Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... If the combustion is complete, the products will be CO2 and H2O. If the combustion is incomplete, the products will be CO (or possibly just ...
... If the combustion is complete, the products will be CO2 and H2O. If the combustion is incomplete, the products will be CO (or possibly just ...
complete outlines
... 2) The atom that can make the most bonds is the central atom. 3) Fill up the outer atoms first. 4) Place any remaining electrons on the central atom. 5) If the central atom isn’t satisfied then use the outer atoms electrons to make double/triple bonds to the central atom. ...
... 2) The atom that can make the most bonds is the central atom. 3) Fill up the outer atoms first. 4) Place any remaining electrons on the central atom. 5) If the central atom isn’t satisfied then use the outer atoms electrons to make double/triple bonds to the central atom. ...
PREP Chemistry 2008 Final Exam Review Problems
... 17. How many liters of a 0.340 M HCl solution are required if you need 0.25 moles of HCl? 18. Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the following reactions that involve acids and bases. Identify the types of reactions for each (list all that apply: combustion, SR, DR, synthesis, decompositi ...
... 17. How many liters of a 0.340 M HCl solution are required if you need 0.25 moles of HCl? 18. Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the following reactions that involve acids and bases. Identify the types of reactions for each (list all that apply: combustion, SR, DR, synthesis, decompositi ...
chemical reaction - Peoria Public Schools
... A word equation is an equation in which the reactants and products in a chemical reaction are represented with words methane + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water ...
... A word equation is an equation in which the reactants and products in a chemical reaction are represented with words methane + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water ...
2004 AP Chemistry Free-Response Questions Form B
... 2004 AP® CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS (Form B) Your responses to the rest of the questions in this part of the examination will be graded on the basis of the accuracy and relevance of the information cited. Explanations should be clear and well organized. Examples and equations may be included ...
... 2004 AP® CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS (Form B) Your responses to the rest of the questions in this part of the examination will be graded on the basis of the accuracy and relevance of the information cited. Explanations should be clear and well organized. Examples and equations may be included ...
chemistry 110 final exam
... take to heat the steel for recycling from 20 °C to a liquid at 1500 °C if the steel melts at 1450 °C? Cp(s) = 0.49 kJ/kg-°C Cp(!) = 1.19 kJ/kg-°C "Hfus = 274.0 kJ/kg A. 4.358 $105 kJ B. 7.942 $105 kJ C. 8.238 $105 kJ D. 1.135 $106 kJ E. 2.369 $106 kJ ...
... take to heat the steel for recycling from 20 °C to a liquid at 1500 °C if the steel melts at 1450 °C? Cp(s) = 0.49 kJ/kg-°C Cp(!) = 1.19 kJ/kg-°C "Hfus = 274.0 kJ/kg A. 4.358 $105 kJ B. 7.942 $105 kJ C. 8.238 $105 kJ D. 1.135 $106 kJ E. 2.369 $106 kJ ...
Exam 1, Spring 2000
... 3. (3 points) A gaseous compound with a simple formula is an important material in the chemical industry. You have 0.425 g of the compound in a 178-mL flask. The gas has a pressure of 436 mm Hg, and the temperature is 20.0 ˚C. What is the molecular formula of the gas? (a) CF 2 (b) C2F4 (c) CFCl (d) ...
... 3. (3 points) A gaseous compound with a simple formula is an important material in the chemical industry. You have 0.425 g of the compound in a 178-mL flask. The gas has a pressure of 436 mm Hg, and the temperature is 20.0 ˚C. What is the molecular formula of the gas? (a) CF 2 (b) C2F4 (c) CFCl (d) ...
CH 14-15 Chapter 14-15 review wkey
... 15. According to collision theory, which of the following factors does NOT influence the rate of reaction? a) collision frequency b) collision energy c) collision orientation d) collision rebound direction e) none of these 16. What distance corresponds to the activation energy for the reaction of X ...
... 15. According to collision theory, which of the following factors does NOT influence the rate of reaction? a) collision frequency b) collision energy c) collision orientation d) collision rebound direction e) none of these 16. What distance corresponds to the activation energy for the reaction of X ...
Chemical equilibrium
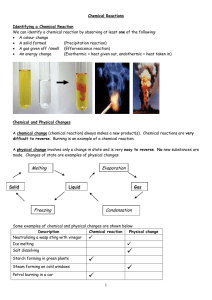
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.