splittings associated with these two vall ...
chapter 2 - Scranton Prep Biology
... An atom's electronconfigurationdeterminesits chemicalbehavior. ' Electron conJiguration= Distributionof electronsin an atom's electron shells The first l8 elementsof a periodicchartare arrangedsequentially by atomic numberinto threerows (periods).In referenceto theserepresentotive elements, note the ...
... An atom's electronconfigurationdeterminesits chemicalbehavior. ' Electron conJiguration= Distributionof electronsin an atom's electron shells The first l8 elementsof a periodicchartare arrangedsequentially by atomic numberinto threerows (periods).In referenceto theserepresentotive elements, note the ...
A. Atomic and Nuclear Structure
... nucleus tend to push the nucleus apart, the nucleus is held together by the strong nuclear force that operates at extremely short distances. The strong nuclear force is believed to result from attractions between even smaller particles (quarks) that compose the neutrons and protons. 3. Electrons The ...
... nucleus tend to push the nucleus apart, the nucleus is held together by the strong nuclear force that operates at extremely short distances. The strong nuclear force is believed to result from attractions between even smaller particles (quarks) that compose the neutrons and protons. 3. Electrons The ...
Assignment 30 STRUCTURE OF MOLECULES AND MULTI
... C-H bonds mutually perpendicular to each other. Neither of these attributes is observed experimentally! Recall that for a CH4 molecule, the procedures of this Assignment would predict a tetrahedral geometry in which four identical C-H bonds are spaced as far apart from each other as possible (109.5° ...
... C-H bonds mutually perpendicular to each other. Neither of these attributes is observed experimentally! Recall that for a CH4 molecule, the procedures of this Assignment would predict a tetrahedral geometry in which four identical C-H bonds are spaced as far apart from each other as possible (109.5° ...
CH 5-7 Chapter 5-7 review wkey
... 21. If you need 1.00 L of 0.125 M H2SO4, how would you prepare this solution? a) Add 950. mL of water to 50.0 mL of 3.00 M H2SO4. b) Add 500. mL of water to 500. mL of 0.500 M H2SO4. c) Add 750 mL of water to 250 mL of 0.375 M H2SO4. d) Dilute 36.0 mL of 1.25 M H2SO4 to a volume of 1.00 L. e) Dilute ...
... 21. If you need 1.00 L of 0.125 M H2SO4, how would you prepare this solution? a) Add 950. mL of water to 50.0 mL of 3.00 M H2SO4. b) Add 500. mL of water to 500. mL of 0.500 M H2SO4. c) Add 750 mL of water to 250 mL of 0.375 M H2SO4. d) Dilute 36.0 mL of 1.25 M H2SO4 to a volume of 1.00 L. e) Dilute ...
Document
... 9. Which quantity represents the number of protons in an atom? a. Atomic number b. Oxidation number c. Number of neutrons d. Number of valence electrons 10. Compared to the charge of a proton, the charge of an electron has a. A greater magnitude and the same sign b. A greater magnitude and the oppos ...
... 9. Which quantity represents the number of protons in an atom? a. Atomic number b. Oxidation number c. Number of neutrons d. Number of valence electrons 10. Compared to the charge of a proton, the charge of an electron has a. A greater magnitude and the same sign b. A greater magnitude and the oppos ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.